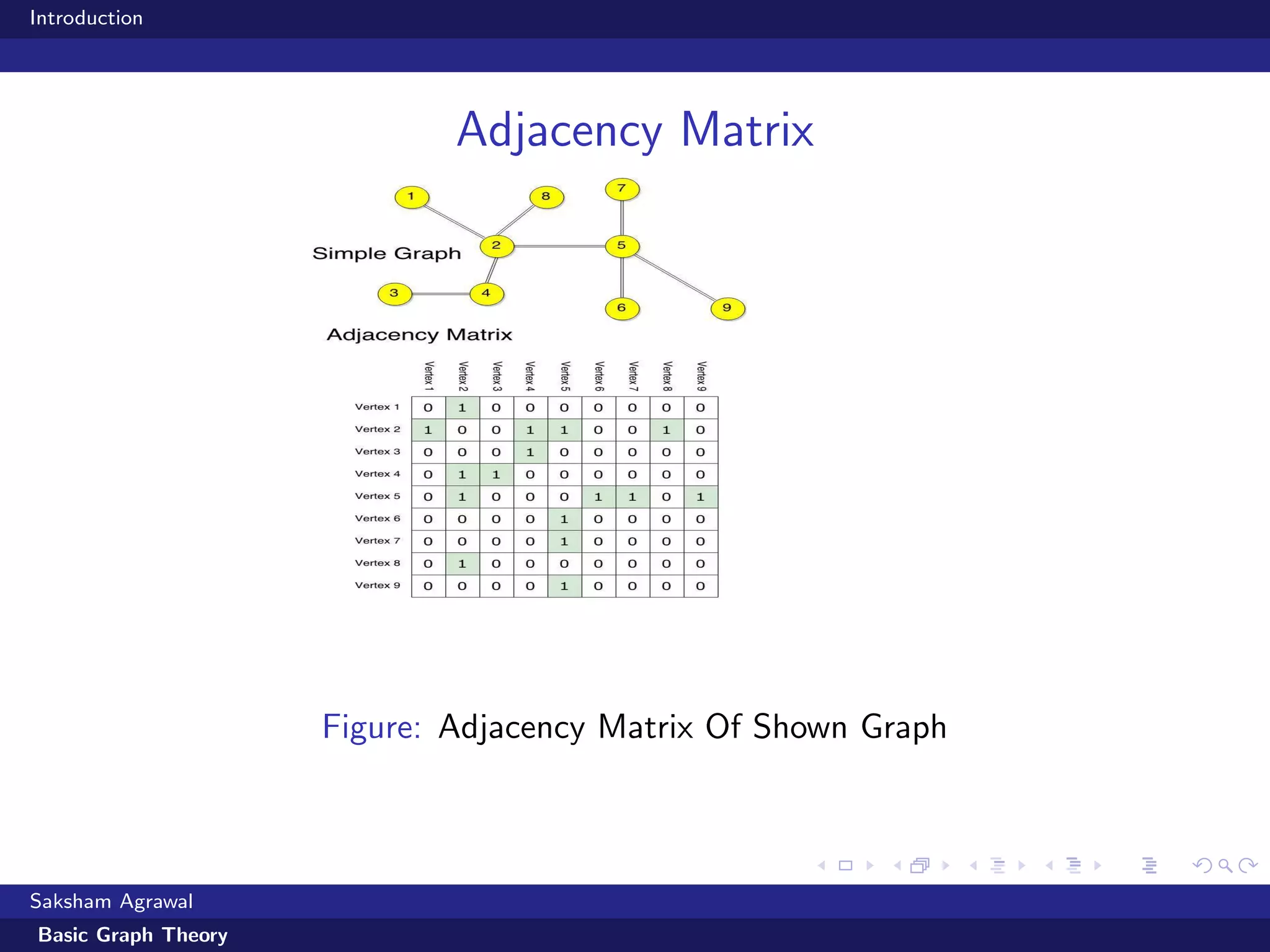
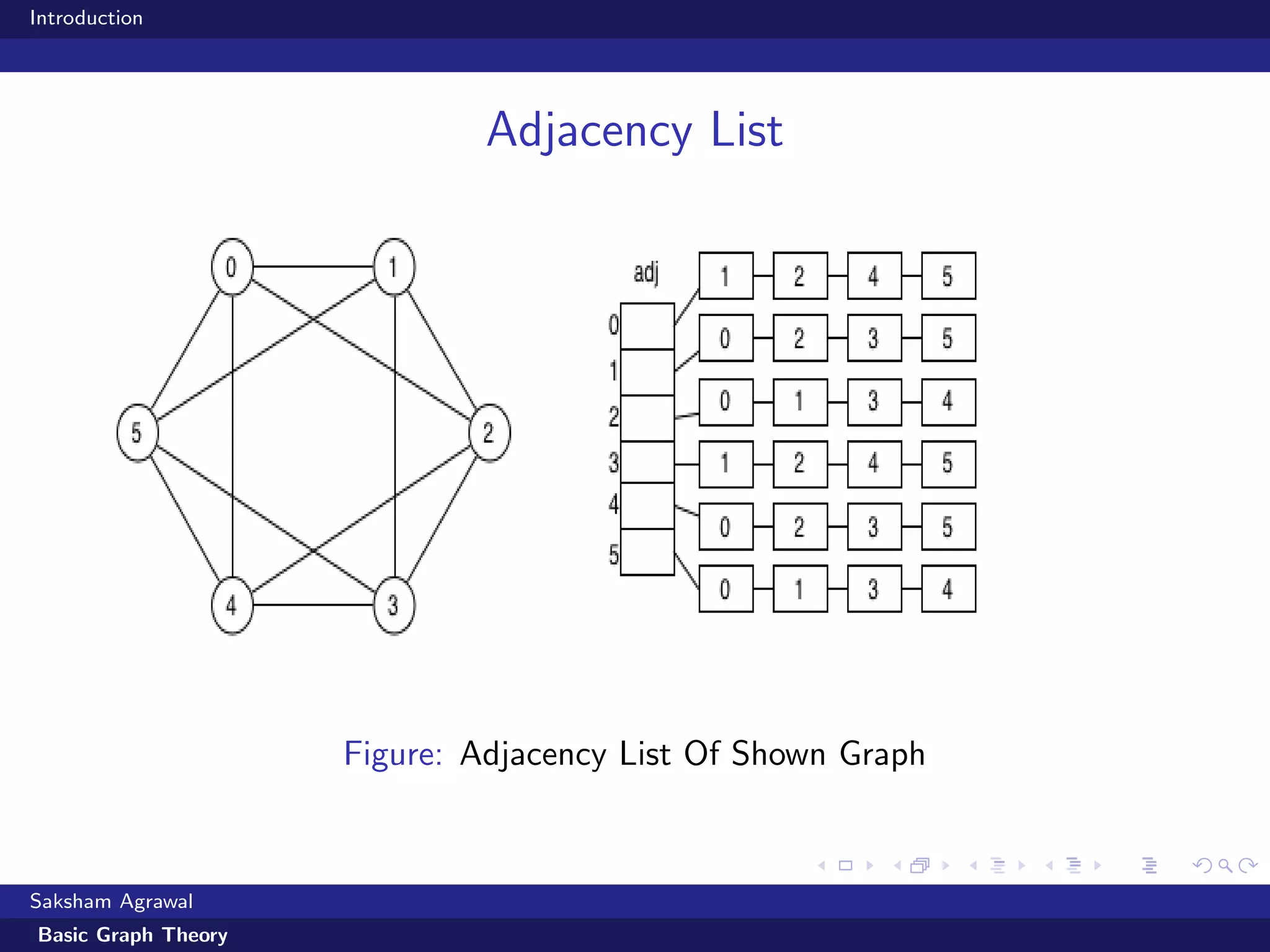
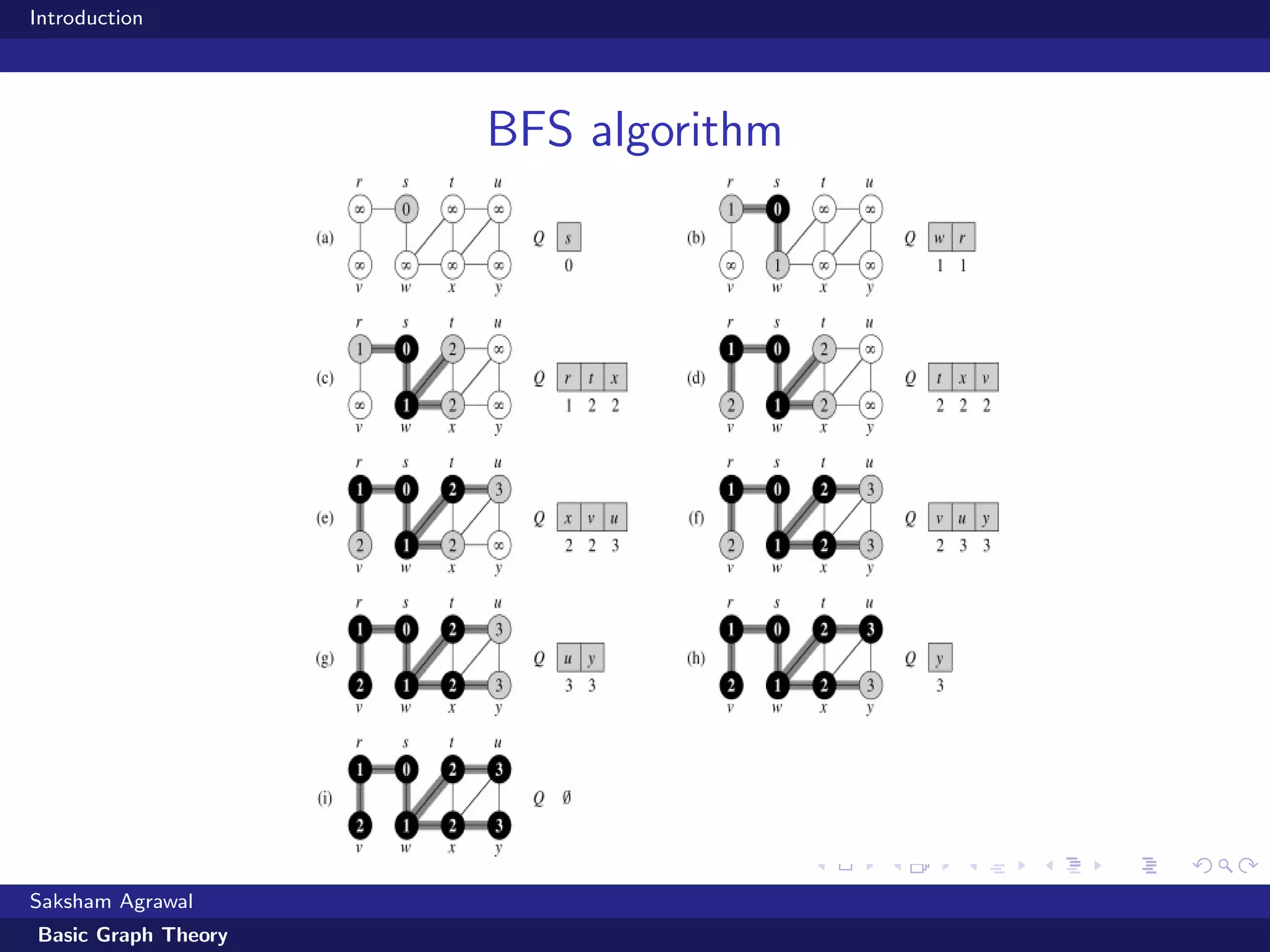
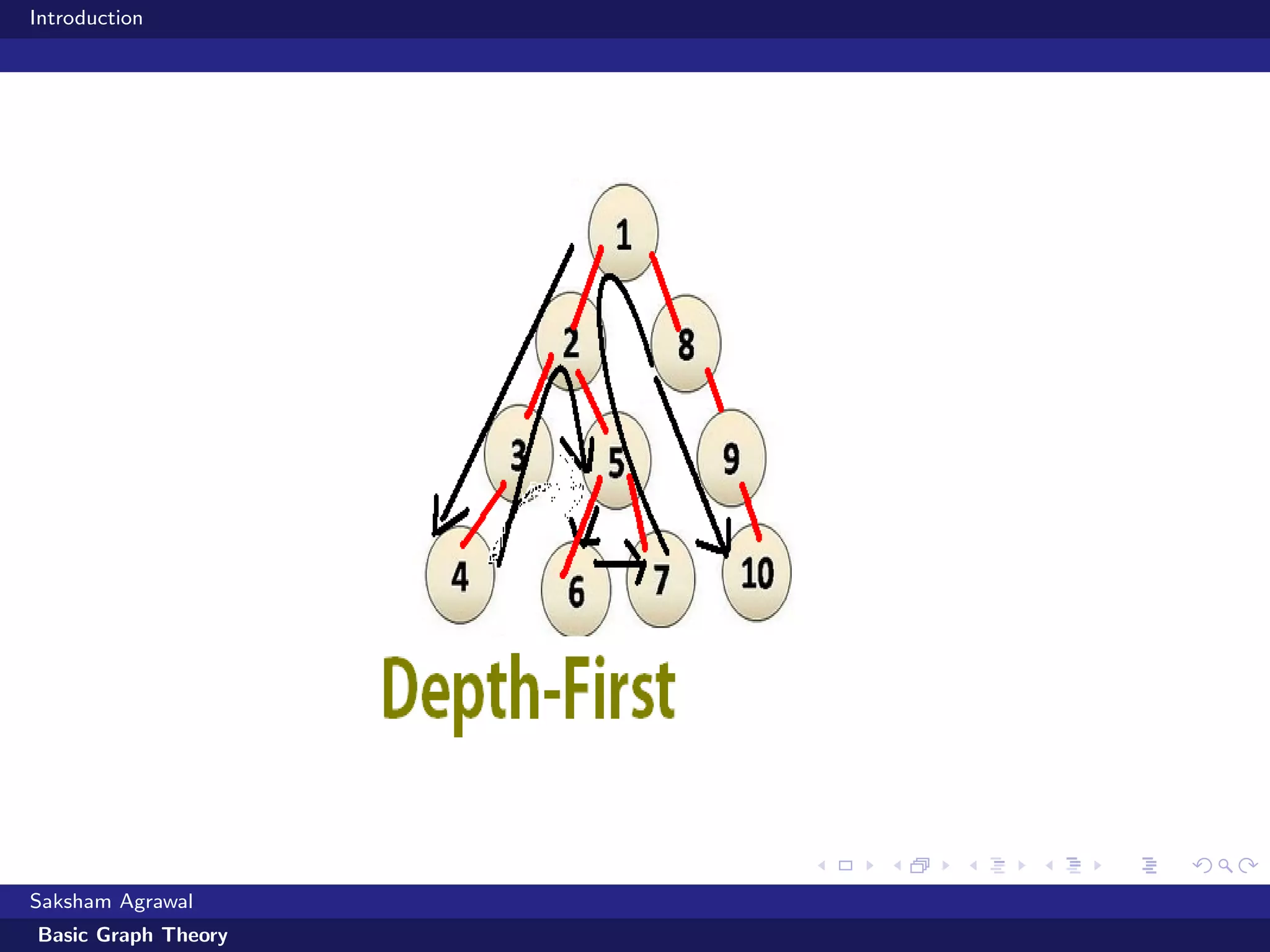
This document is an introduction to basic graph theory. It defines what a graph is made up of (vertices and edges) and describes different types of graphs (directed vs undirected). It also defines common graph terminology. The document outlines different ways to represent graphs using adjacency matrices and lists. It then describes algorithms for traversing graphs, including breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS), and provides examples of applications for each type of search.