Embed presentation
Downloaded 103 times
![Manual Work
E. N. Sathishkumar M.Sc., M.Phil., [Ph.d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/k-meansmanualwork-140807041110-phpapp02/85/K-Means-manual-work-1-320.jpg)

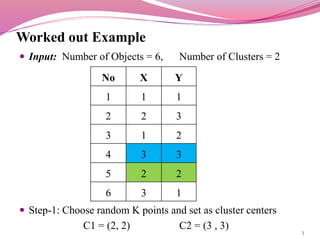
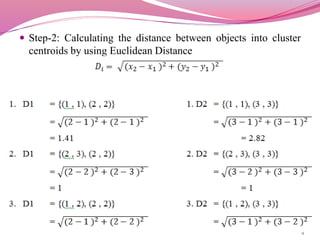


The k-means clustering algorithm takes as input the number of clusters k and a set of data points, and assigns each data point to one of k clusters. It works by first randomly selecting k data points as initial cluster centroids. It then assigns each remaining point to the closest centroid, and recalculates the centroid positions. This process repeats until the centroids are stable or a stopping criteria is reached. As an example, the document applies k-means to cluster 6 data points into 2 groups, showing the random selection of initial centroids, assignment of points, and recalculation of centroids over multiple steps.
![Manual Work
E. N. Sathishkumar M.Sc., M.Phil., [Ph.d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/k-meansmanualwork-140807041110-phpapp02/85/K-Means-manual-work-1-320.jpg)




