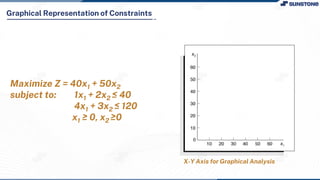
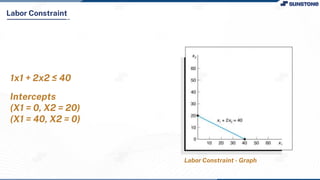
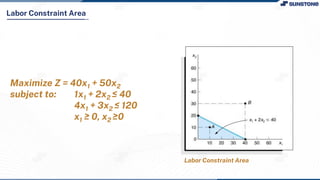
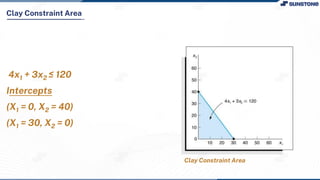
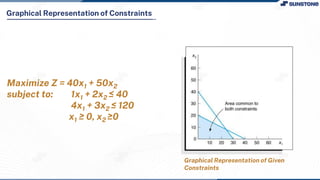
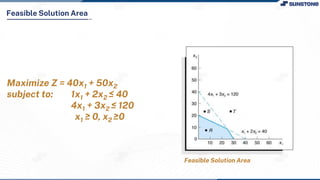
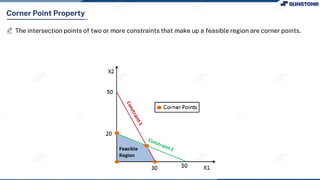
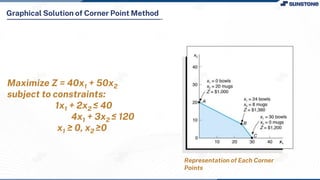
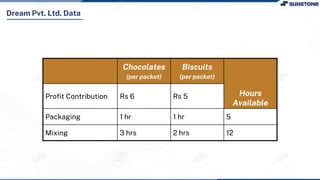
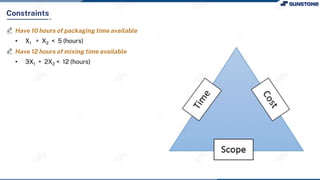
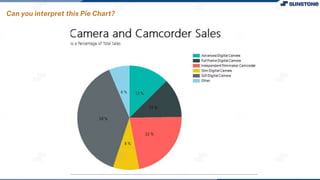
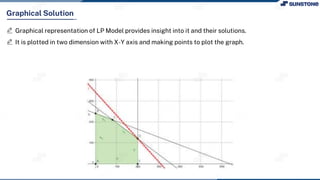
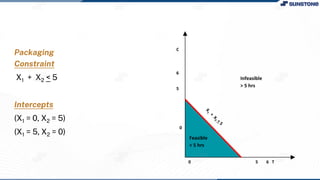
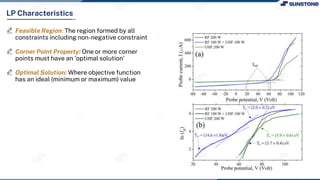
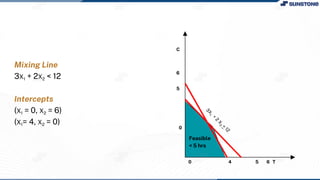
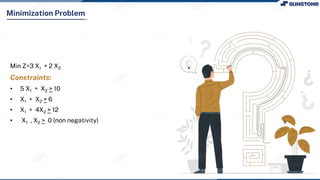
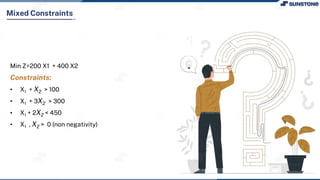
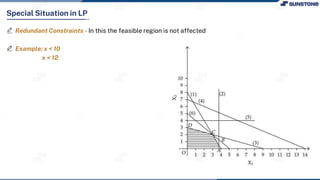
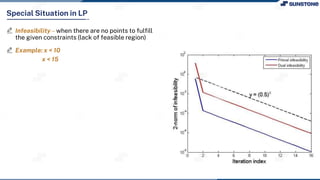
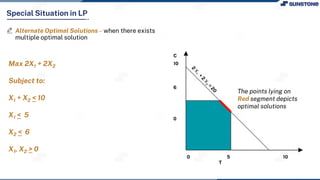
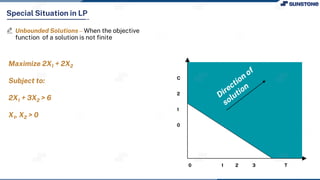
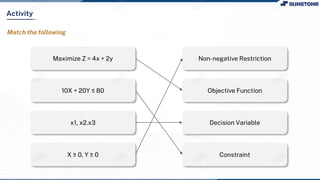
This lecture discusses solving linear programming problems graphically. It explains how to represent constraints and the feasible region on a graph with two decision variables. The optimal solution will occur at a corner point of the feasible region where the objective function is maximized or minimized. An example problem about a company choosing how many chocolate packets and biscuits to produce is presented and solved graphically. Key aspects covered include the corner point property, characteristics of linear programs, and special situations that can occur.