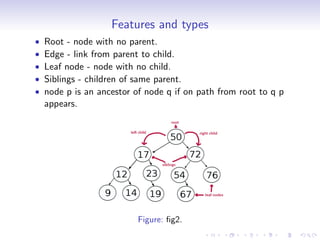
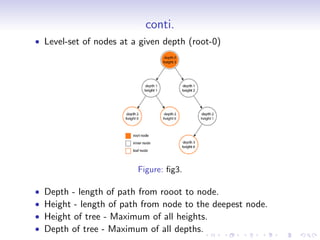
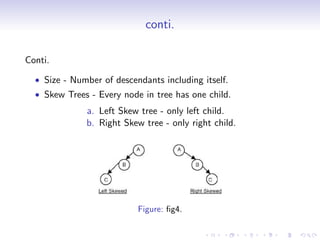
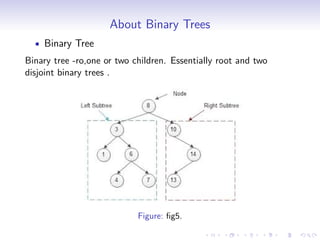
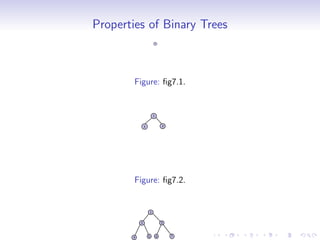
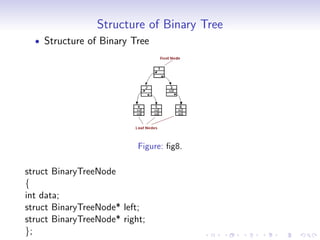
A tree is a hierarchical data structure where each node can have many children. It consists of a root node, edges that link parents to children, and leaf nodes without children. A binary tree restricts each node to having at most two children. Binary trees can be full, complete, or strict depending on how nodes are structured. Common operations on binary trees include inserting, deleting, searching, and traversing nodes. Binary trees have applications in compilers, data compression, search trees, and priority queues.