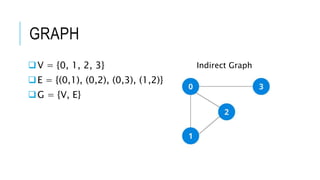
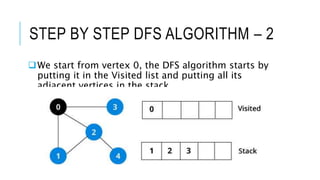
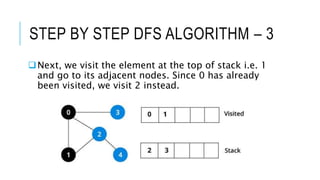
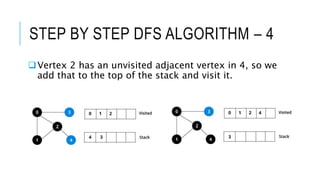
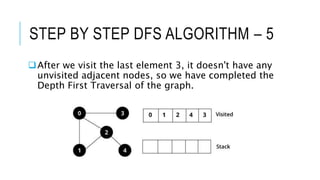
The document discusses the Depth First Search (DFS) algorithm used in graph theory, highlighting its operational steps and the concept of graph terminology such as adjacency and paths. It includes a step-by-step example of DFS applied to an undirected graph and provides pseudocode implementations in various programming languages. References for further study and contact information for Dr. Achmad Solichin are also included.