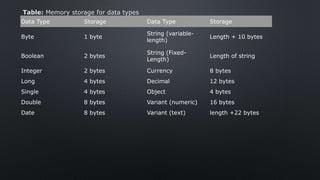
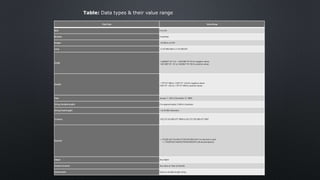
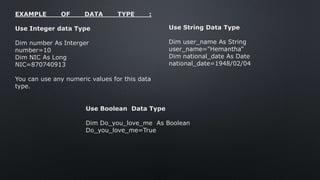
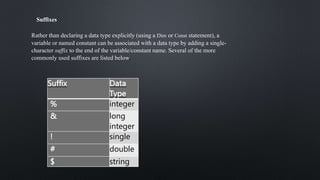
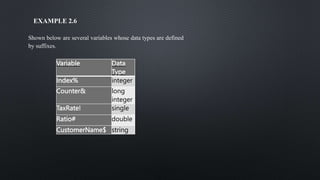
The document provides an overview of constants and variables in Visual Basic, explaining their definitions, rules for naming, and data types. Constants are fixed values that remain unchanged, while variables can store values that may vary during program execution. It also details the memory allocation for different data types and how to declare them using the 'dim' keyword or with suffixes for implicit type association.





![You can declare a variable with the 'dim' keyword.
Syntax:
Dim variable As [Type]
Example:
Private Sub cmdSum_Click()
Dim m As Integer
Dim n As Integer
Dim sum As Integer
m = 10 'm is a variable, 10 is a constant
n = 30
sum = m + n
Print "The sum is " & sum
End Sub
Output: The sum is 40
Variable Declaration
• Depending on where the variables are declared and how they are declared, there are many
ways to declare a variable in visual basic.
•When you declare a variable, memory space for the variable is reserved.
•This is called memory allocation.
•Different amount of memory space is reserved for different data types.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2i-221216045705-2867c86d/85/Visual-Basic-Fundamentals-6-320.jpg)