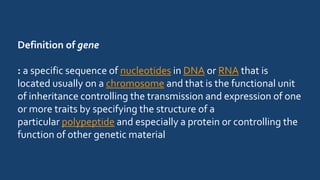
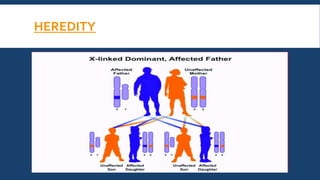
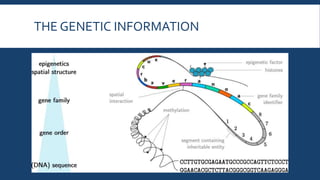
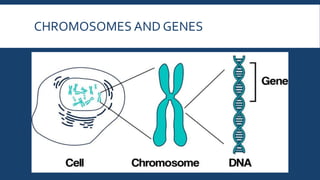
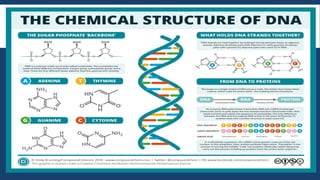
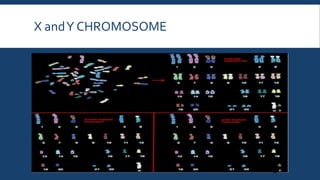
Genetics is the study of heredity and genes. It examines how traits are passed from parents to offspring. Genes, which are segments of DNA, are located on chromosomes within cells and contain instructions that determine an organism's traits. During reproduction, chromosomes and genes are transmitted from parents to children, influencing the children's characteristics. Modern genetics research examines gene structure and function, variation, inheritance patterns, and more within cells, organisms, and populations. Genetics helps explain how heredity and environment interact to influence development and behavior.