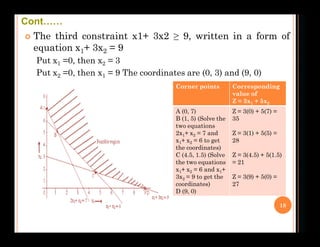
This document discusses different types of solutions that can arise when solving linear programming problems graphically:
1) A unique optimal solution occurs when the feasible region is bounded and the objective function is optimized at a single corner point.
2) Multiple optimal solutions arise if the objective function attains the same optimal value at multiple corner points.
3) An unbounded solution results when the feasible region is unbounded and the objective function can increase indefinitely.
4) No feasible solution exists if the constraints defining the feasible region are inconsistent and do not intersect, leaving an empty feasible region. Examples of each case are presented and solved graphically.