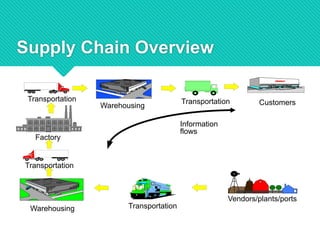
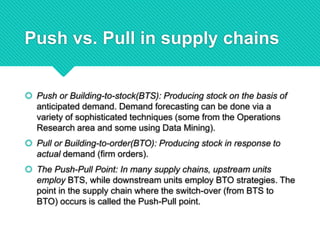
The presentation by Ishwar R. Bulbule covers the essentials of supply chain management, including its definition, components, and the importance of effective coordination among companies. It emphasizes the distinction between push and pull strategies in supply chains and highlights key areas such as customer service and demand planning, along with the challenges faced in SCM. The conclusion underscores that efficient supply chain management is vital for the success of both small and large enterprises, affecting overall project timelines and productivity.