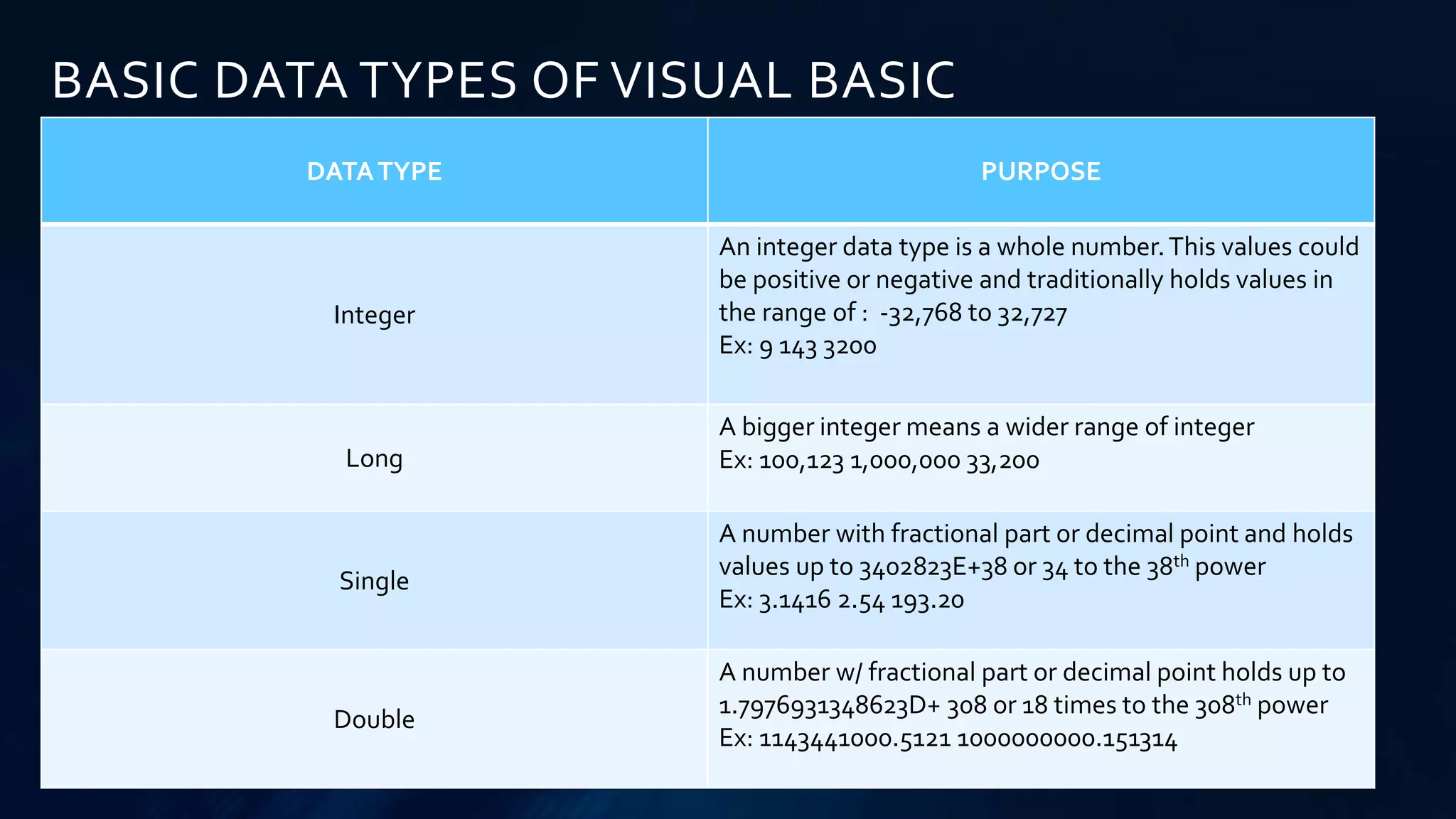
Visual Basic is an event-driven programming language first released by Microsoft in 1991. It is used for beginners and has all-purpose symbolic instruction code. The language uses events, objects, variables, constants, methods, arithmetic operations, comparisons, and data types like integers, strings, Booleans, and dates. Key concepts include events that trigger code execution, objects that combine code and data, and methods like val() and str() that convert between numeric and string data.