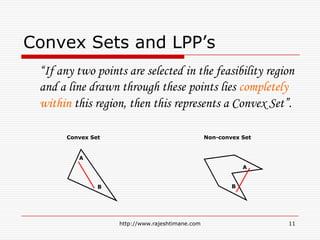
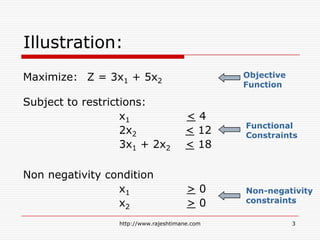
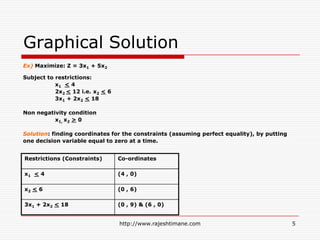
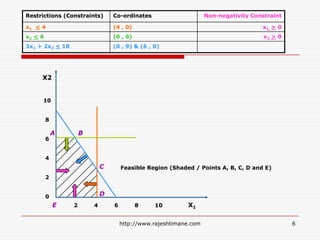
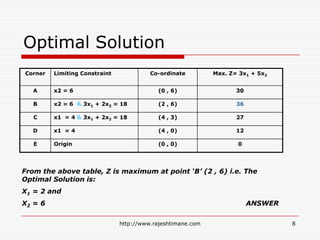
The document explains the fundamentals of linear programming, including definitions of key terms such as decision variables, objective functions, and constraints. It illustrates how to formulate an optimization problem with linear functions and visualizes feasible solutions and optimal outcomes within a constraint graph. The optimal solution is determined by evaluating the corner points of the feasible region to find the best result for the objective function.
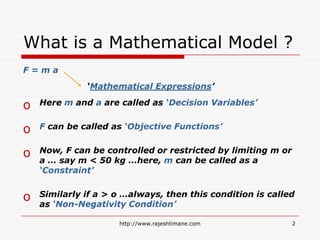


![What is Feasibility ?
Feasibility Region
[Dictionary meaning of feasibility is possibility]
“The region of acceptable values of the
Decision Variables in relation to the
given Constraints (and the Non-Negativity
Restrictions)”
http://www.rajeshtimane.com 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearprogramming-graphicalmethodfeasibility-121108132312-phpapp01/85/Linear-programming-graphical-method-feasibility-9-320.jpg)