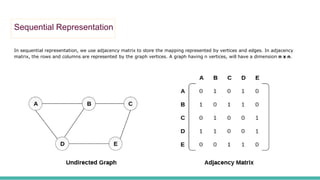
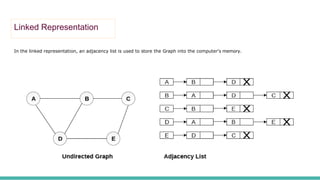
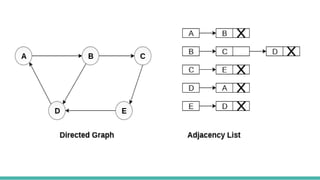
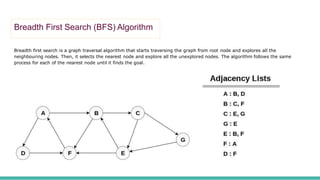
This document discusses graph representations and traversal algorithms. It describes two common ways to represent graphs: sequential representation using an adjacency matrix and linked representation using an adjacency list. It also explains two graph traversal algorithms - breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS). BFS explores all neighboring nodes first before moving to the next level, while DFS goes deeper first before backtracking. Pseudocode is provided to demonstrate the steps of each algorithm.