Embed presentation
Download to read offline



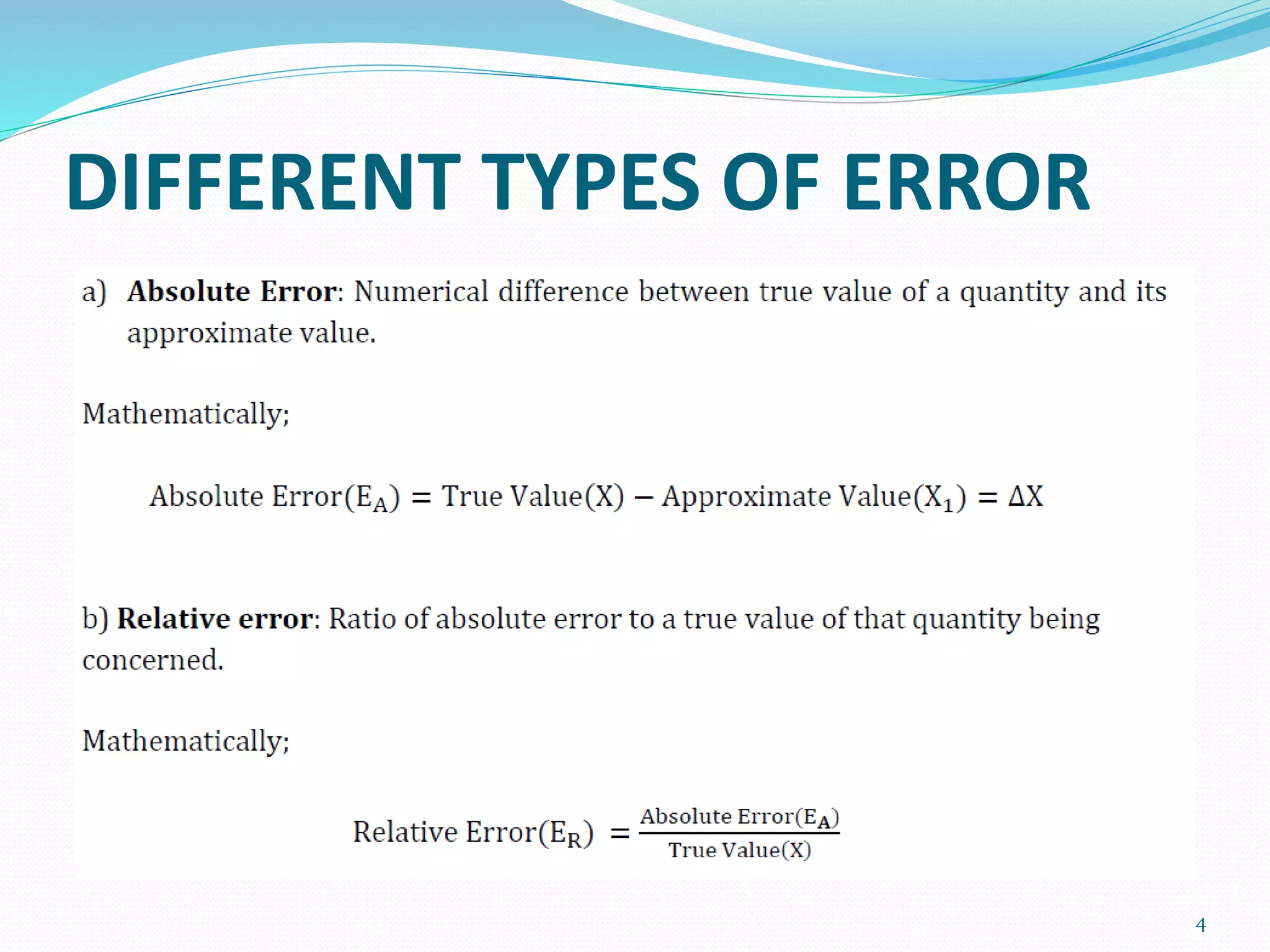








This document introduces different types of numerical errors that can arise when using approximations to represent exact mathematical operations. It defines numerical error as the difference between the true value and approximation. The main type of error discussed is rounding off, which occurs when a large number is truncated to a usable number of figures. The document provides examples of numbers rounded off to four significant figures and references additional resources on the topic.











