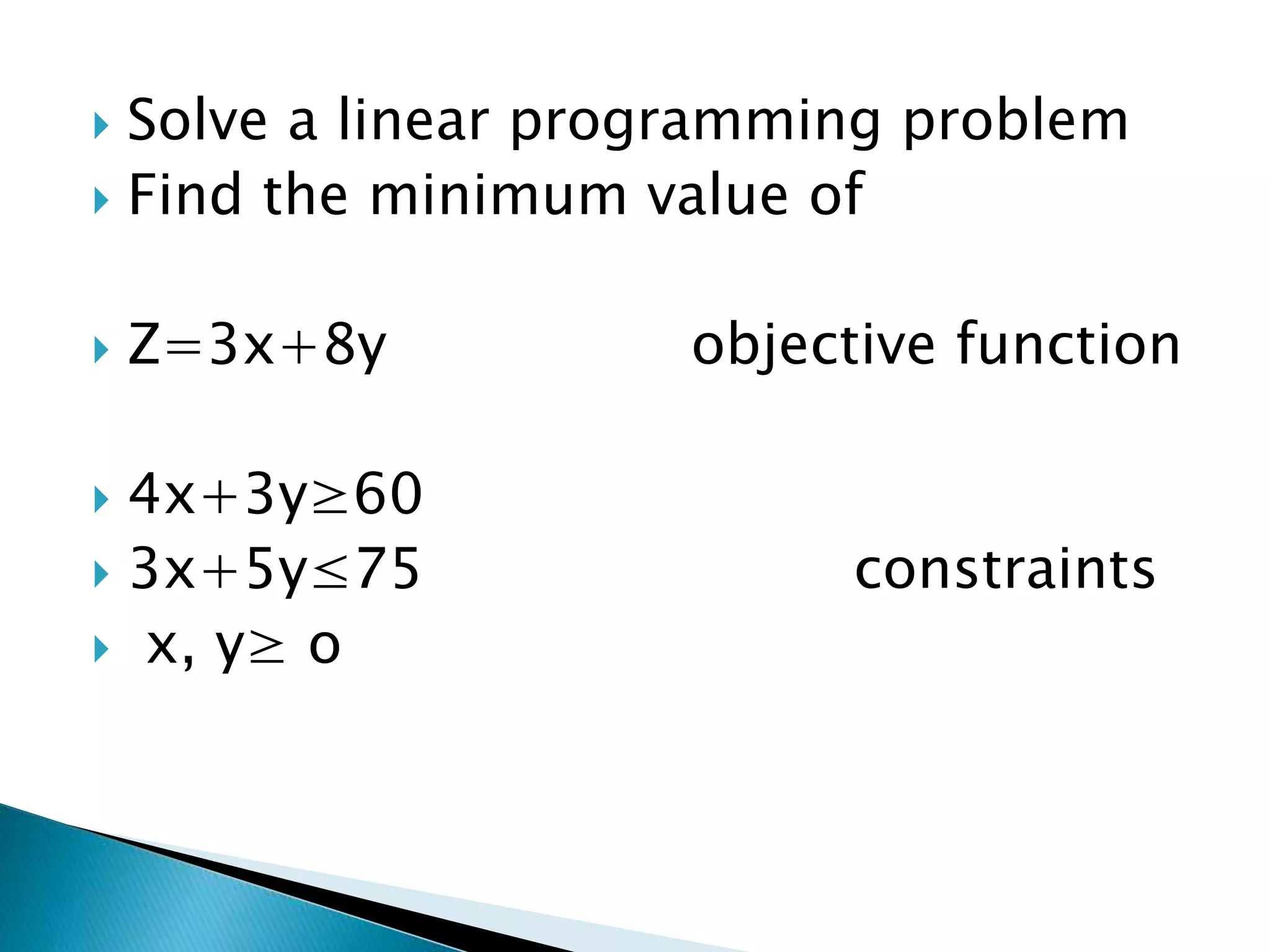
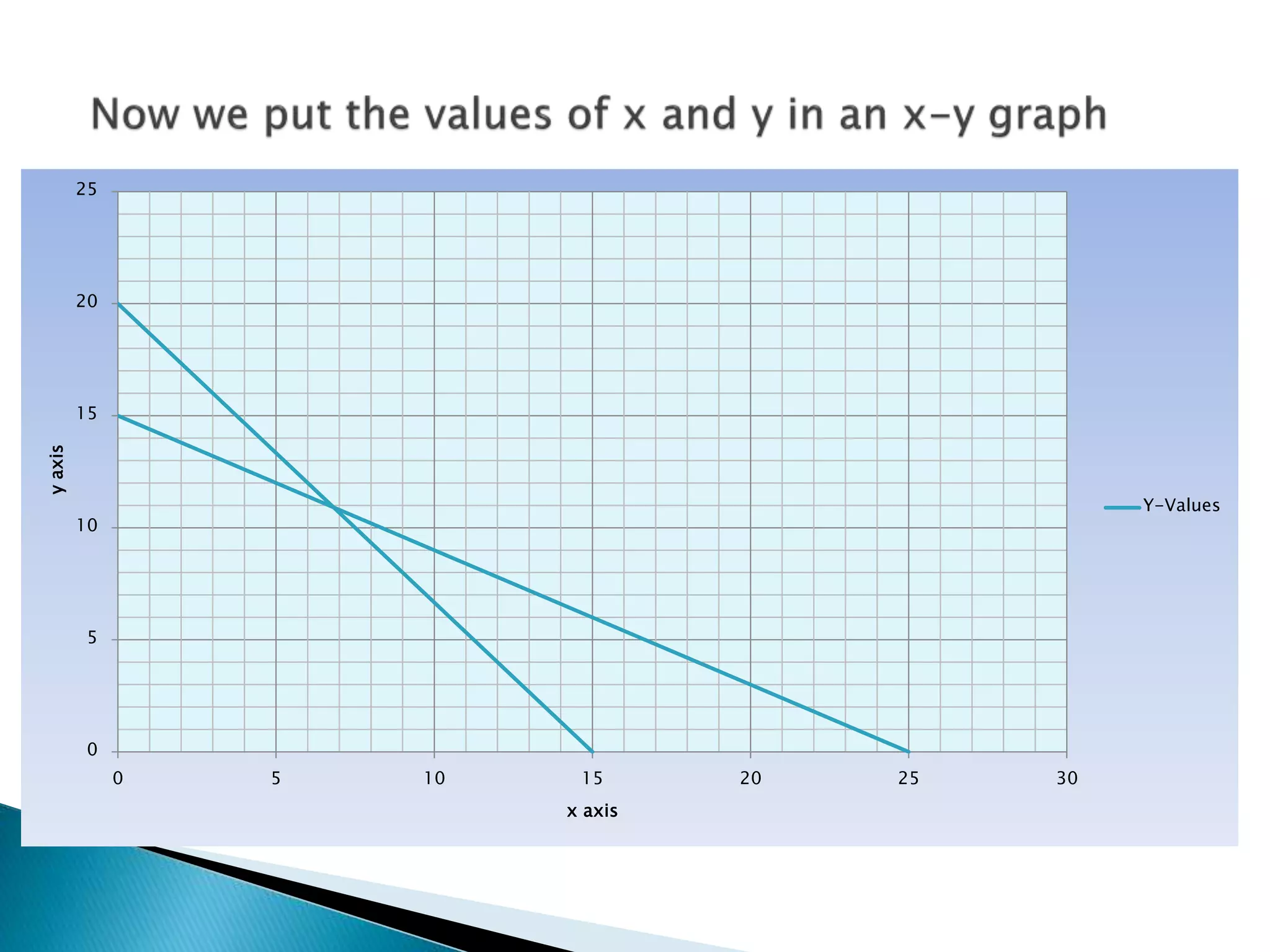
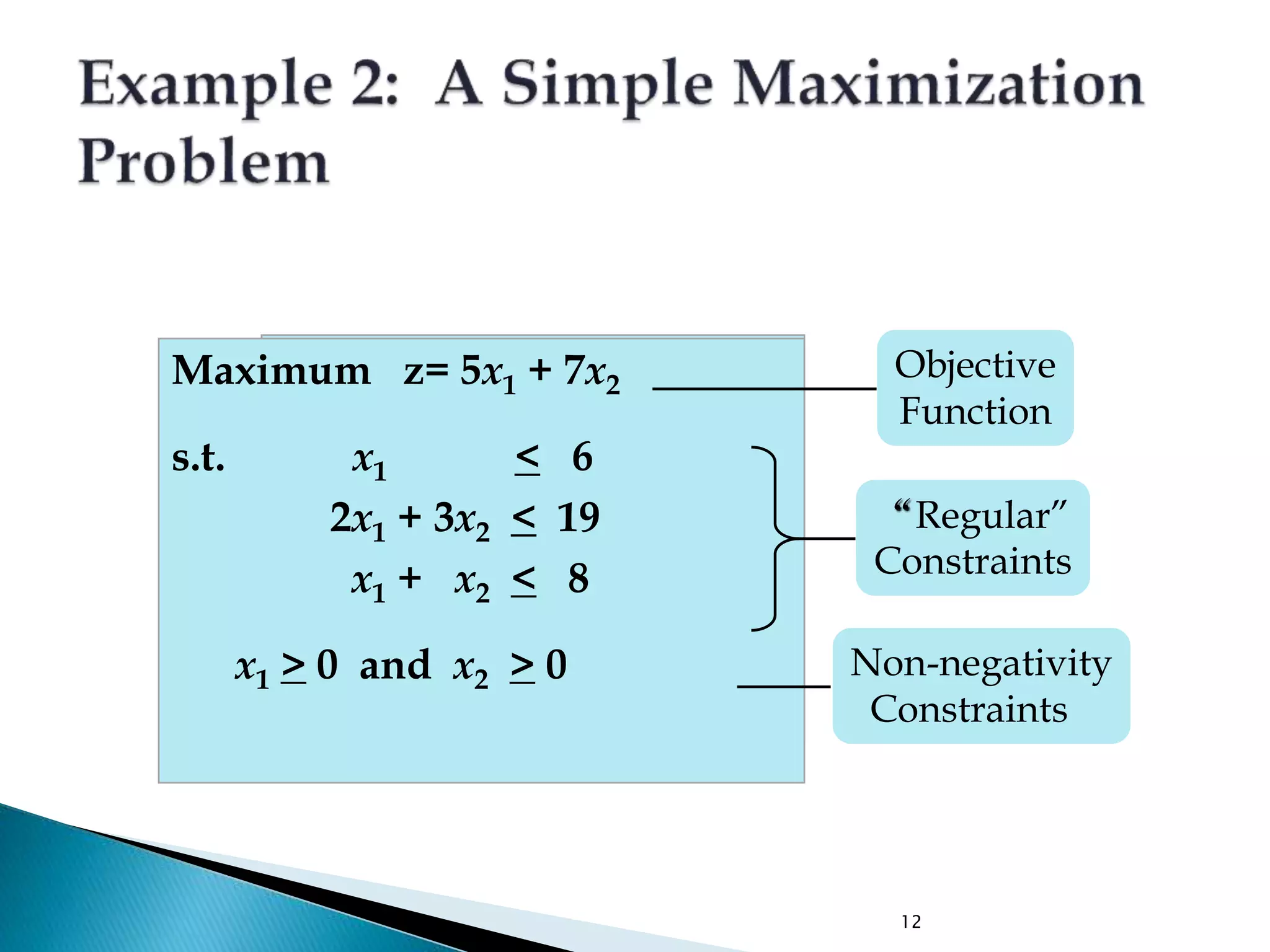
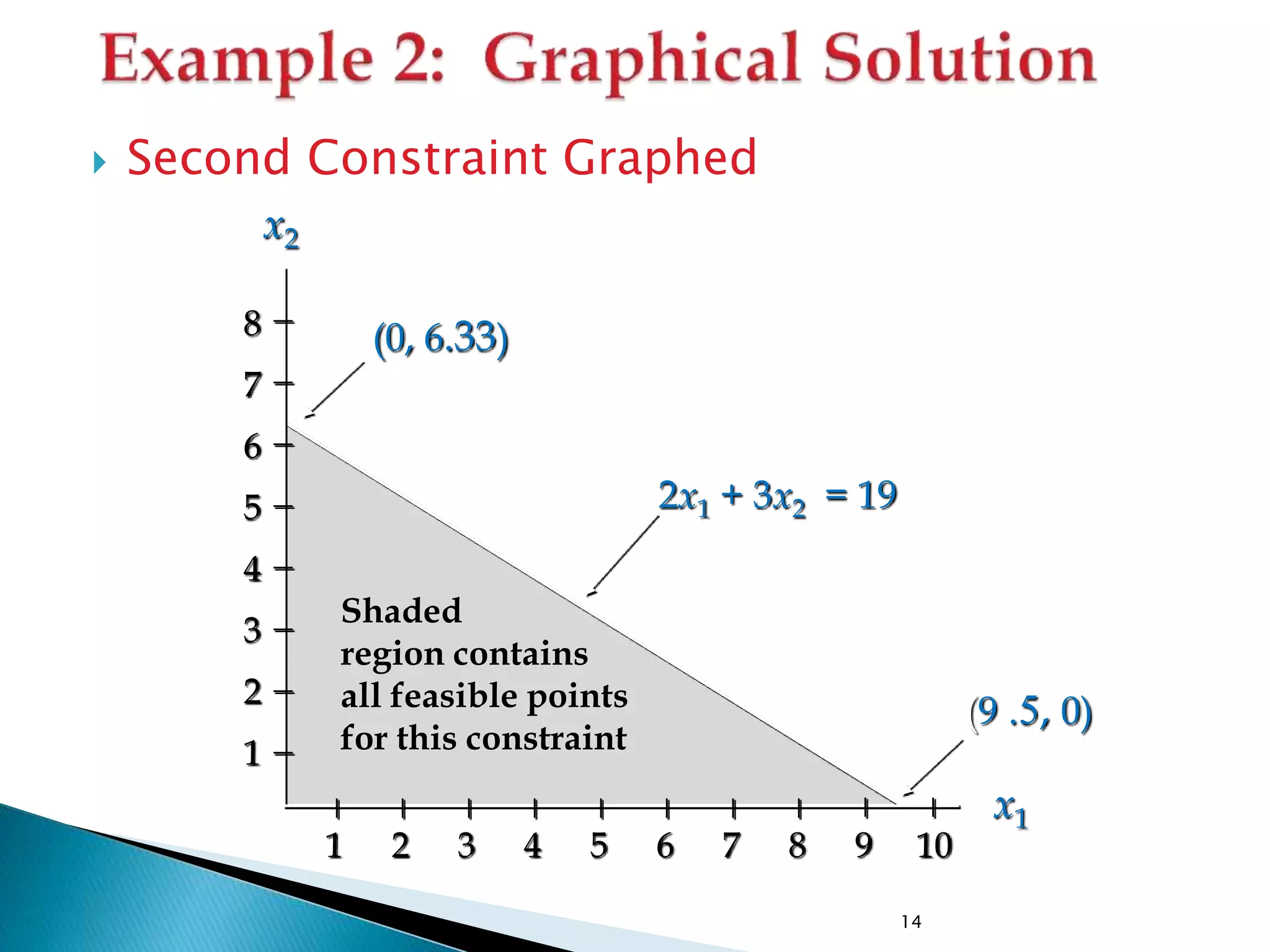
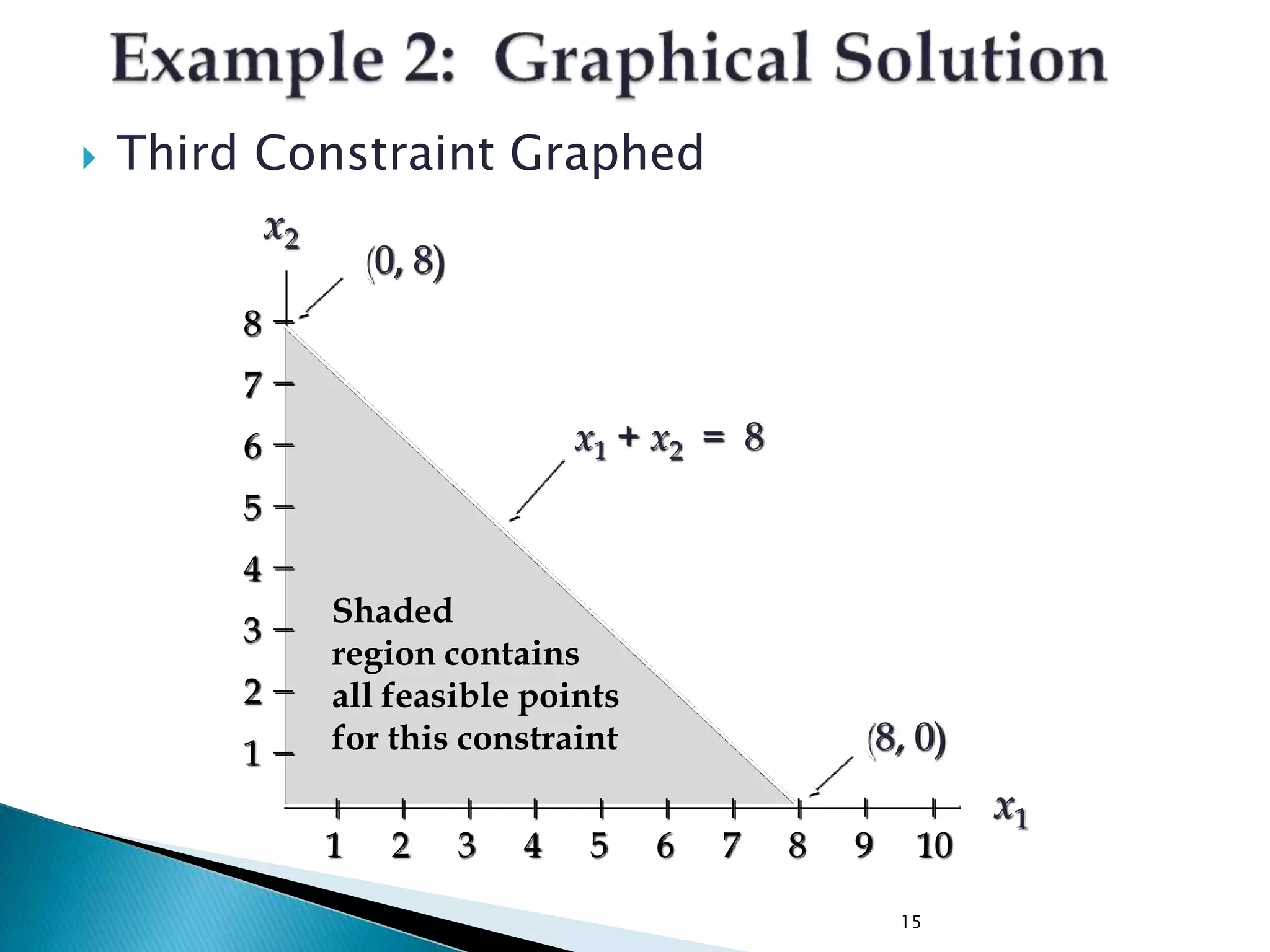
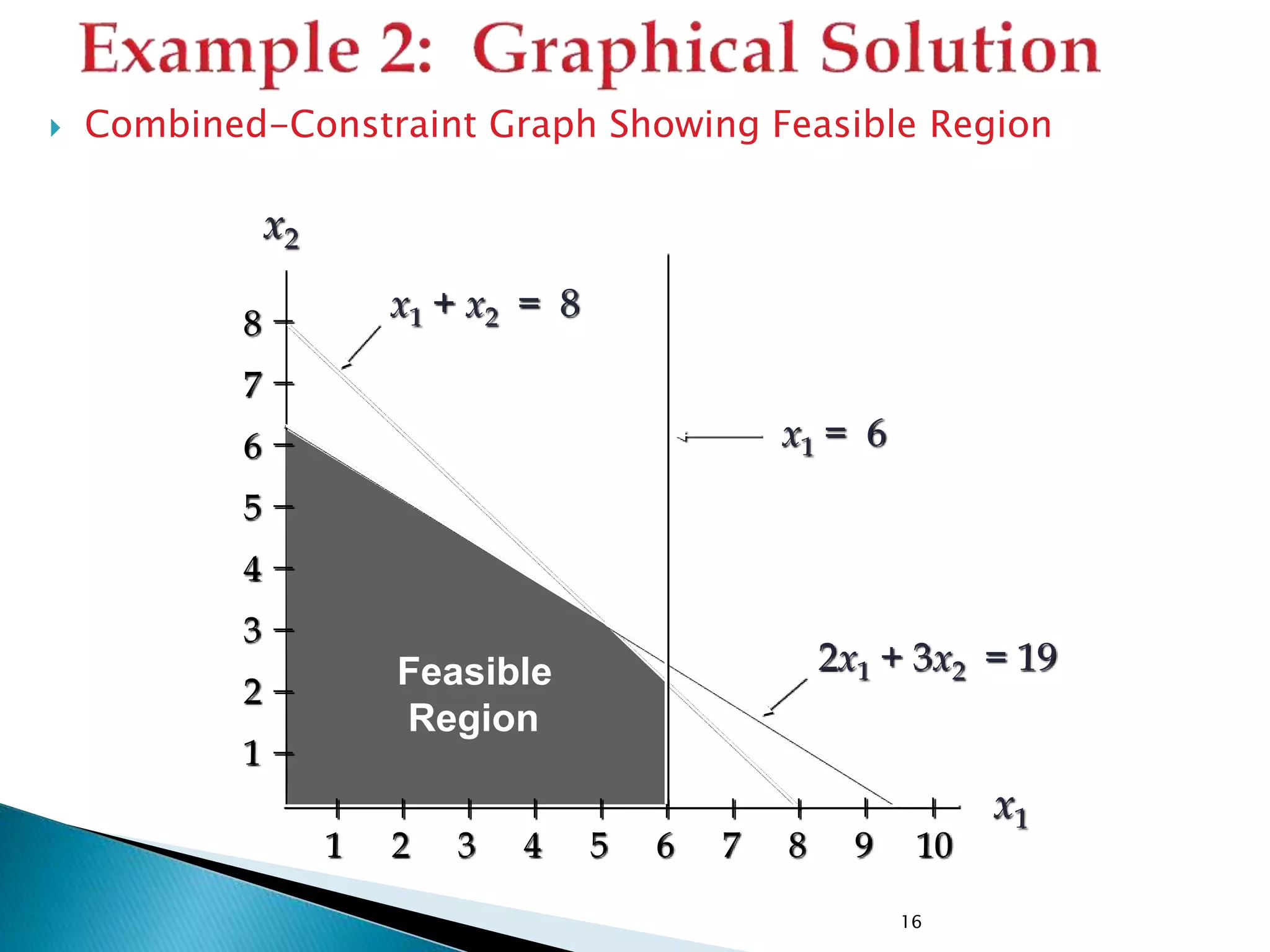
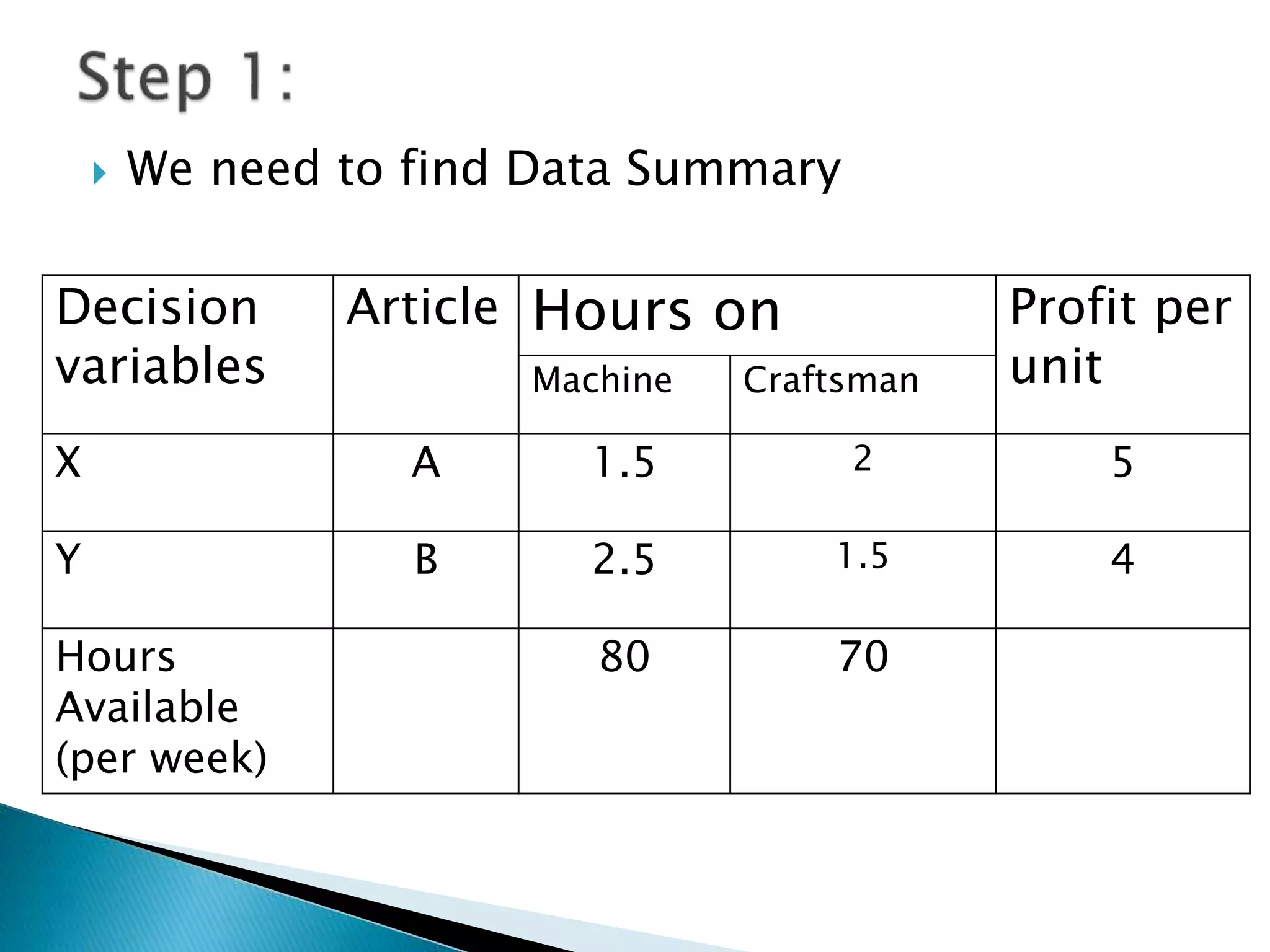
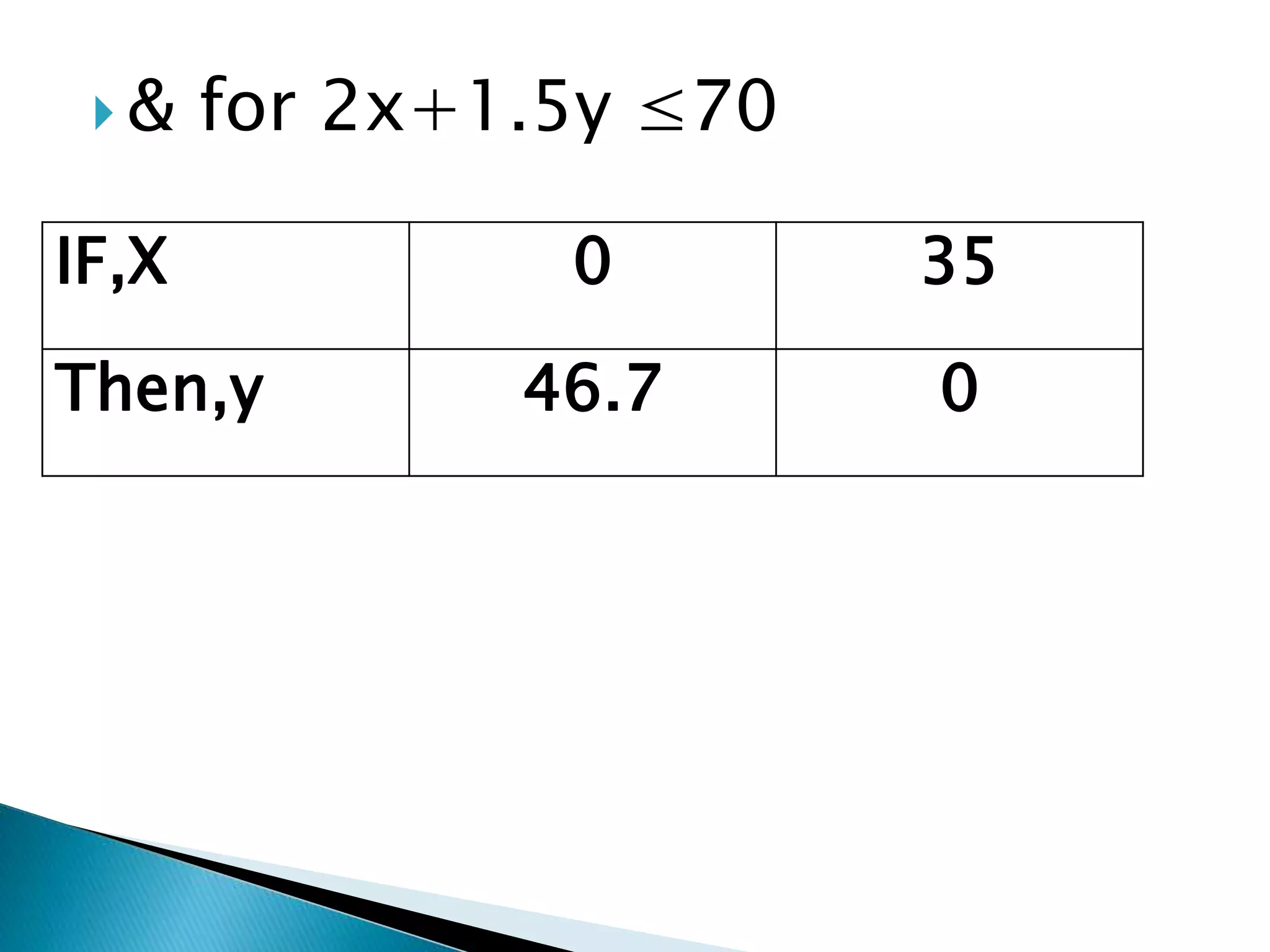
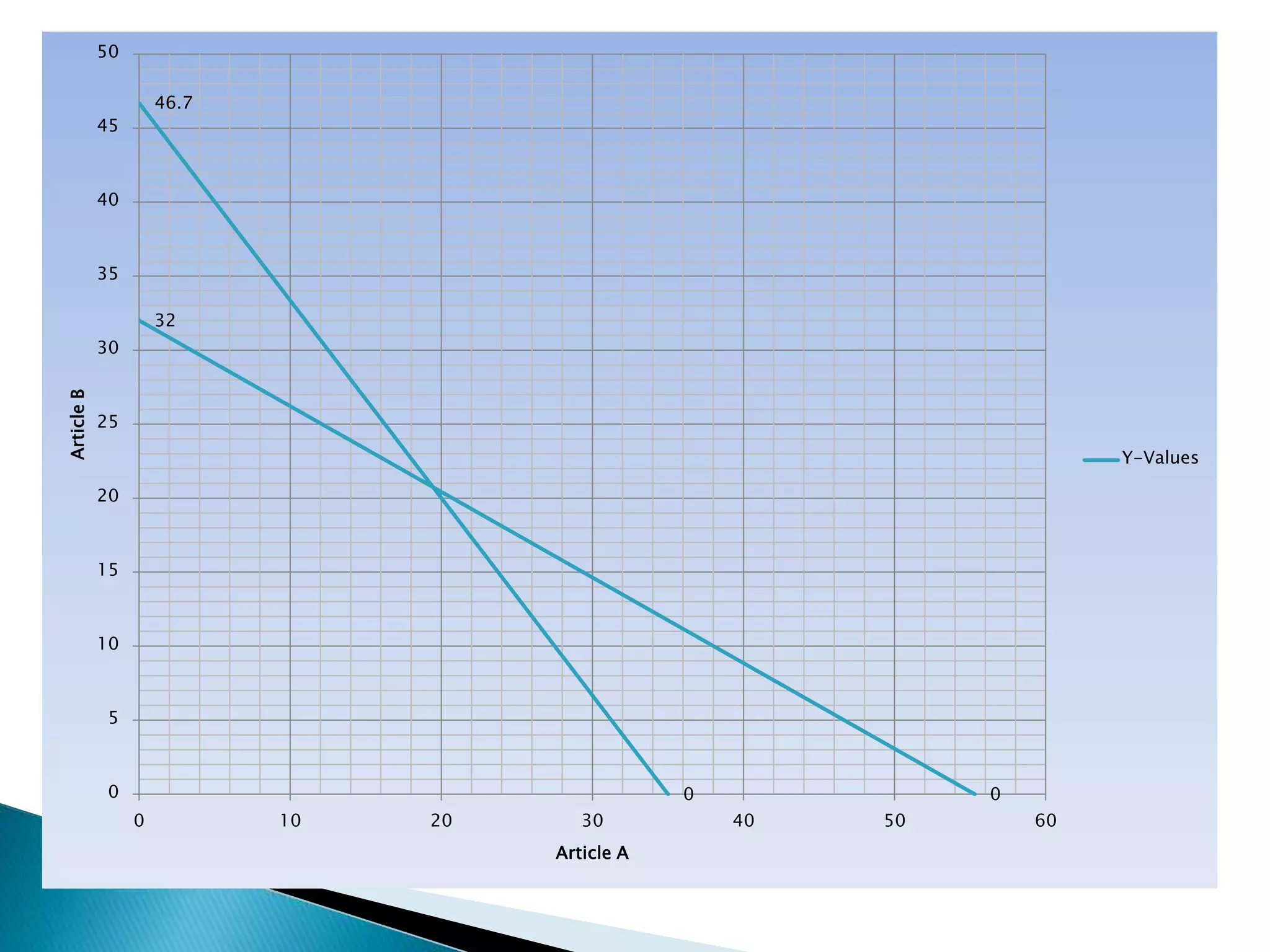
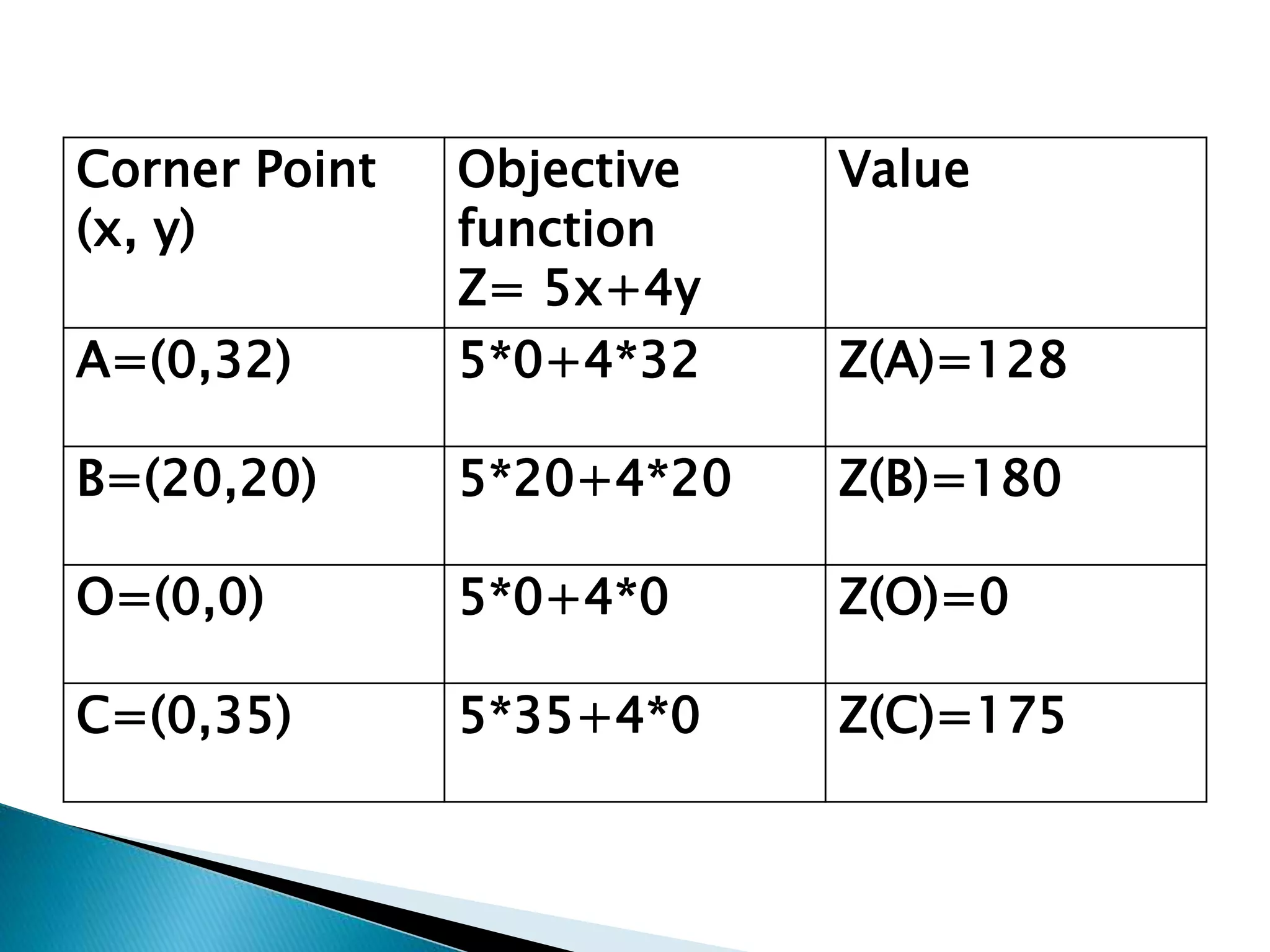
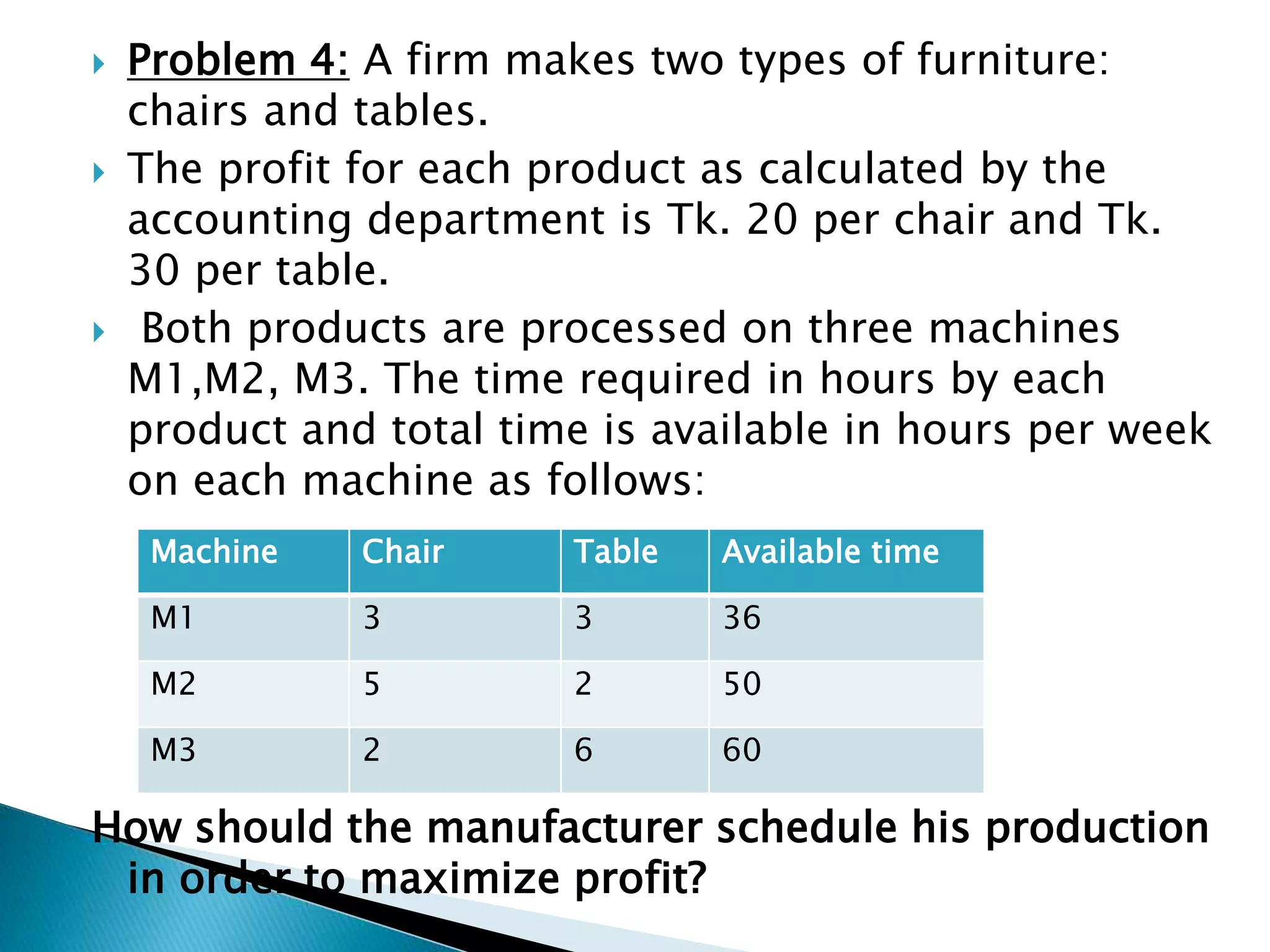
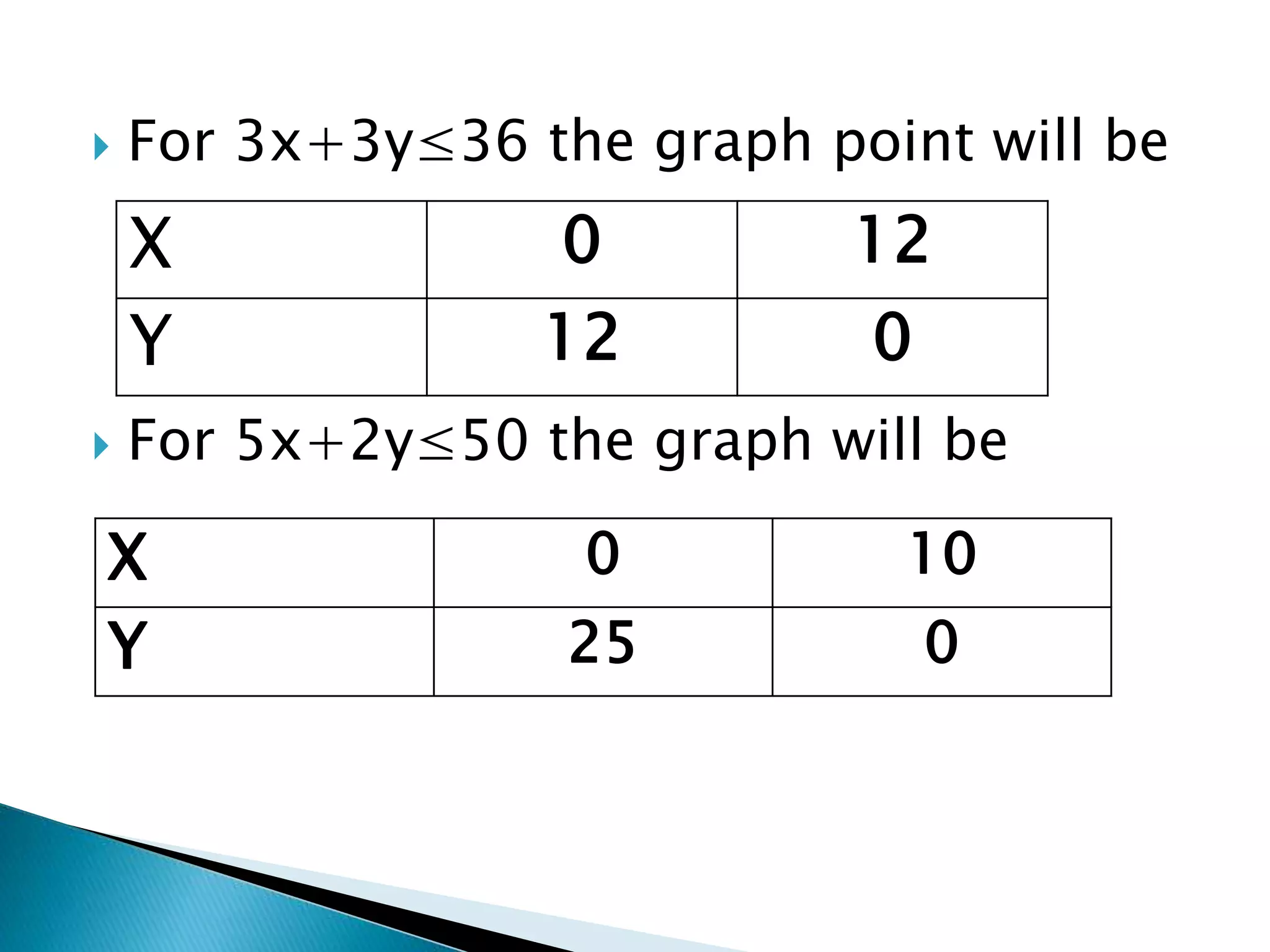
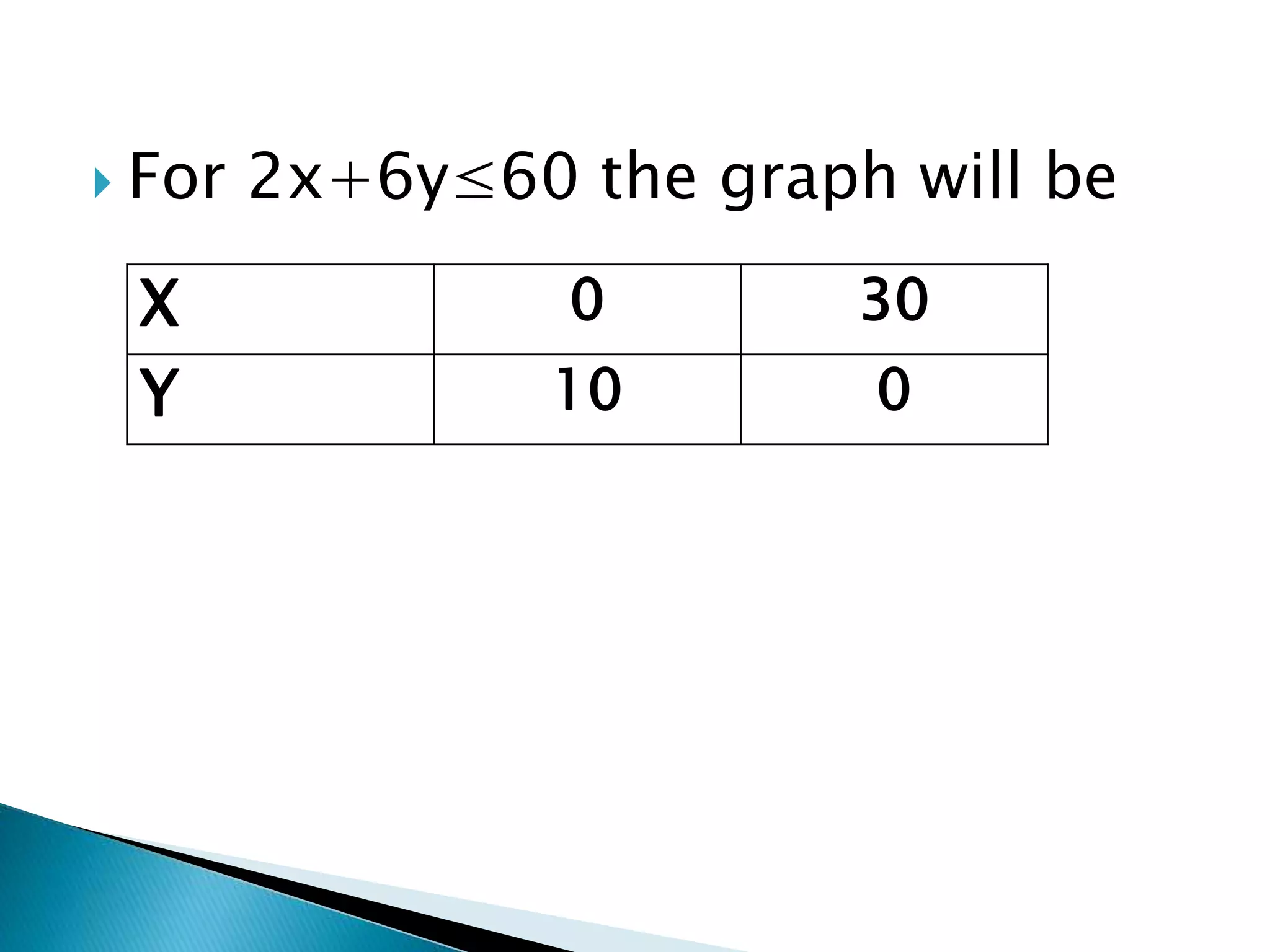
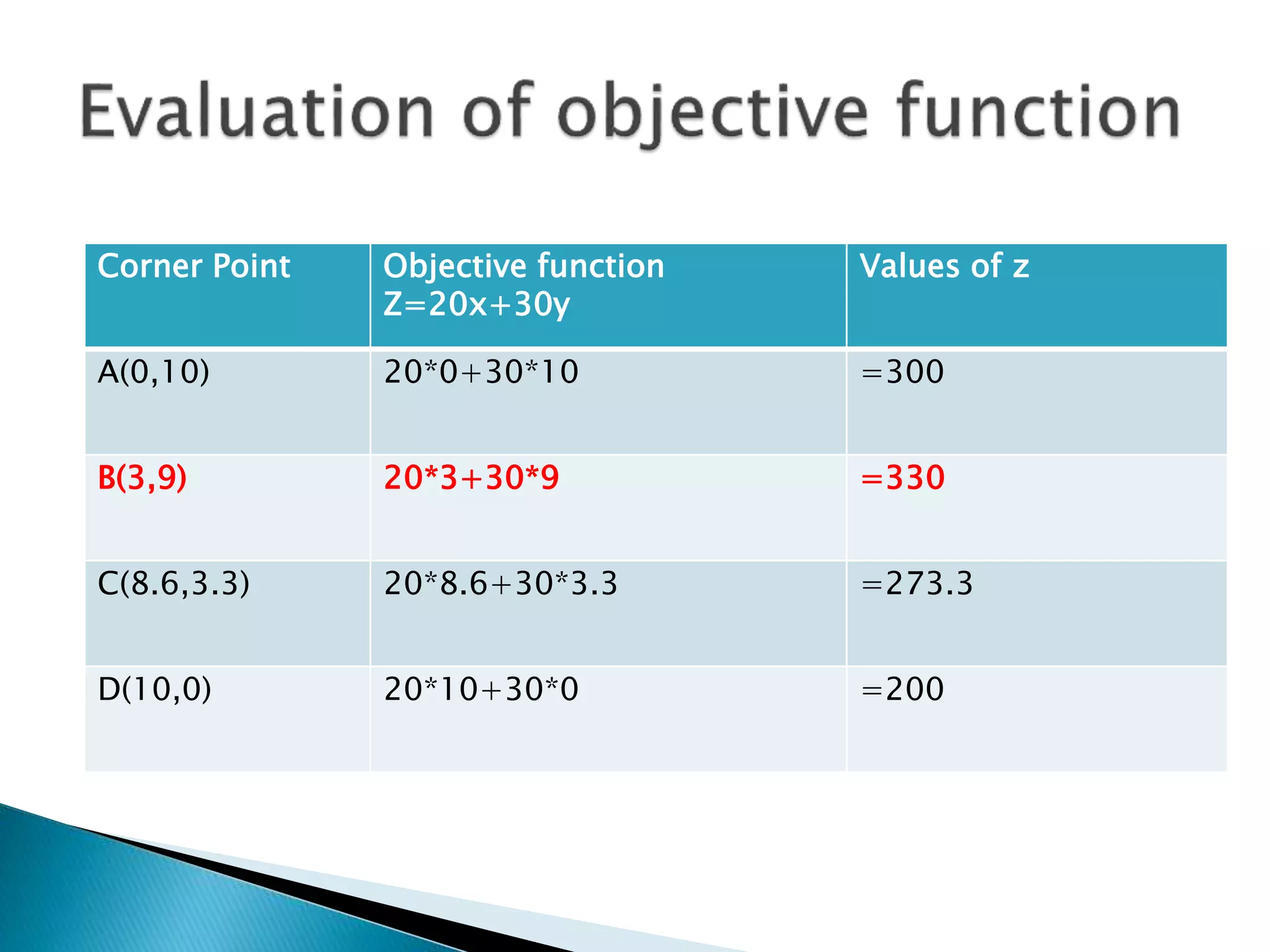
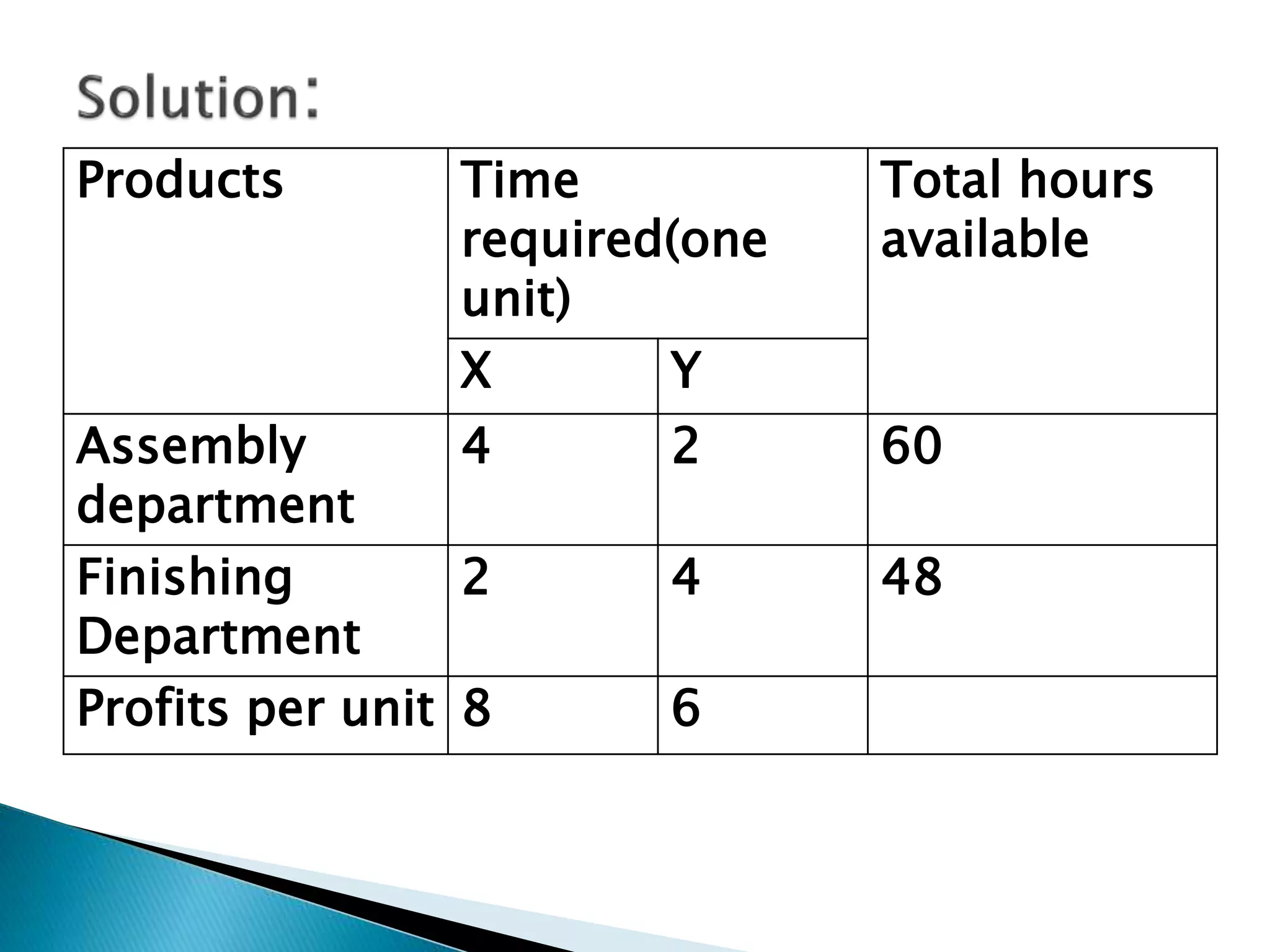
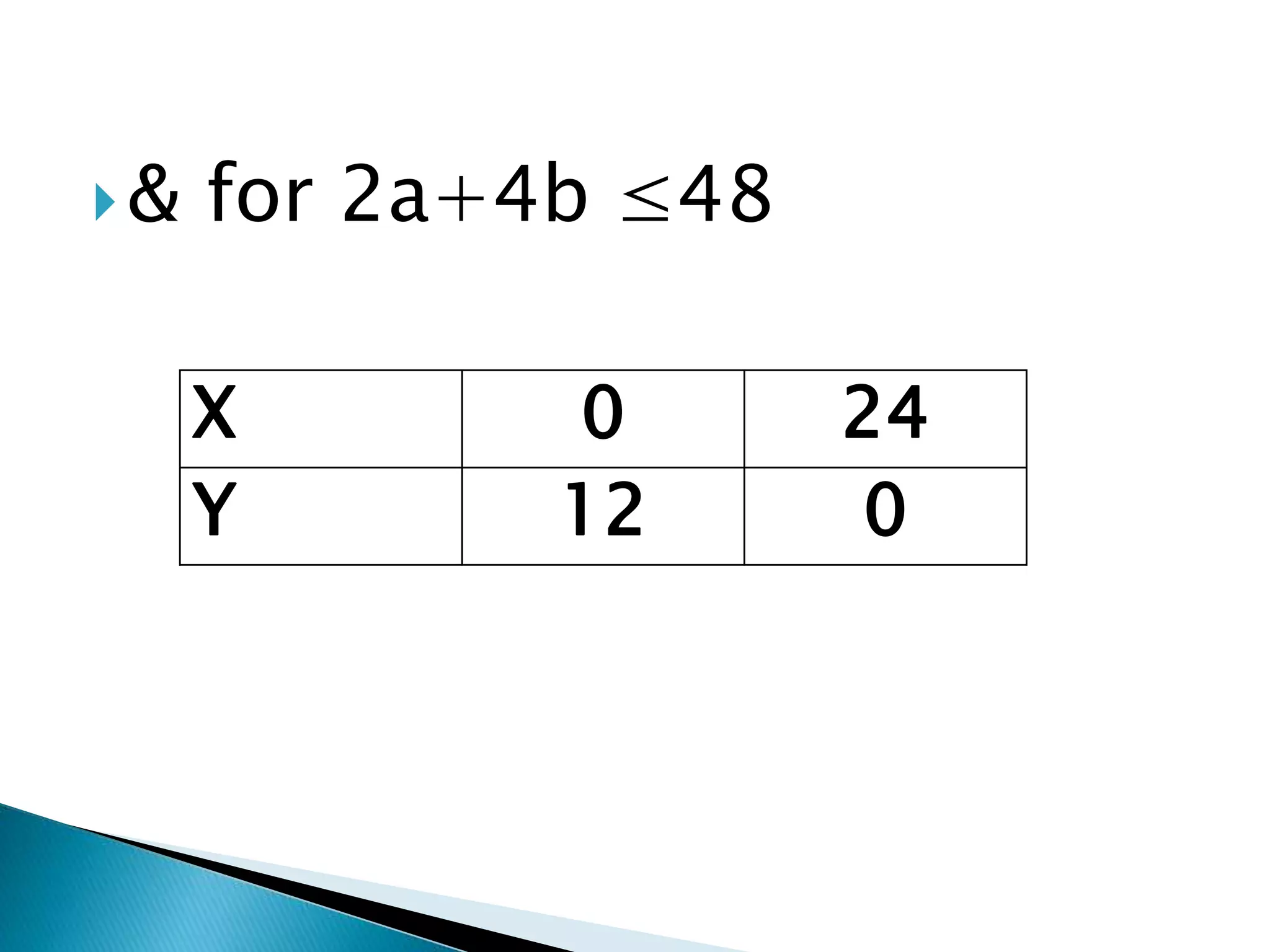
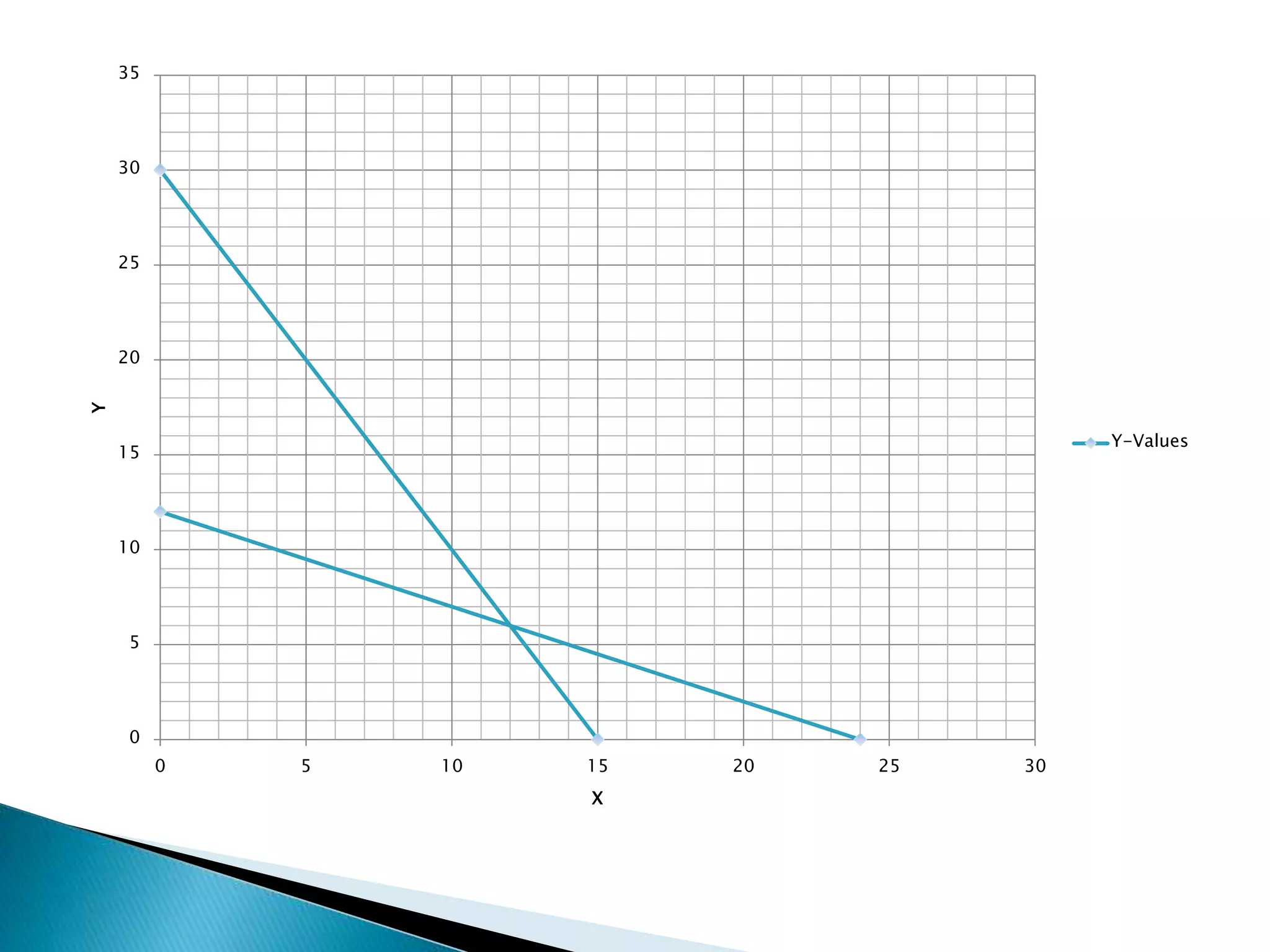
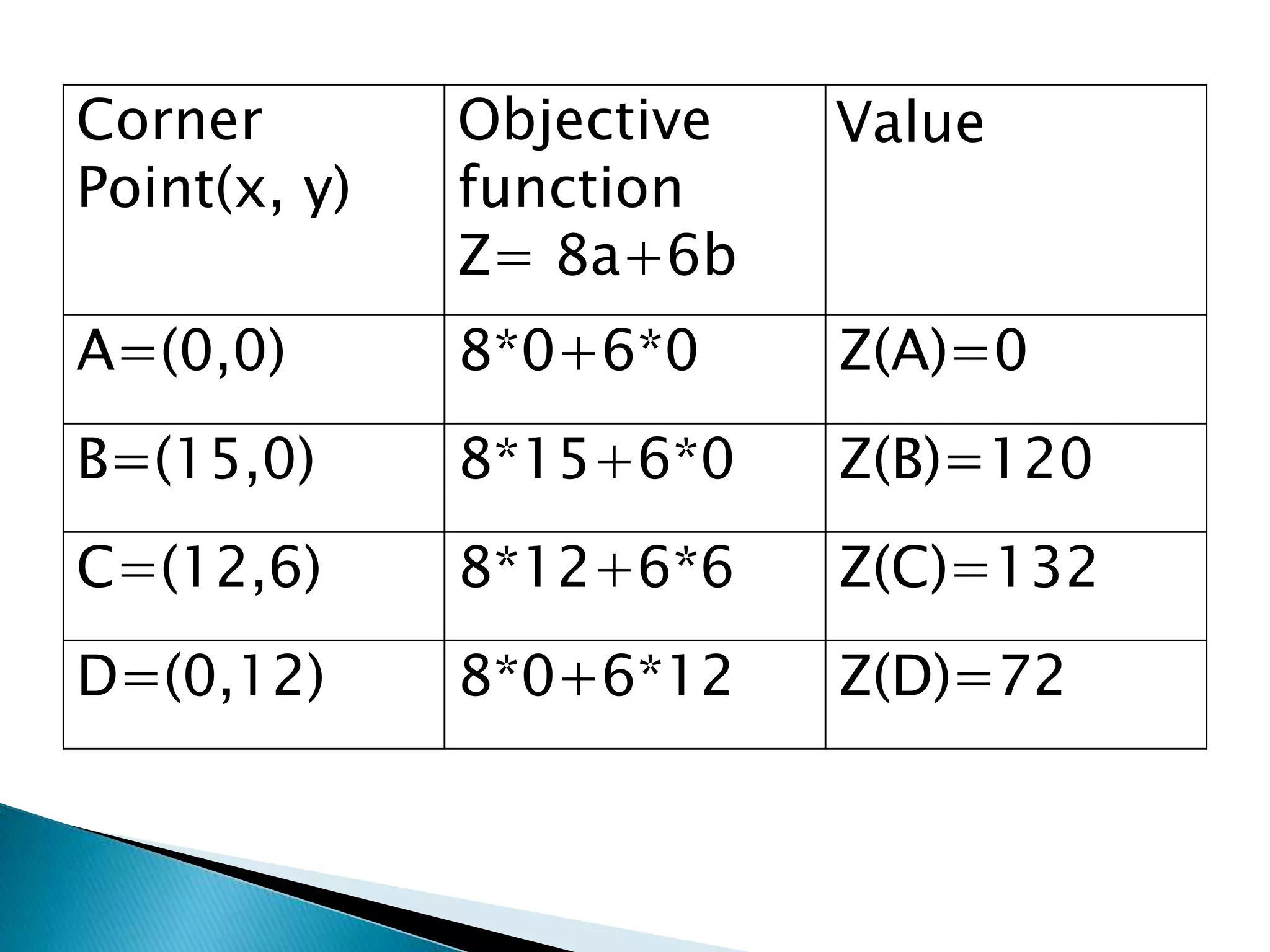
The document describes how to formulate and solve linear programming problems by defining the components of a linear programming problem, describing how to model real-world problems as linear programs, and outlining two methods, graphical and simplex, to solve linear programming problems. It then provides examples of solving linear programming problems using these steps and methods.