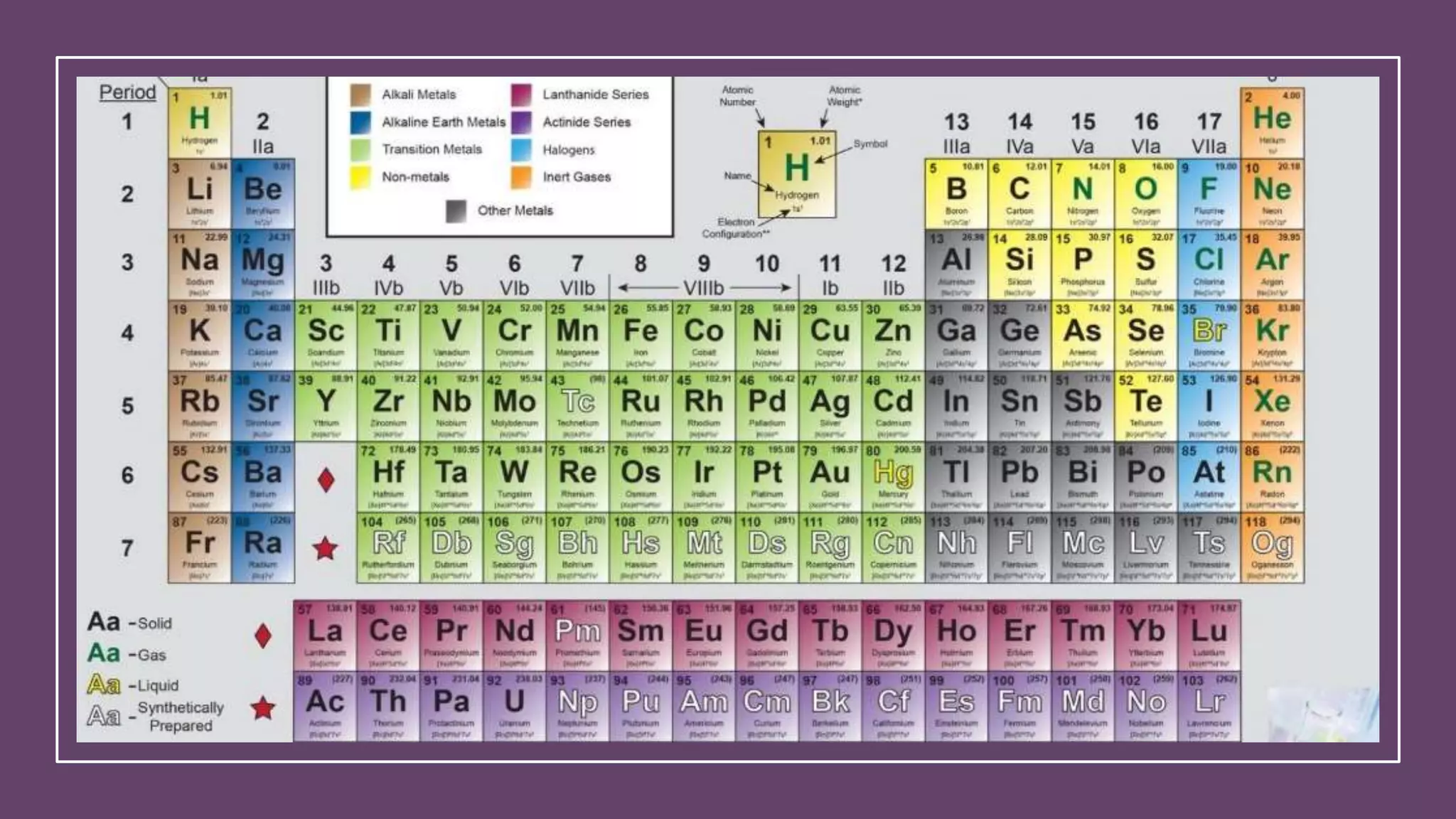
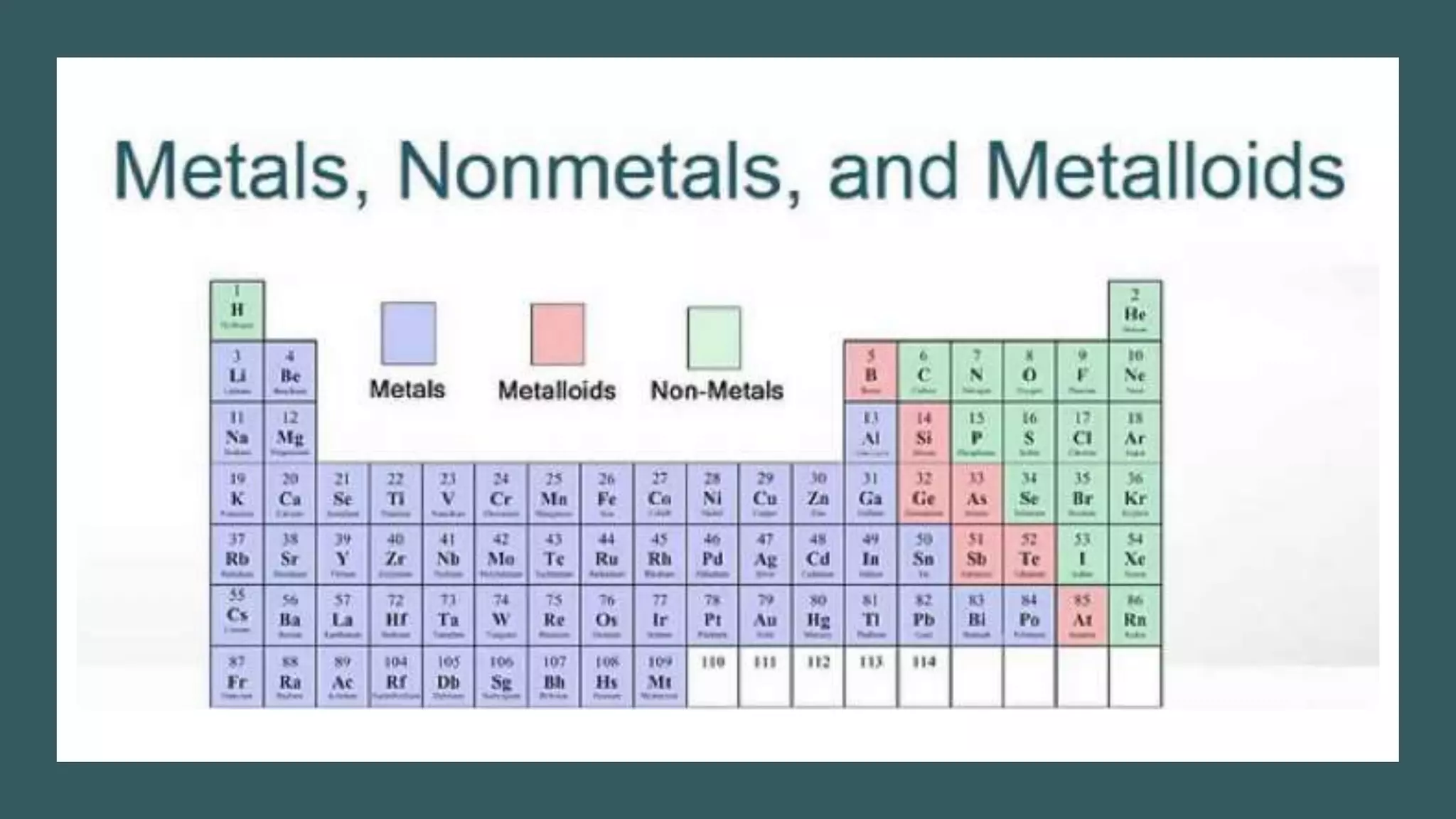
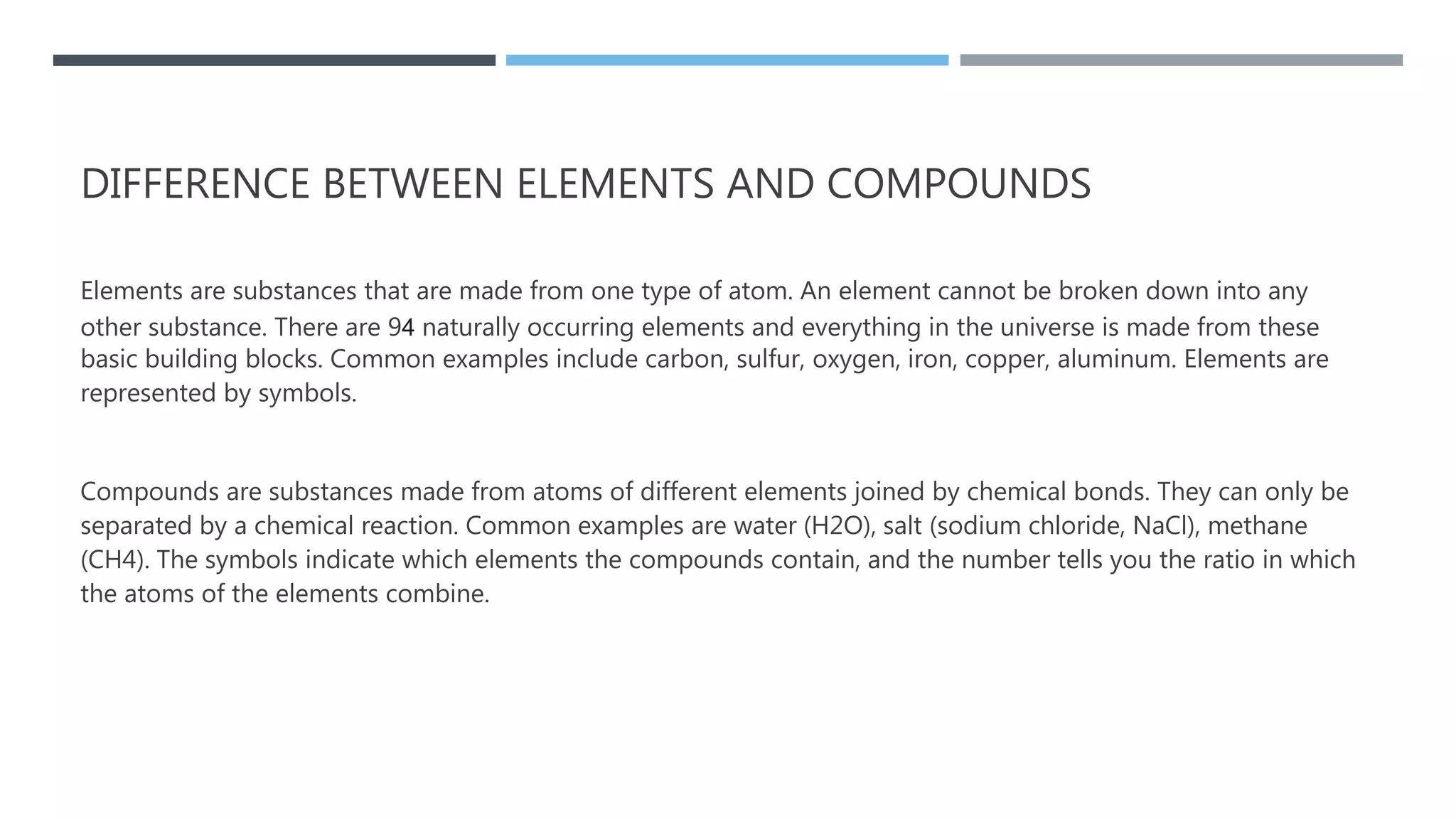
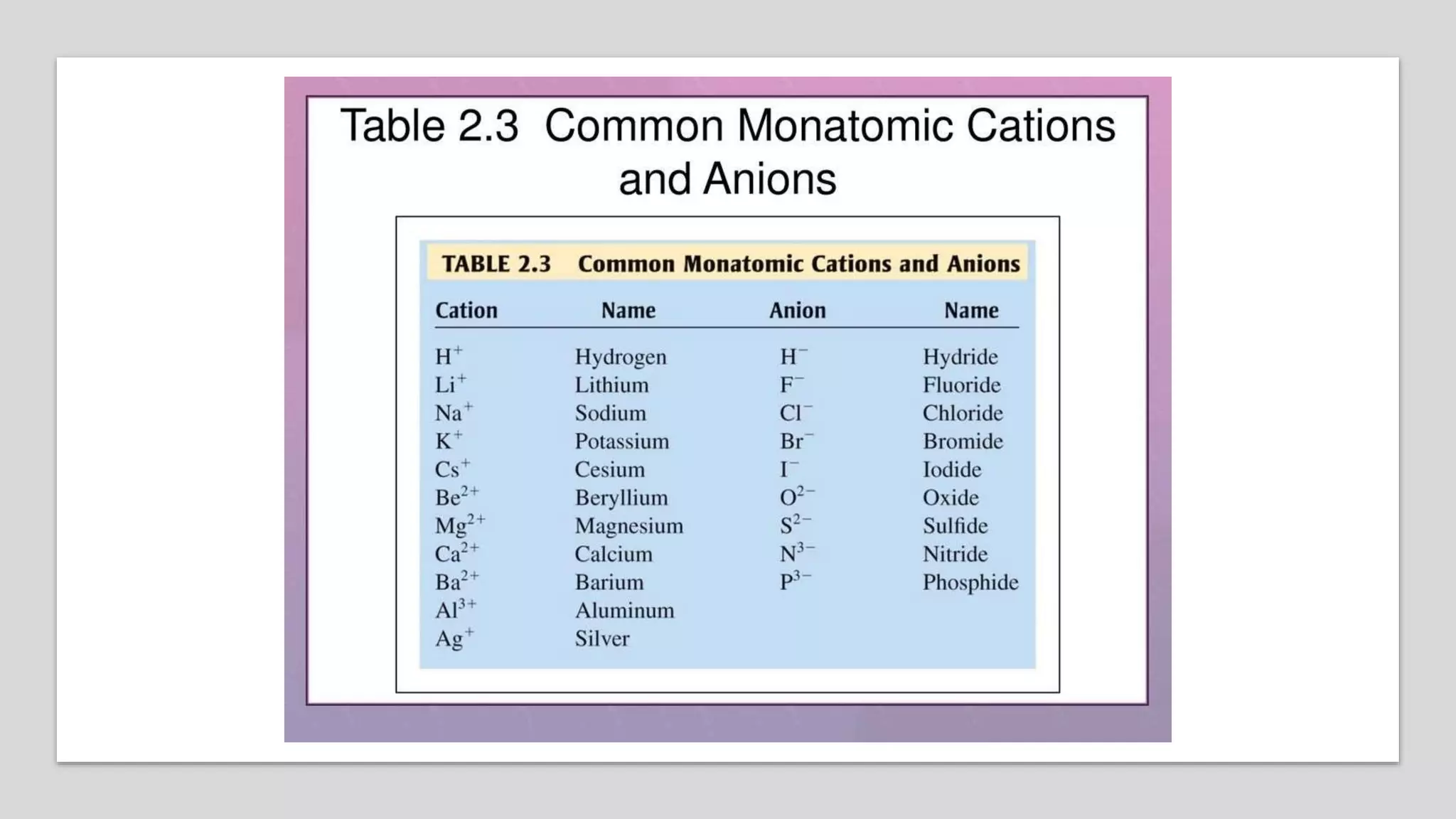
This document provides an overview of elements, compounds, and how they relate. It defines elements as pure substances made of single atom types, while compounds are formed when two or more different elements bond together. Elements are represented by symbols on the periodic table and have distinct properties based on their atomic structure. Compounds have new properties and are represented by formulas showing the elements present and their ratios. The document explains how ionic and covalent bonds form compounds from elements and provides examples of common elements, compounds, and how to determine compound formulas from their constituent ions.