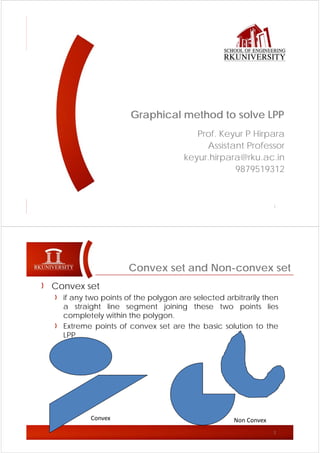
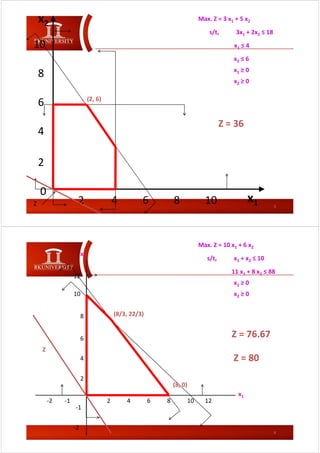
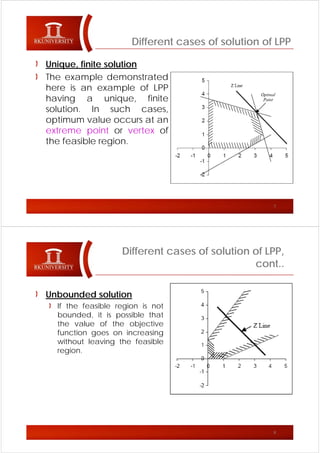
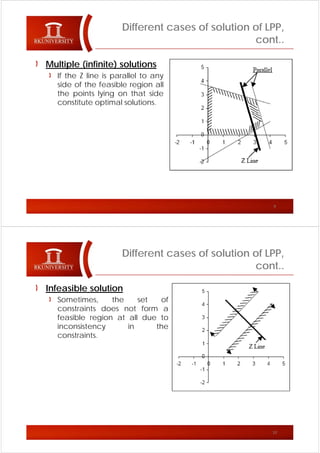
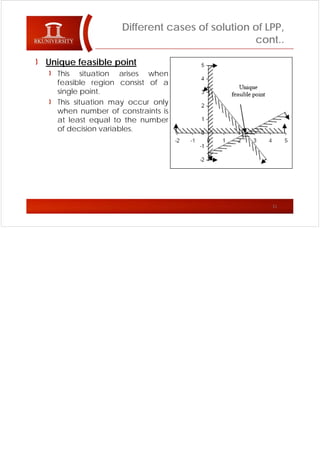
The document discusses the graphical method for solving linear programming problems (LPP), noting that the feasible region must be convex and the optimal solution occurs at an extreme point; it also outlines different cases for the solution such as it being unique and finite, unbounded, having multiple solutions, being infeasible, or having a unique feasible point. The cases discussed include problems having a unique, finite optimal solution; an unbounded feasible region where the objective continues increasing; multiple optimal solutions along a parallel constraint; an infeasible feasible region due to inconsistent constraints; and a single feasible point occurring when constraints equal variables.