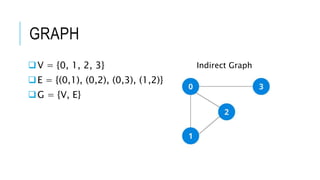
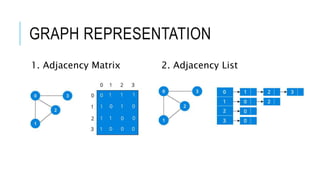
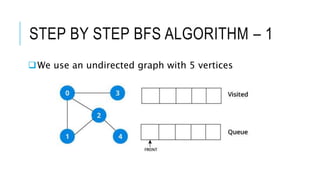
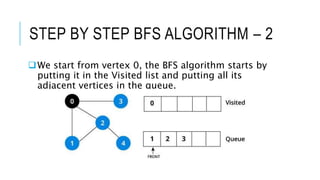
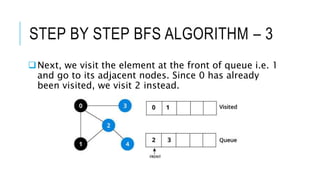
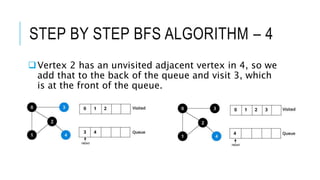
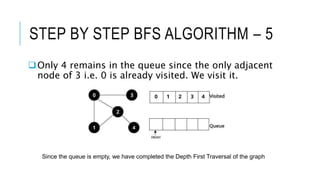
The document discusses the Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm for graph traversal, detailing graph terminology such as adjacency and paths. It outlines the steps of the BFS algorithm using a specific example of an undirected graph and provides pseudocode for its implementation in programming languages like C, C++, and Java. References and contact information for Dr. Achmad Solichin are also included.