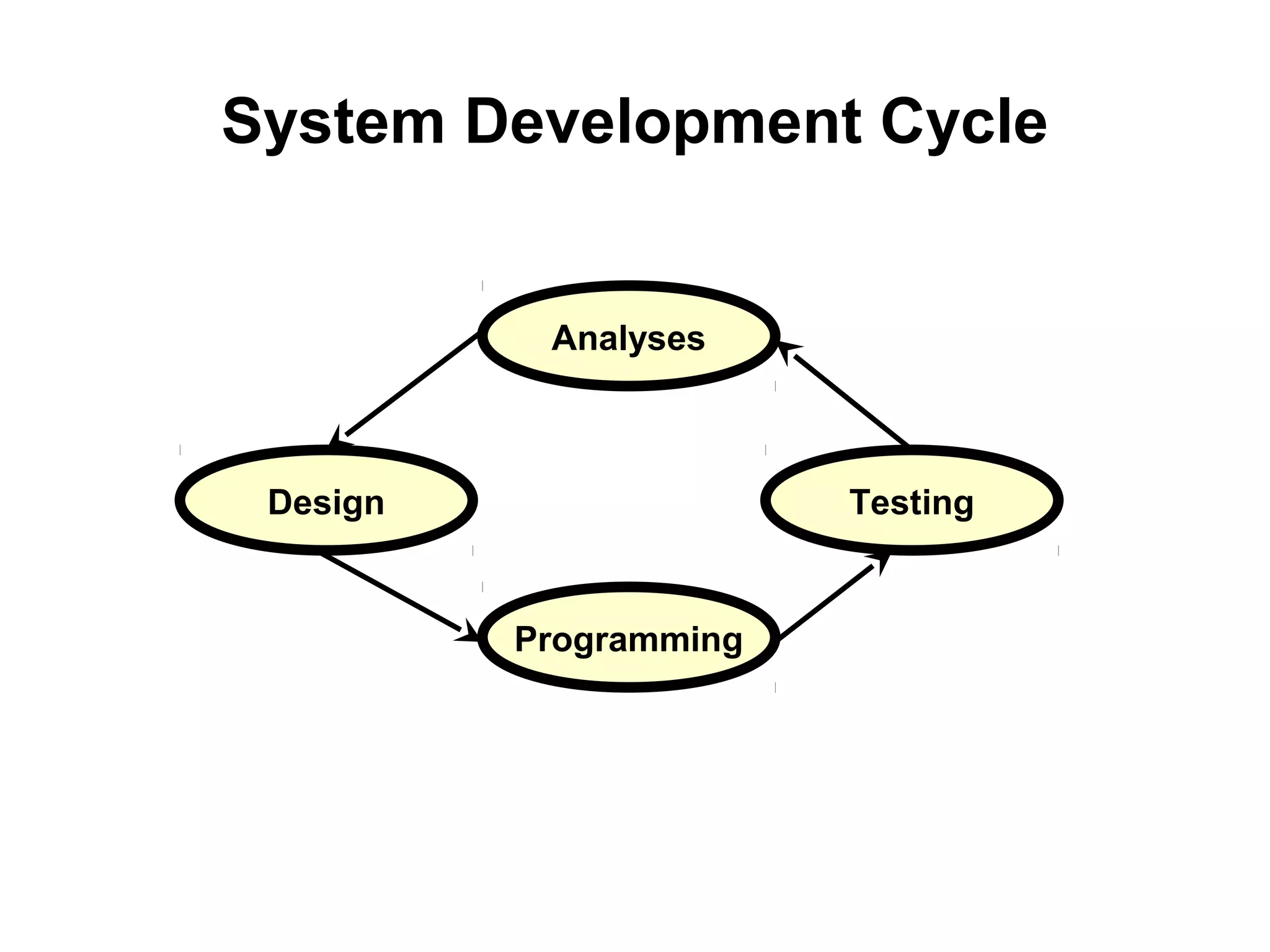
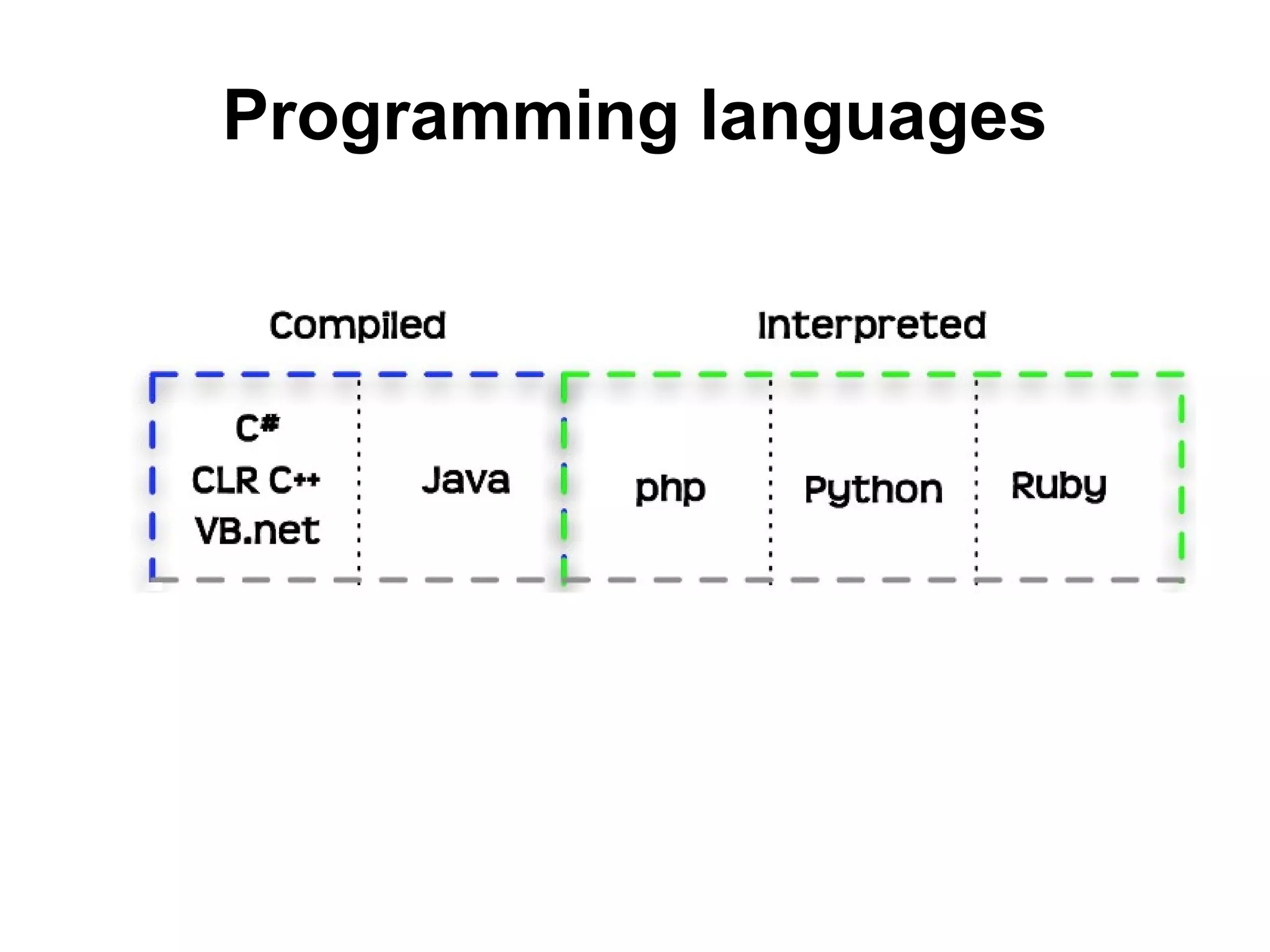
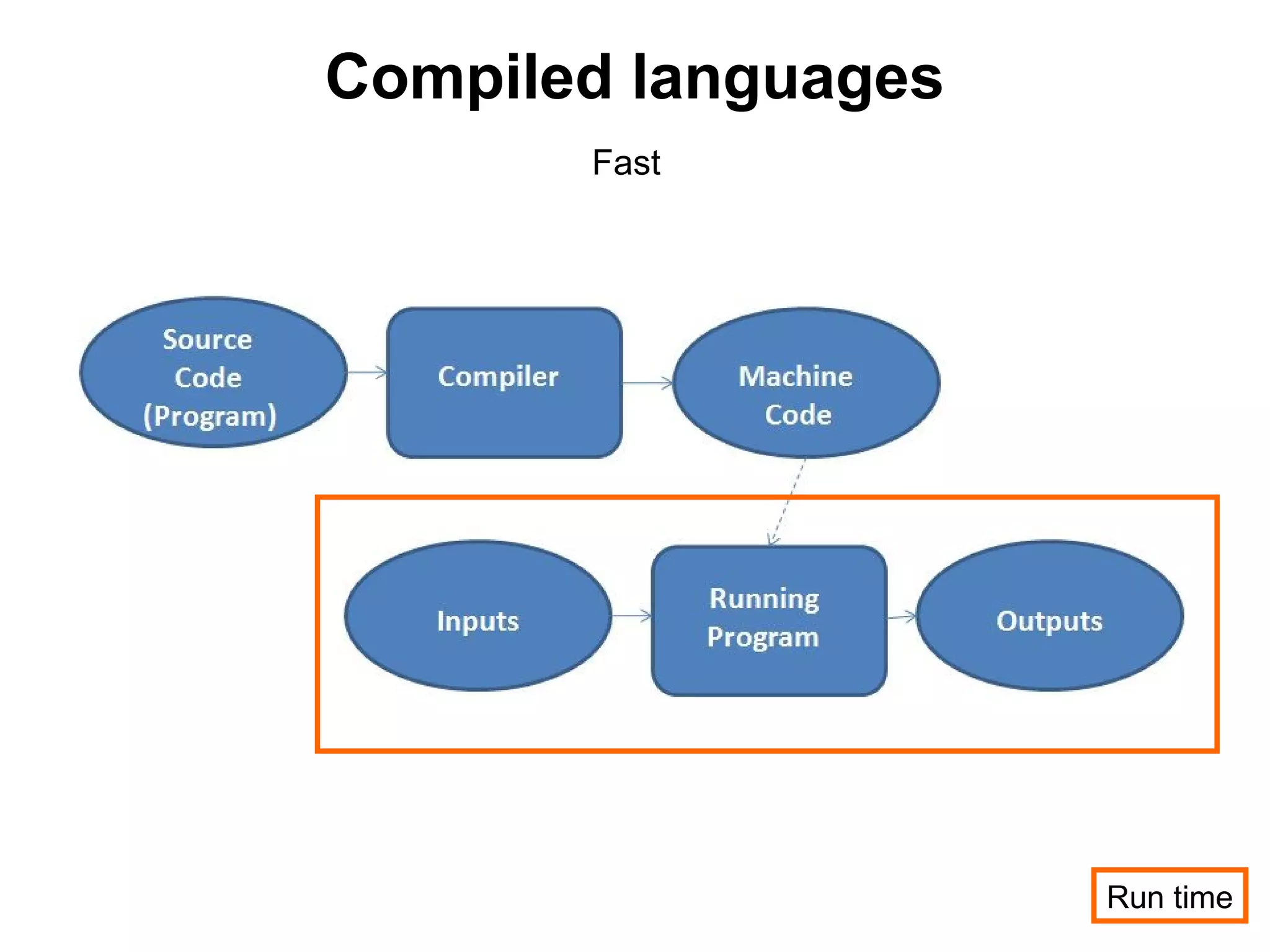
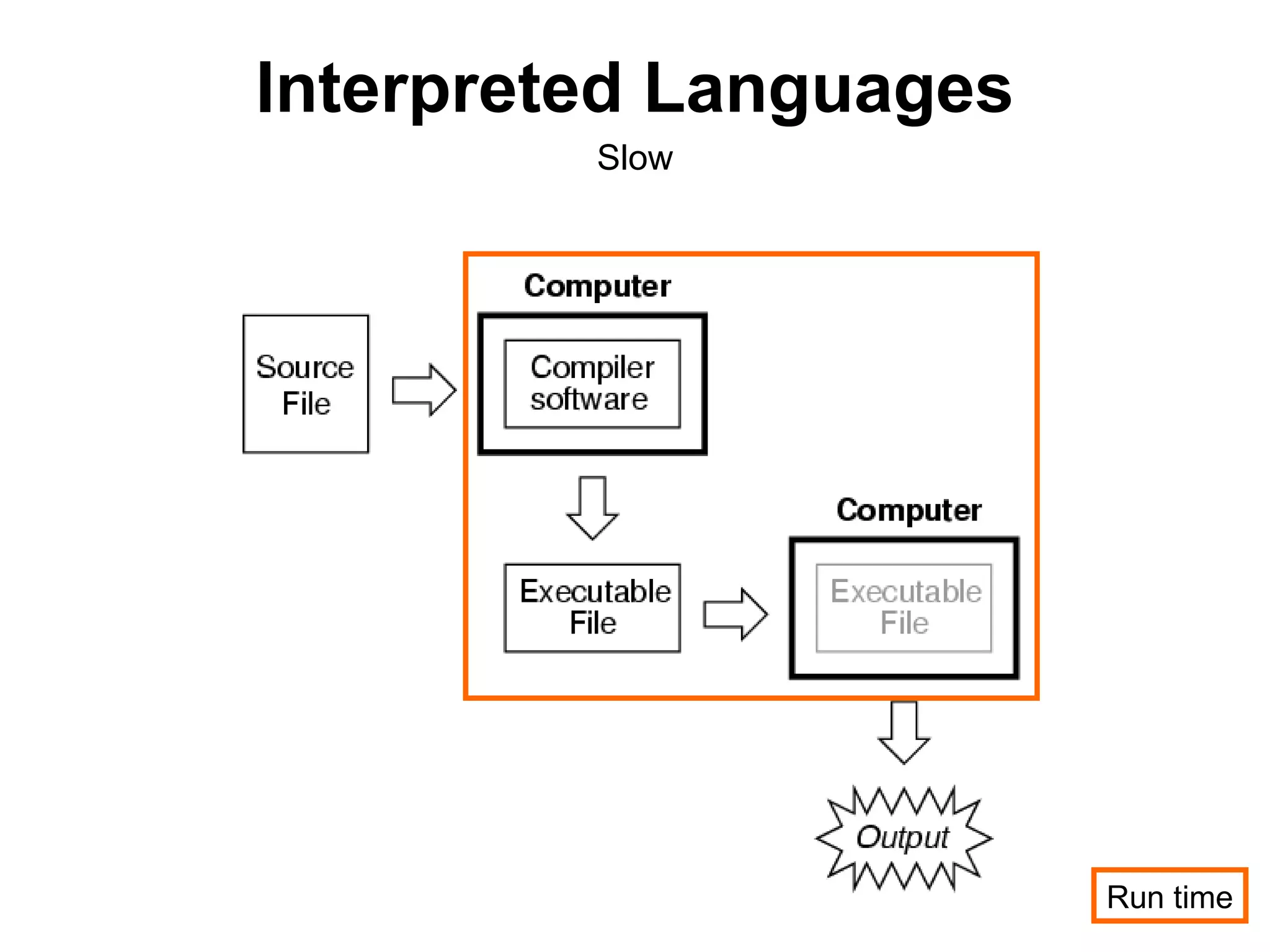
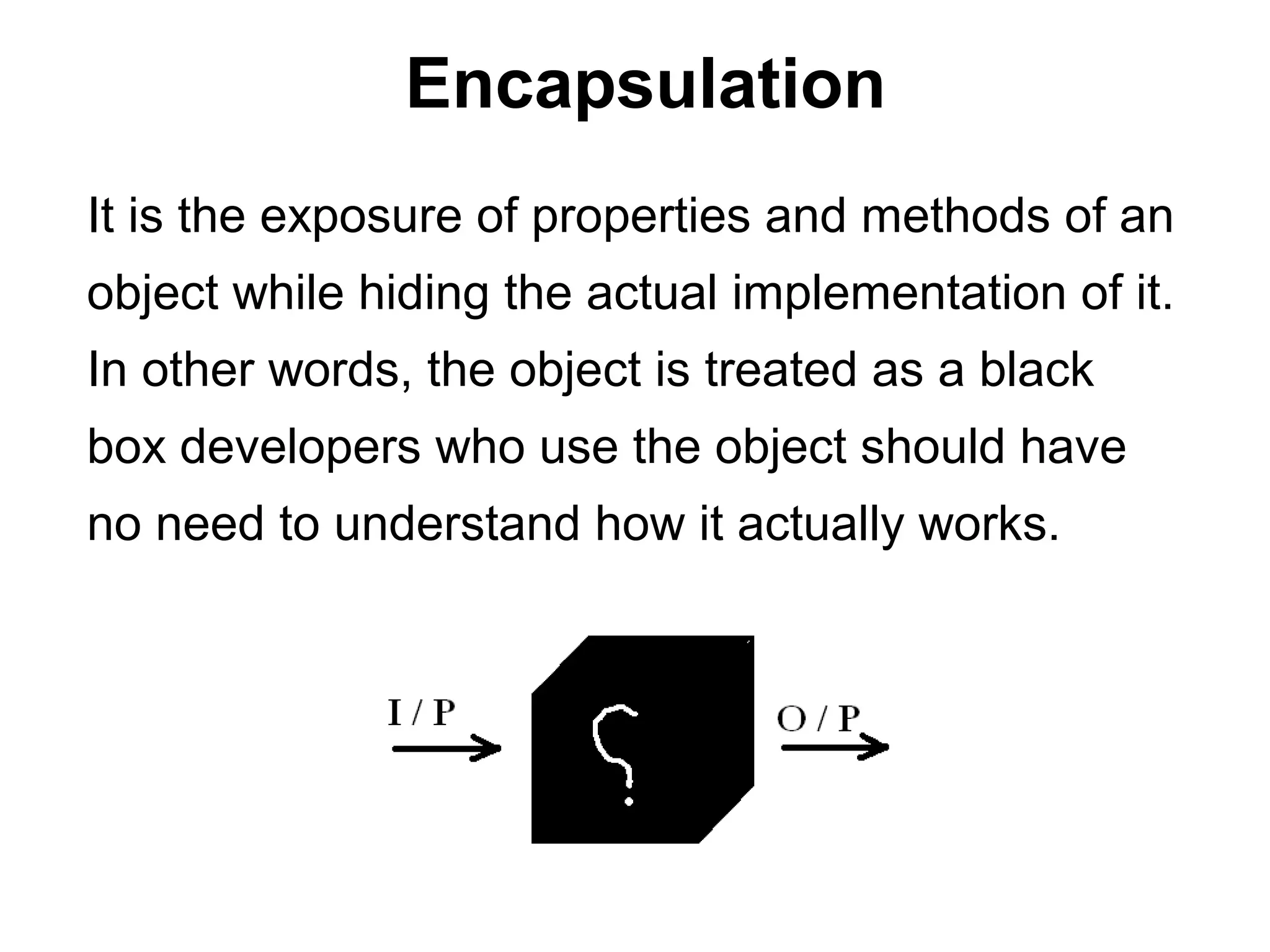
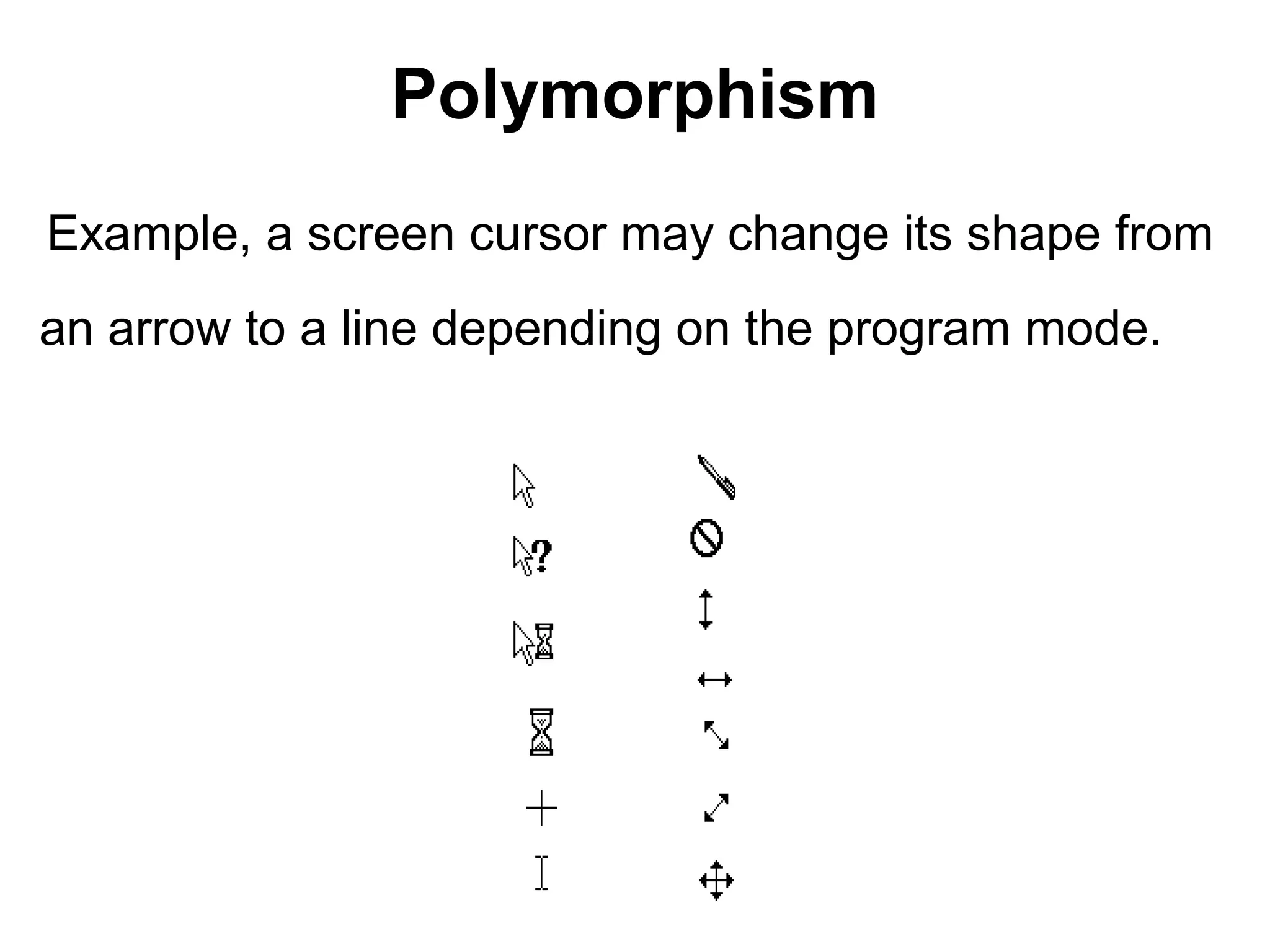
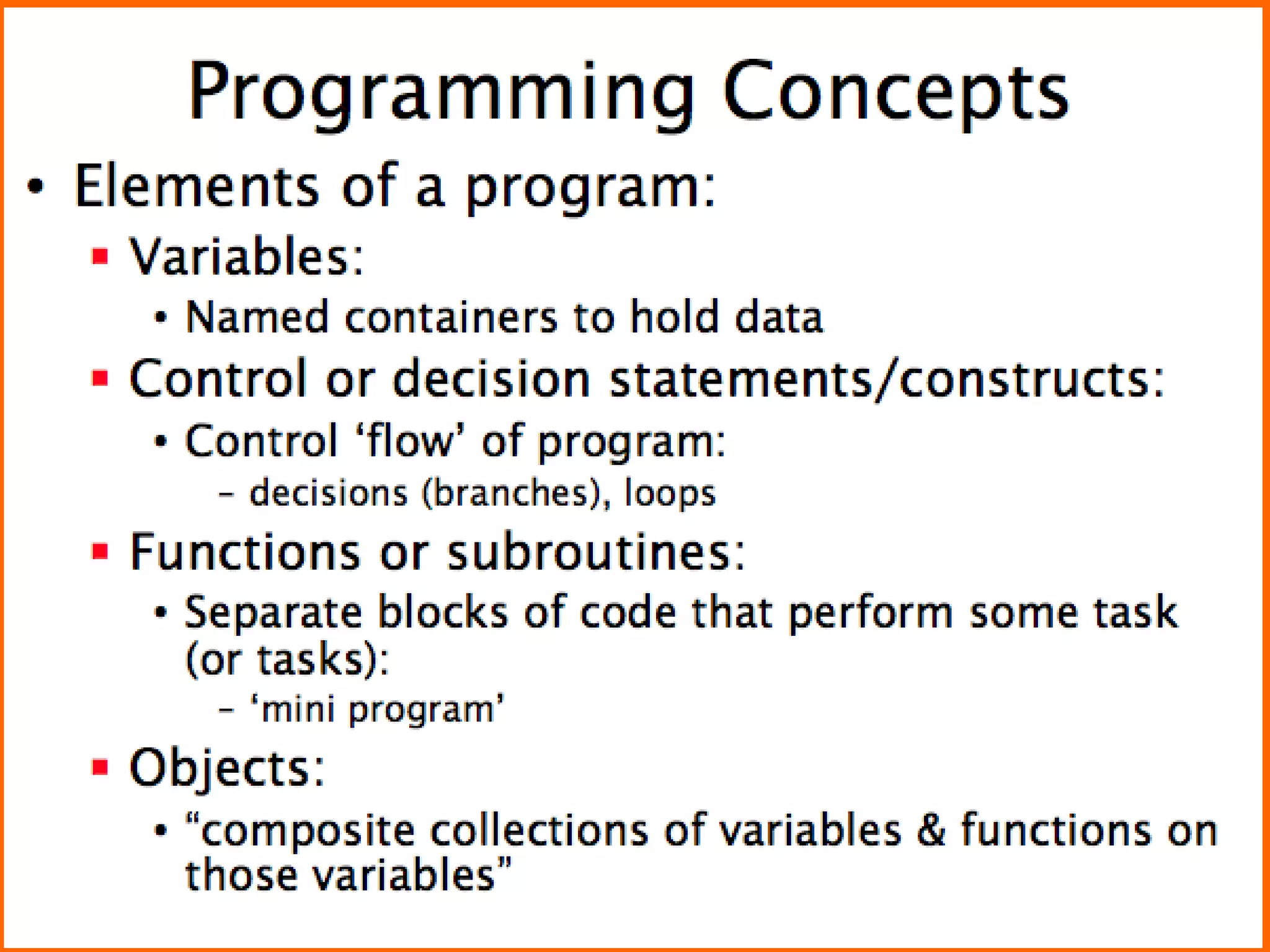
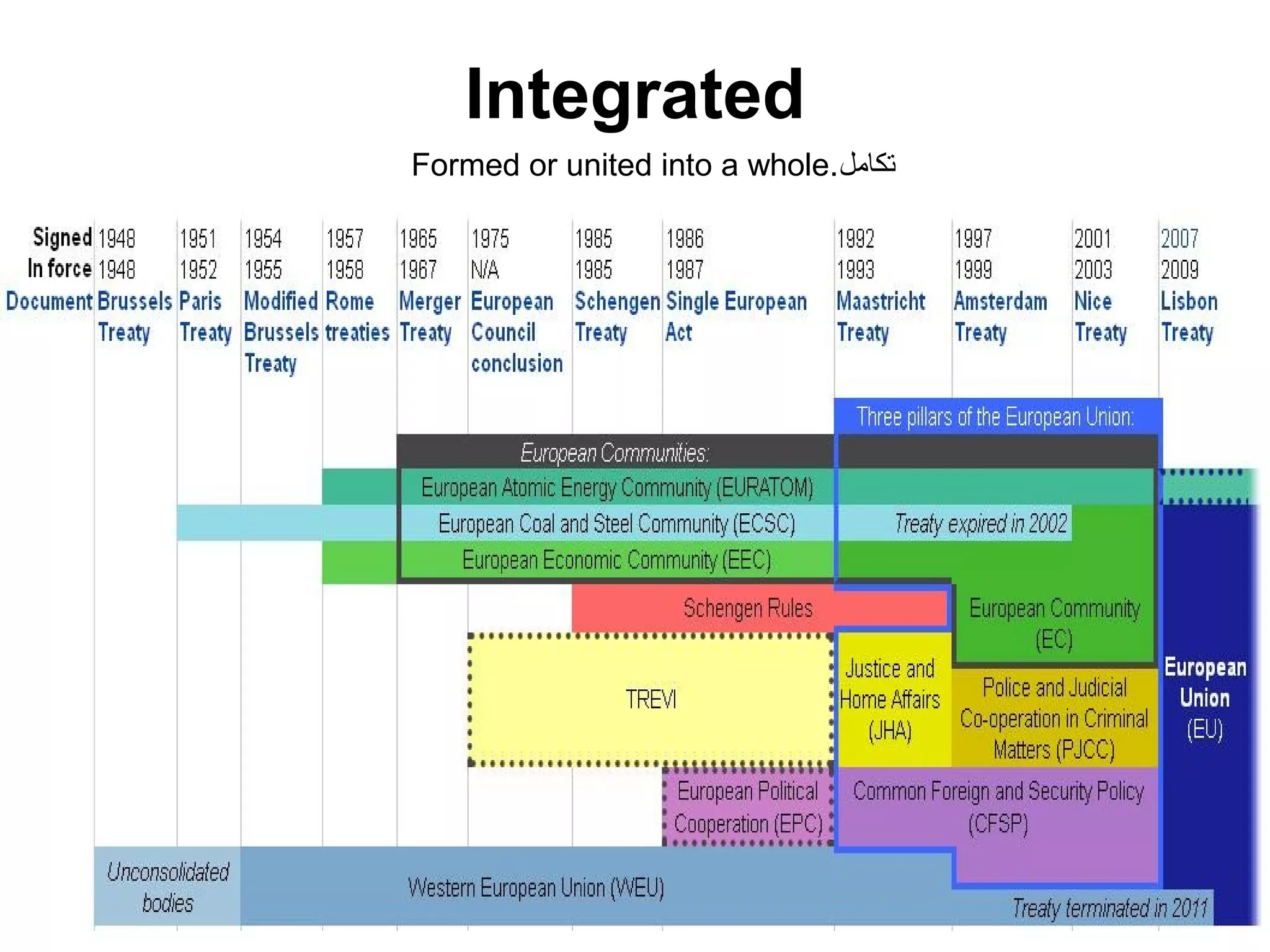
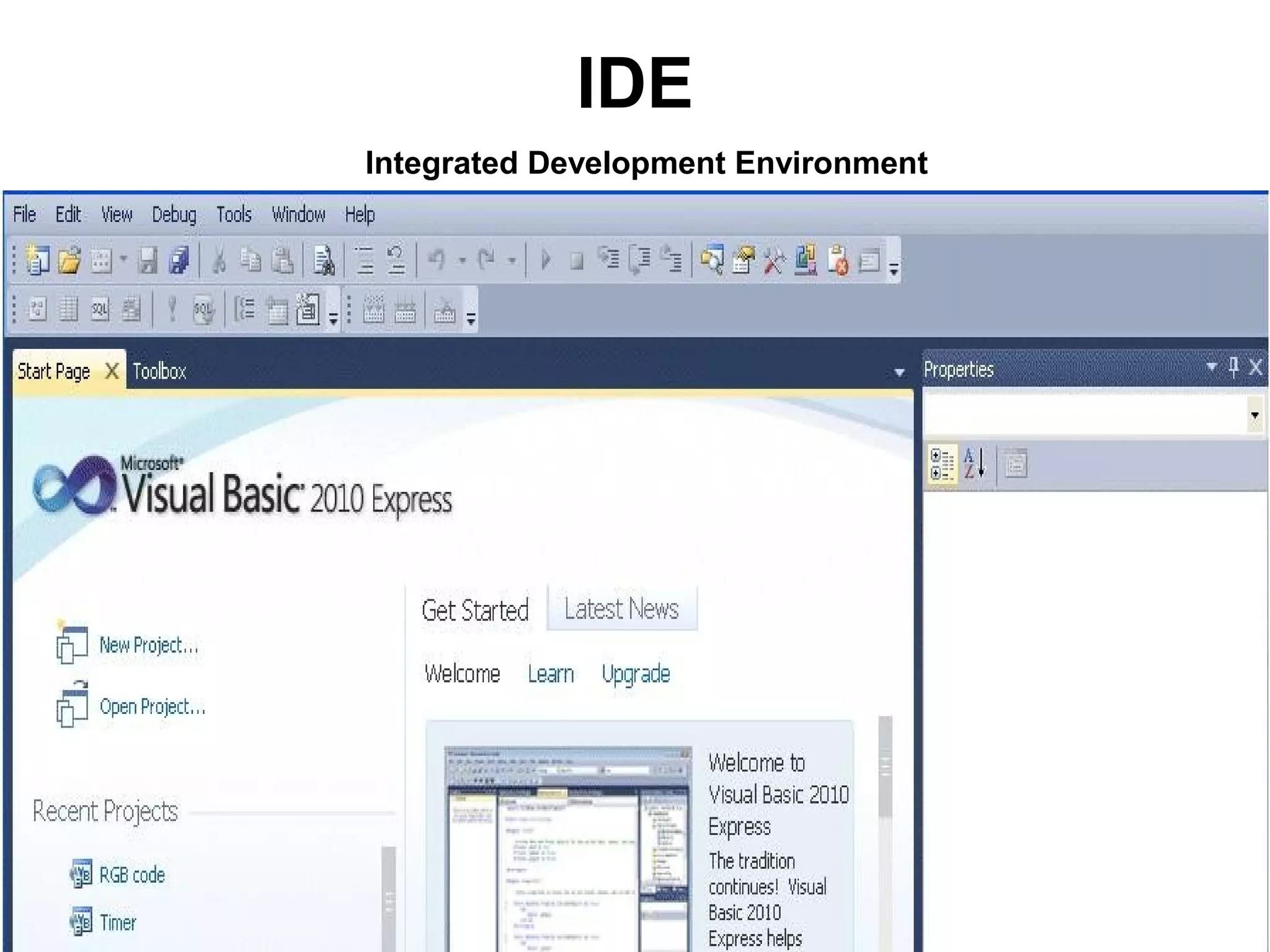
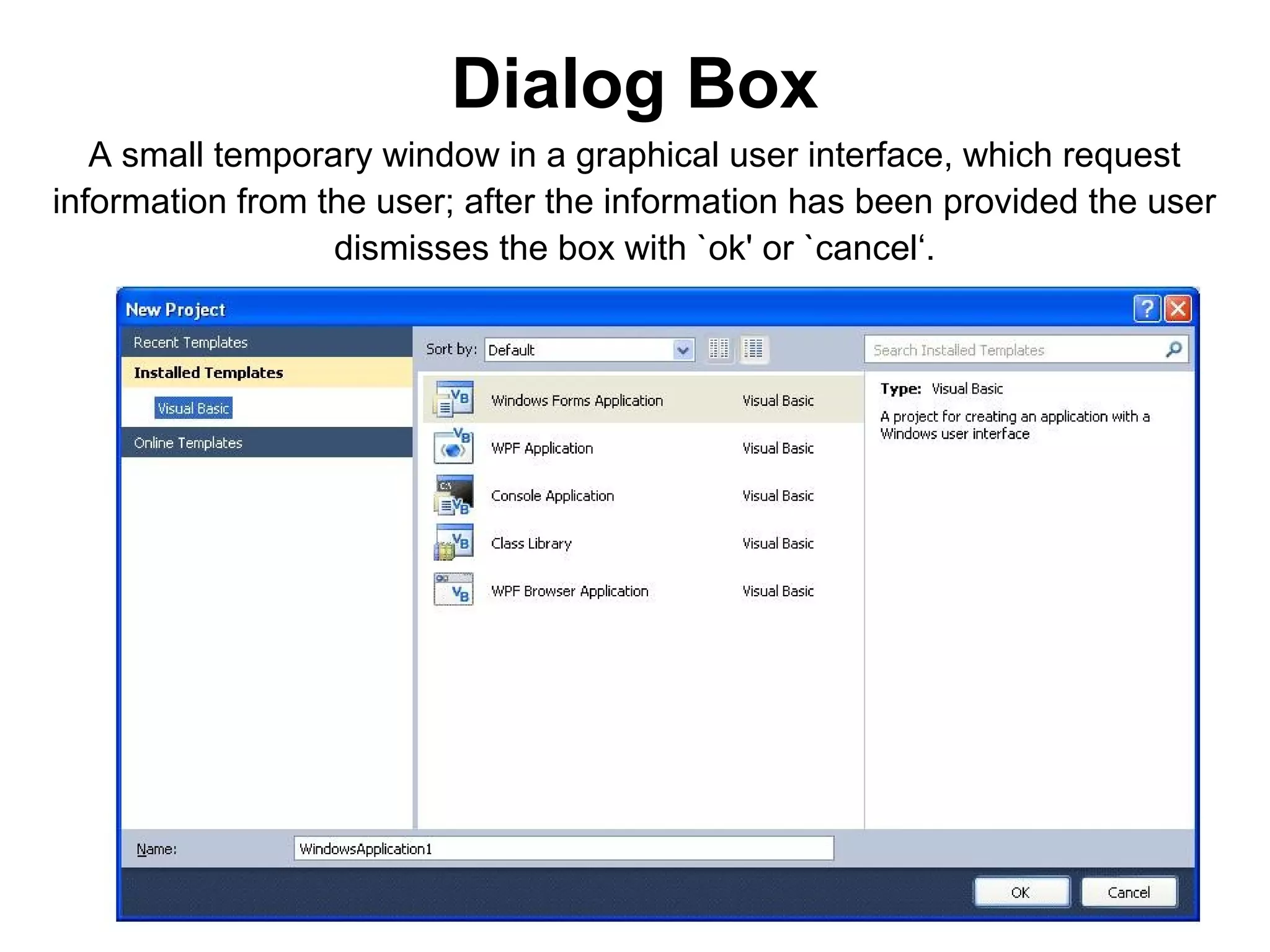
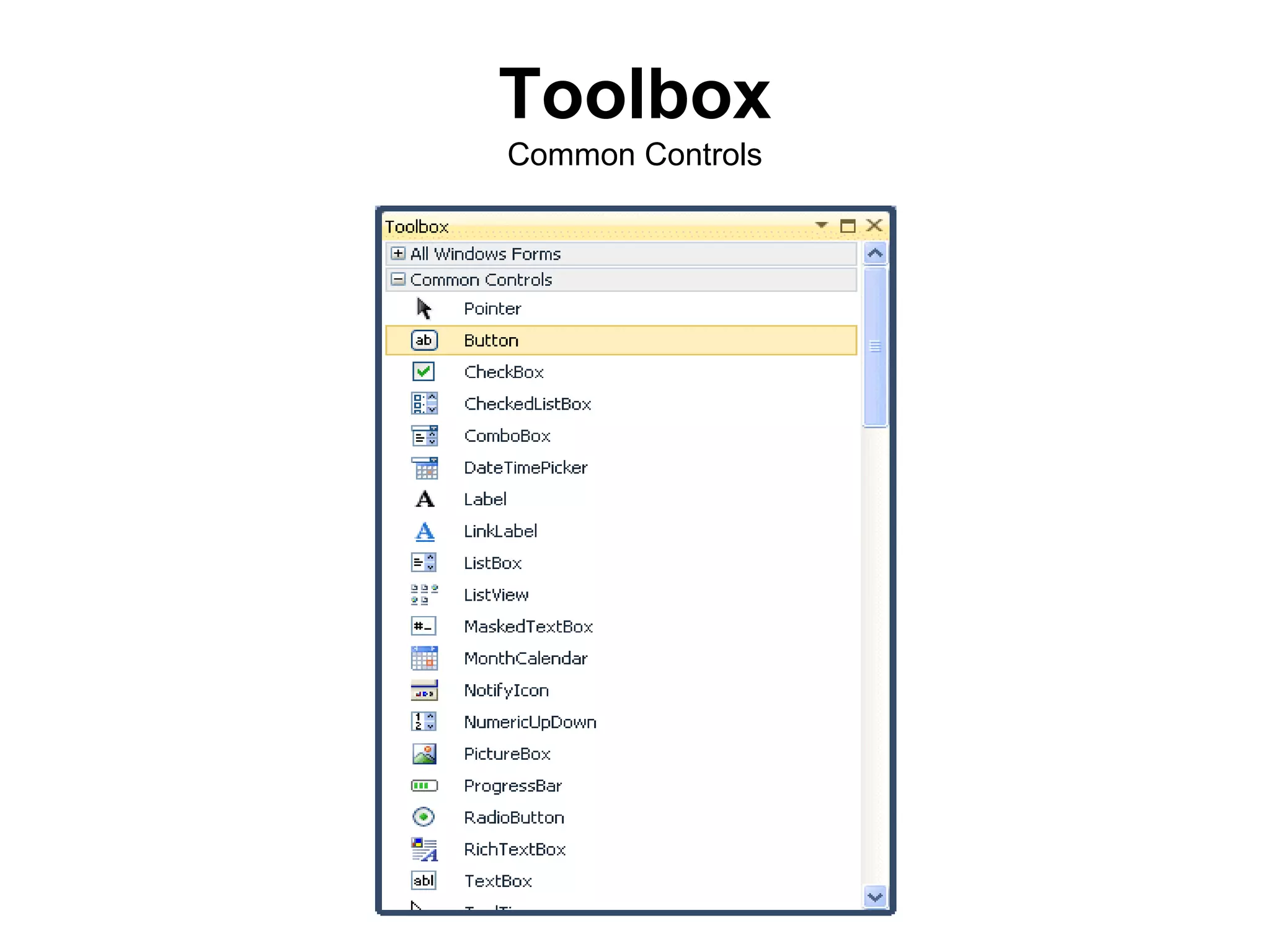
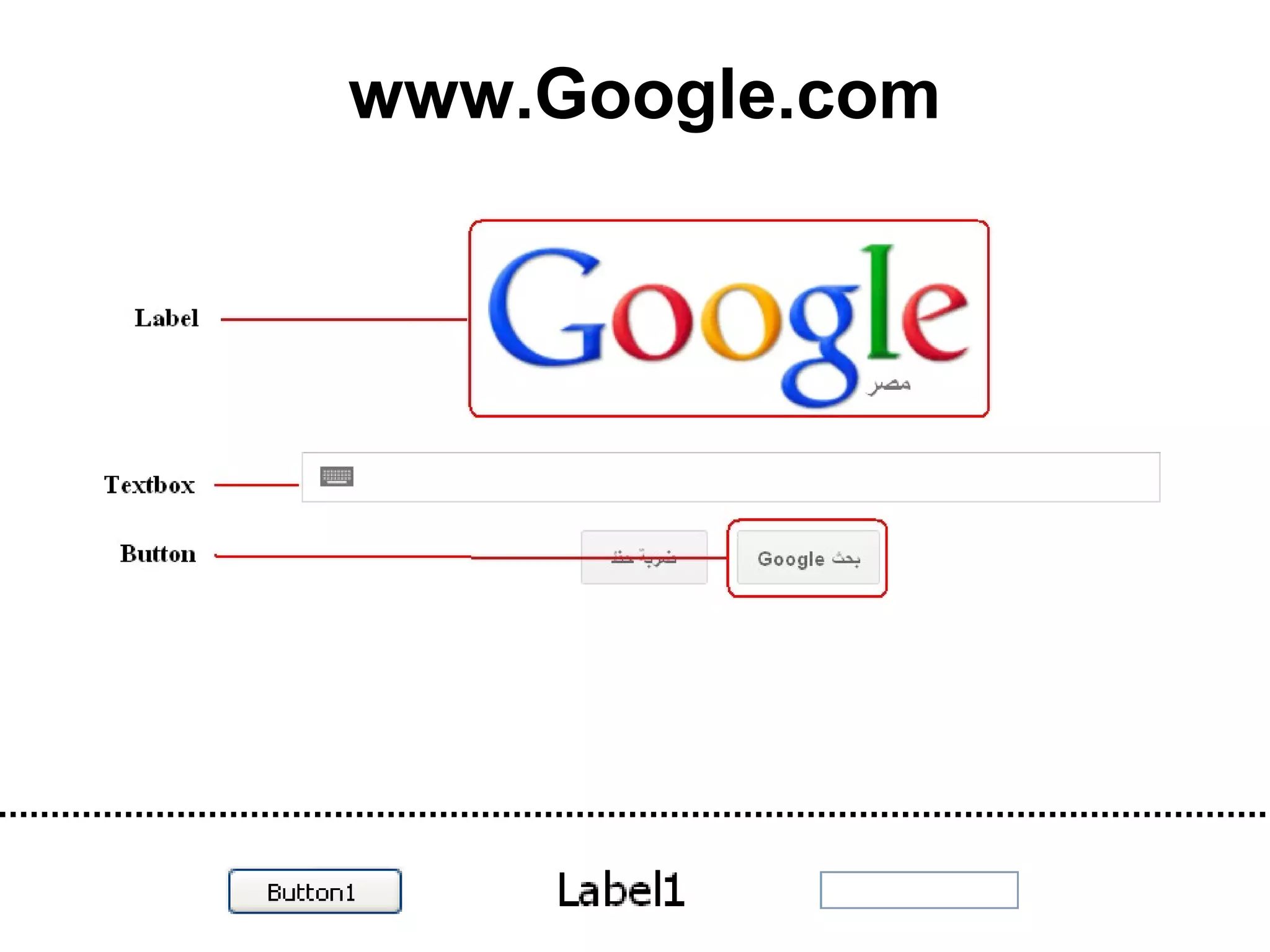
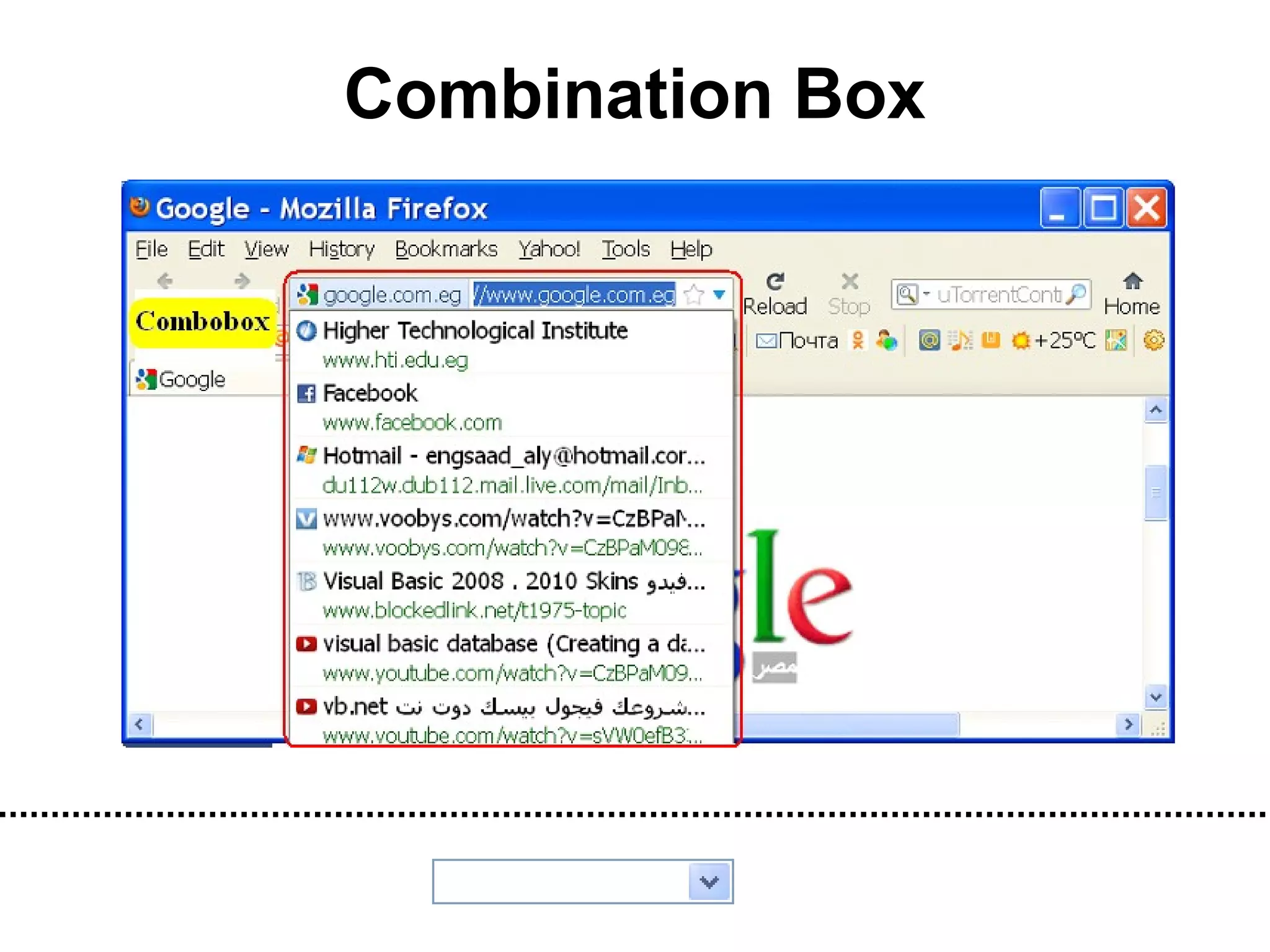
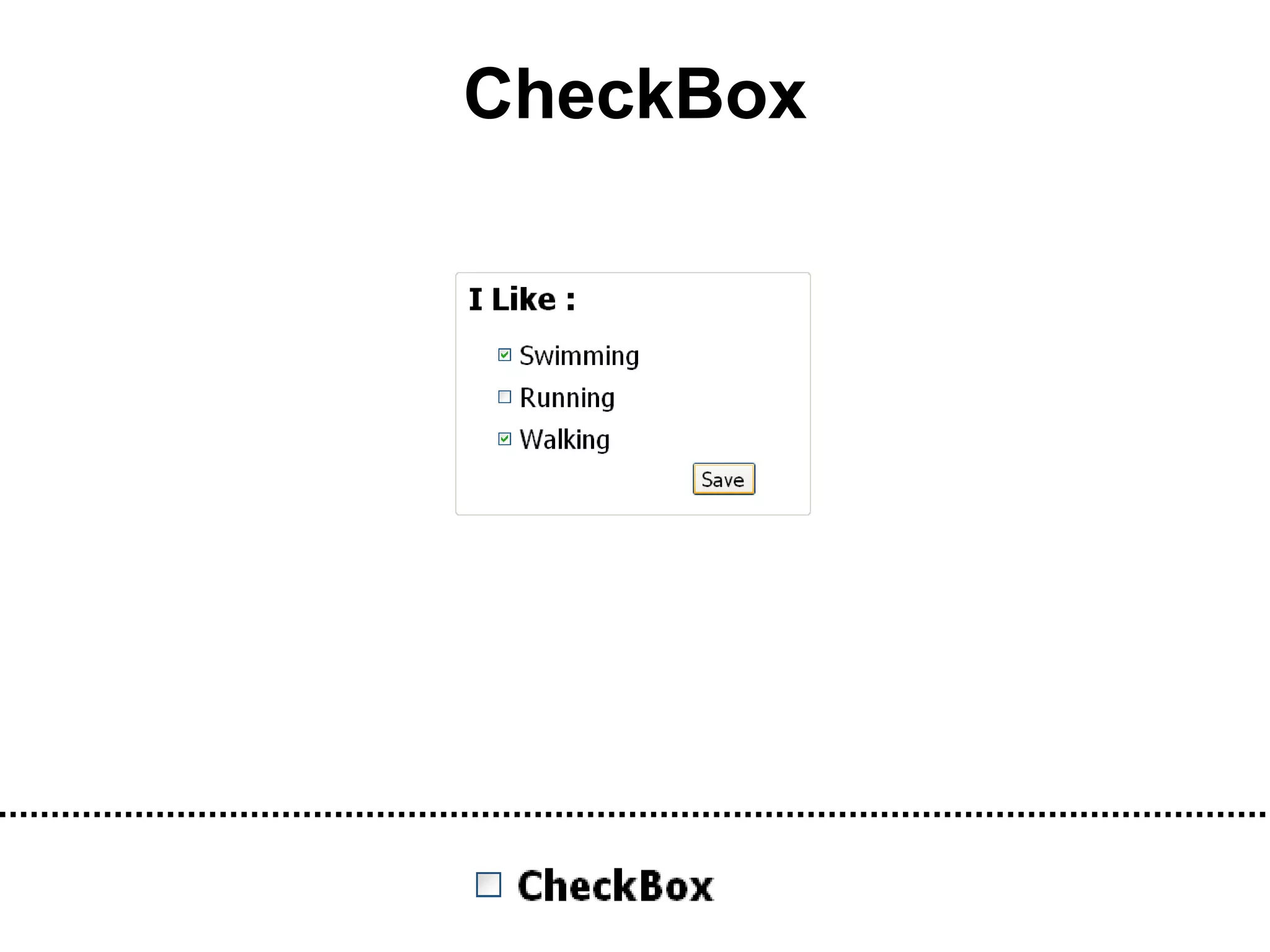
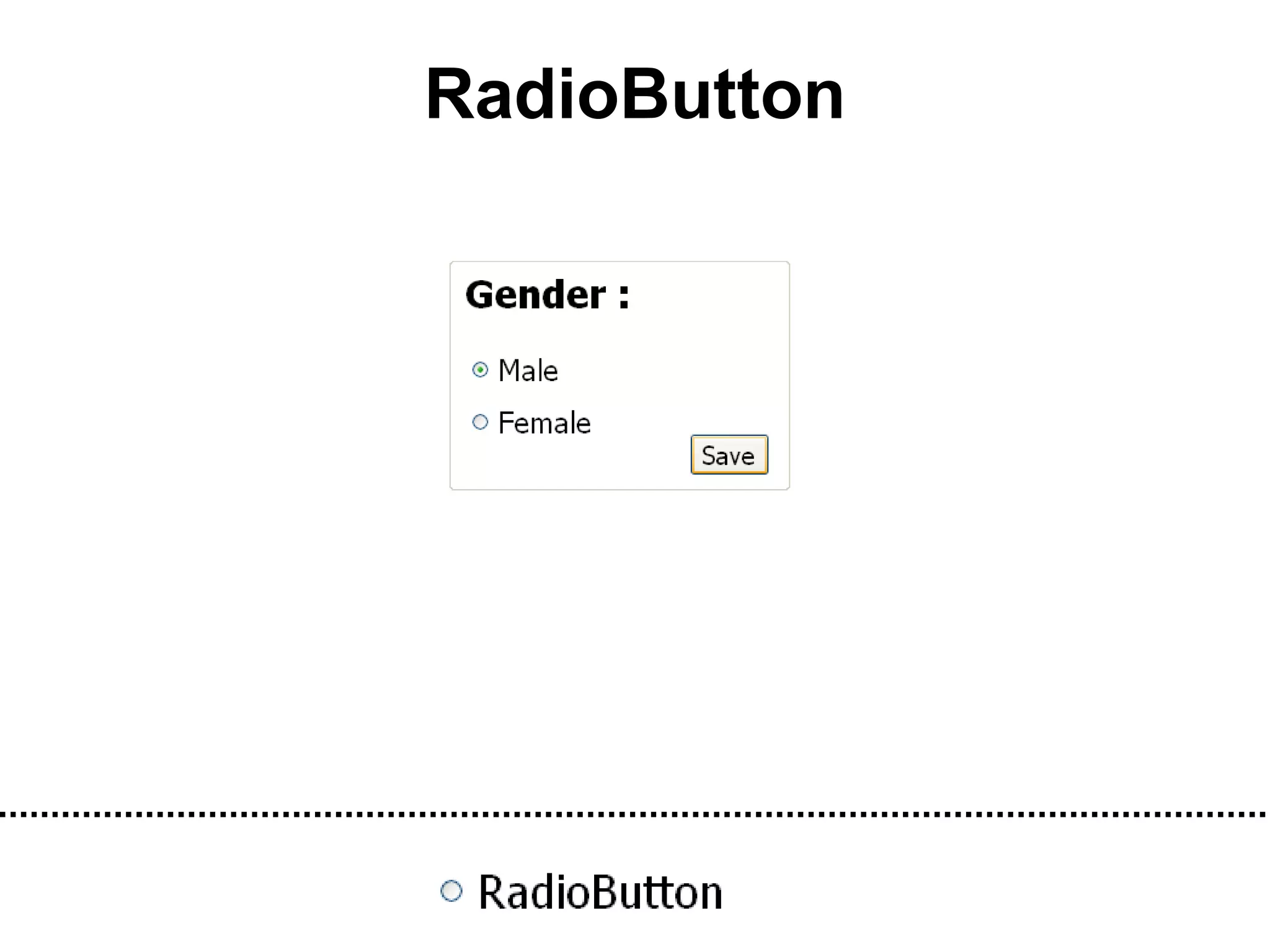
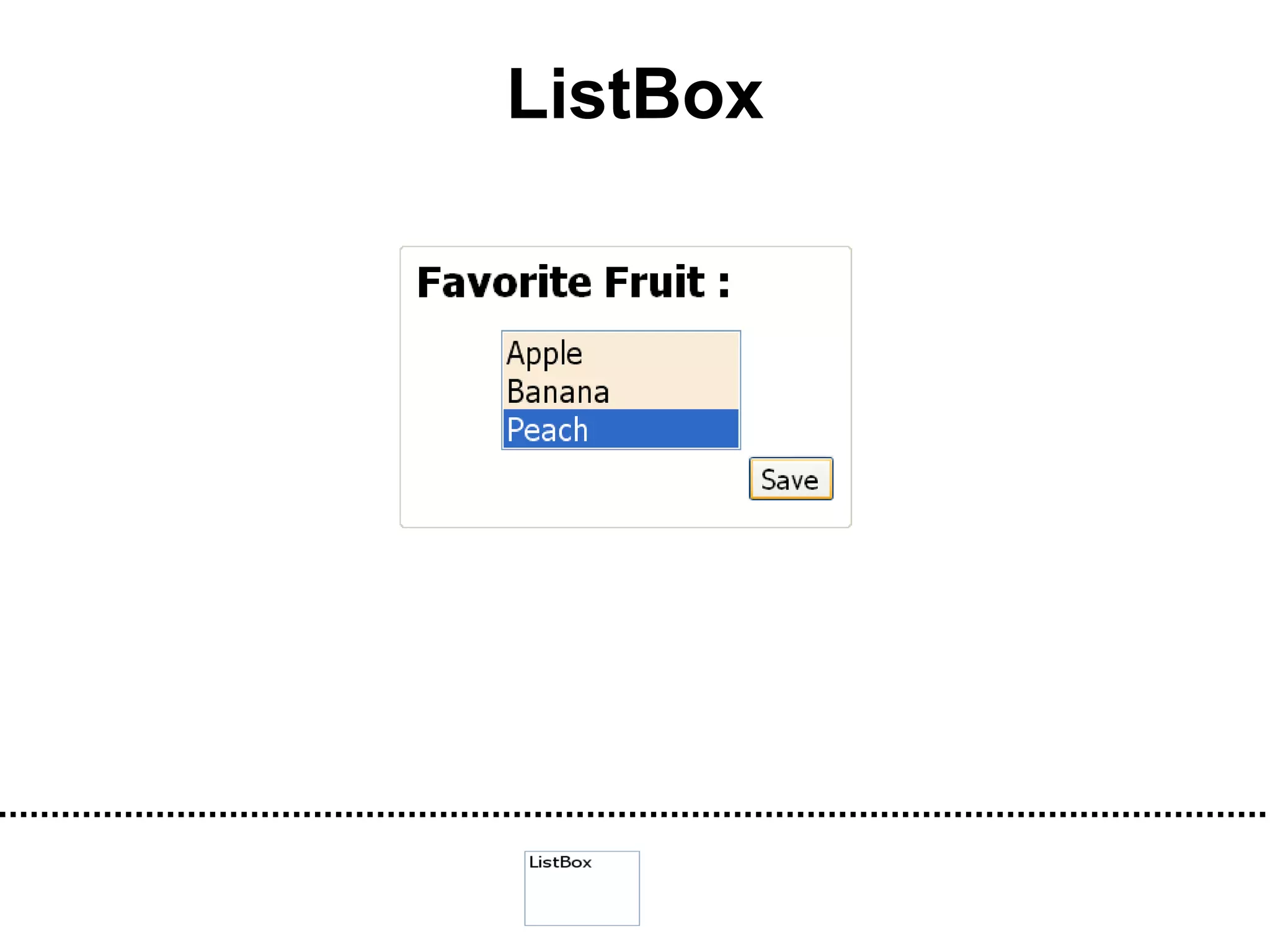
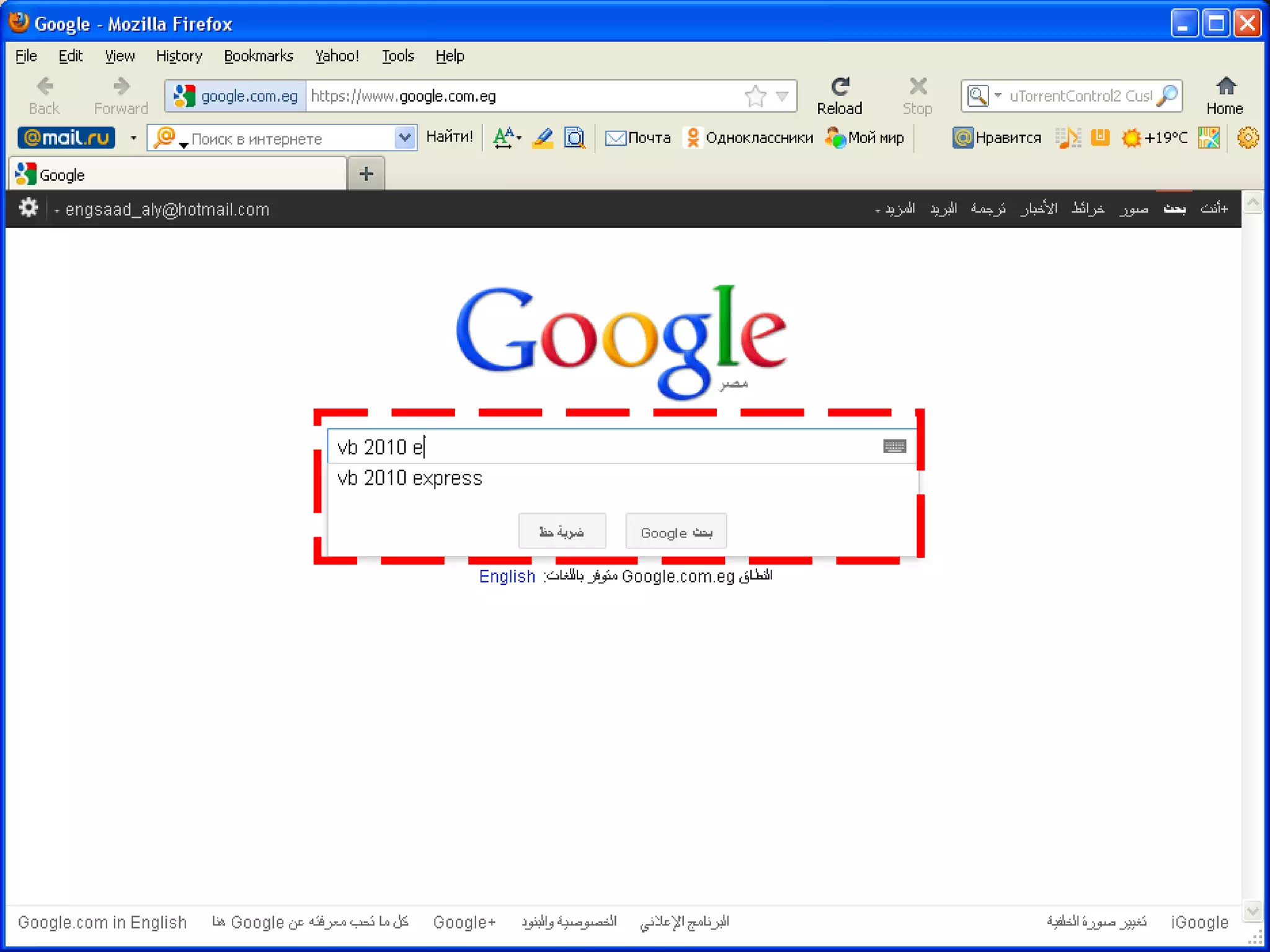
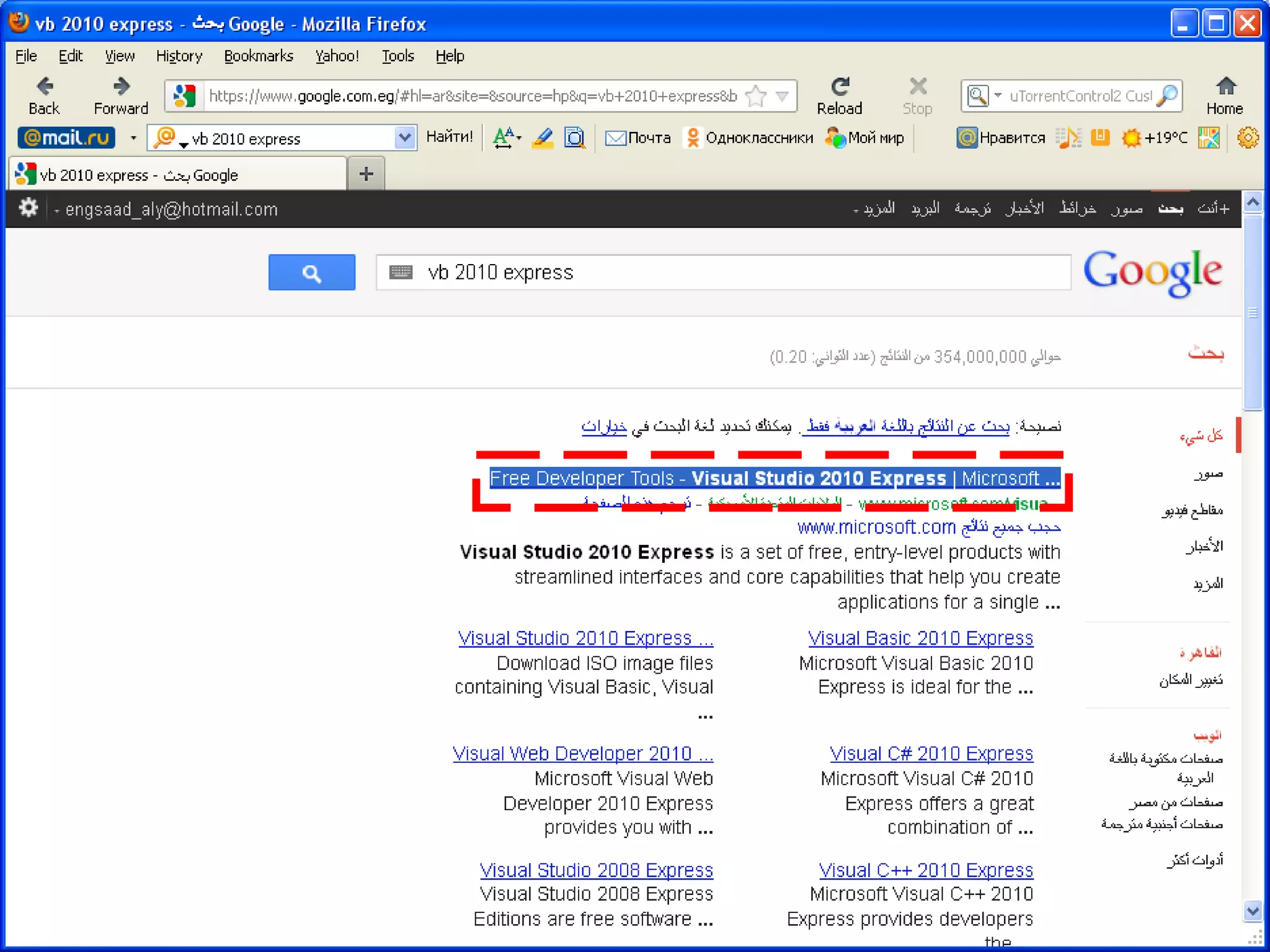
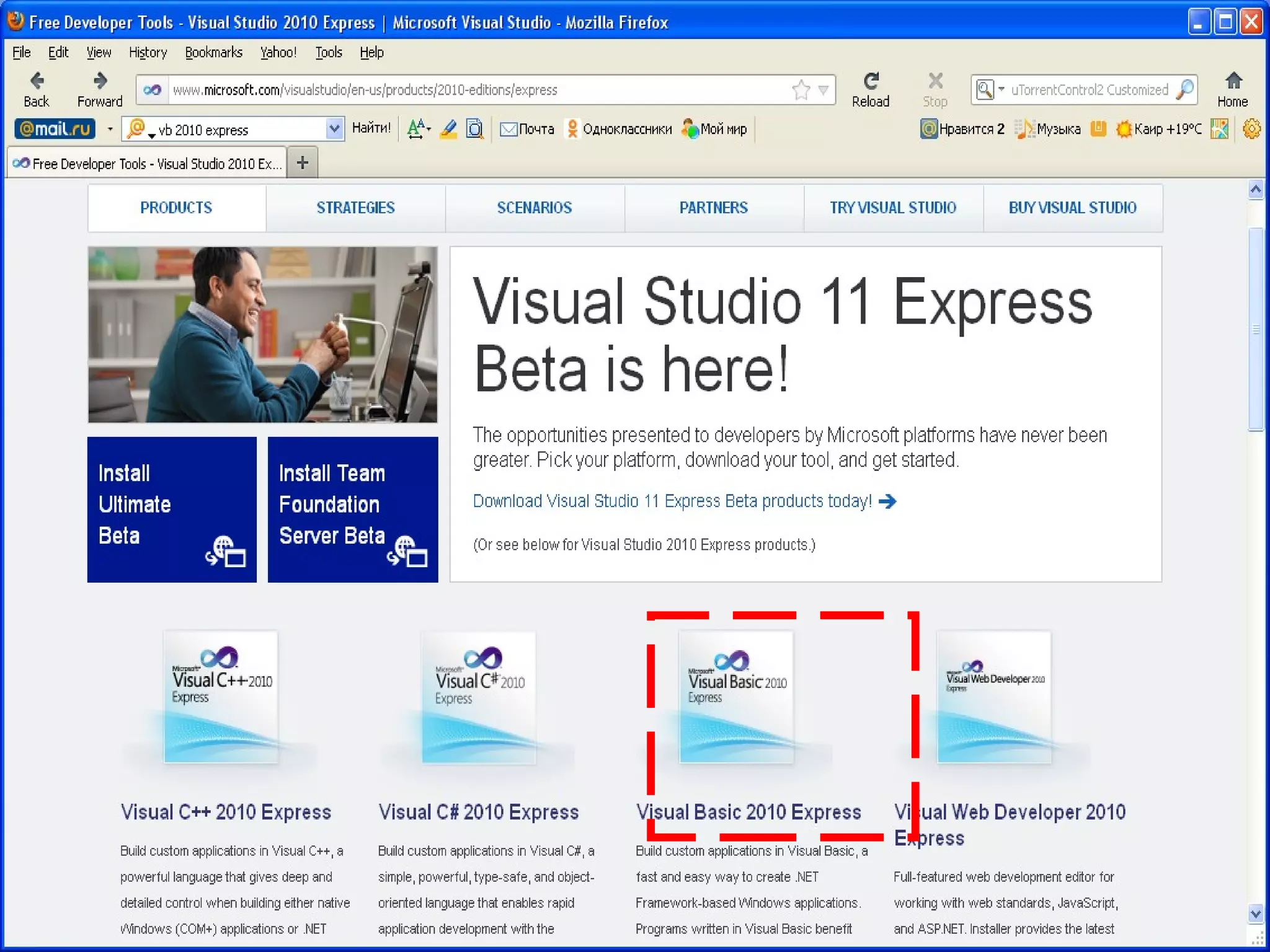
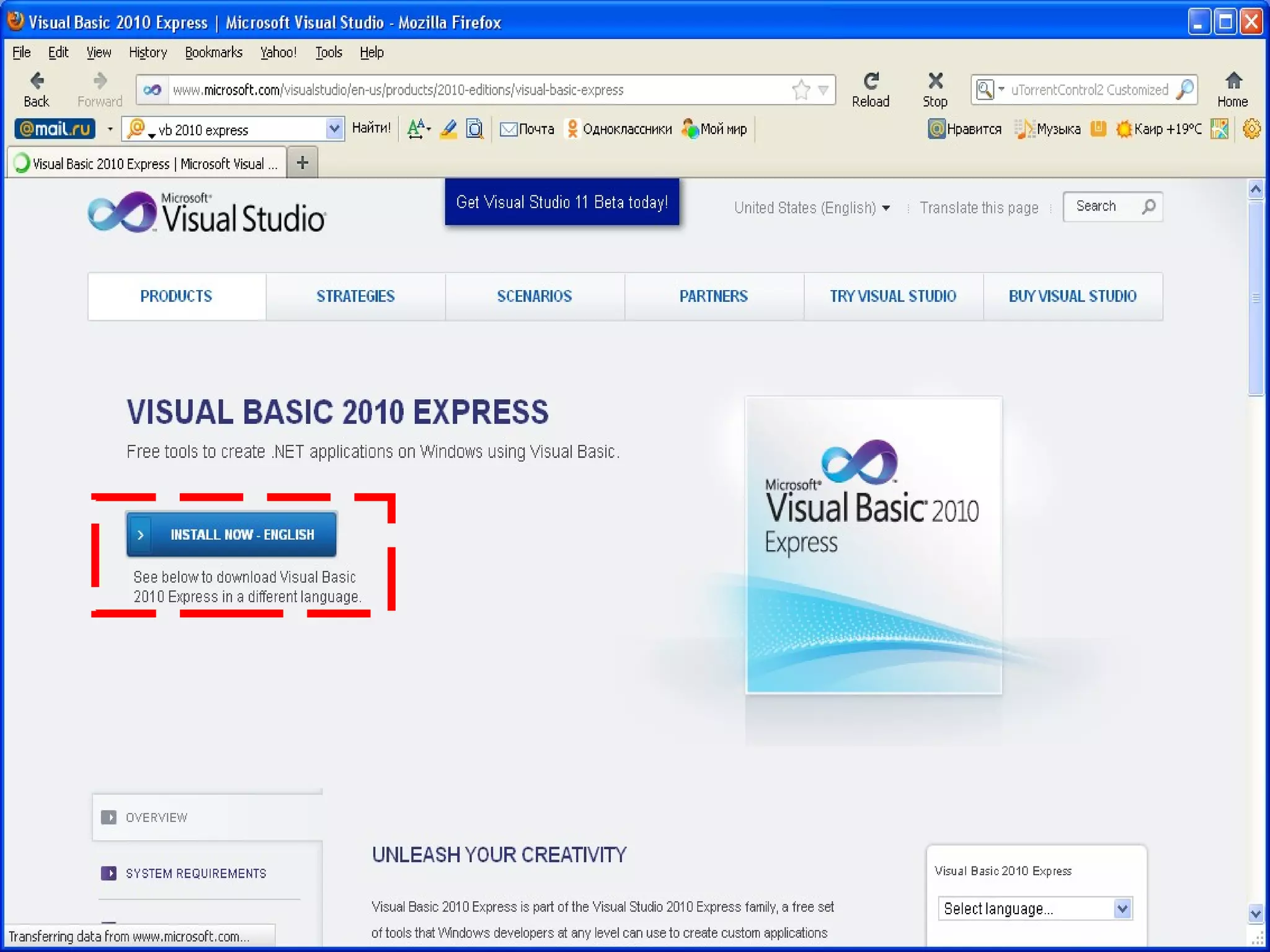
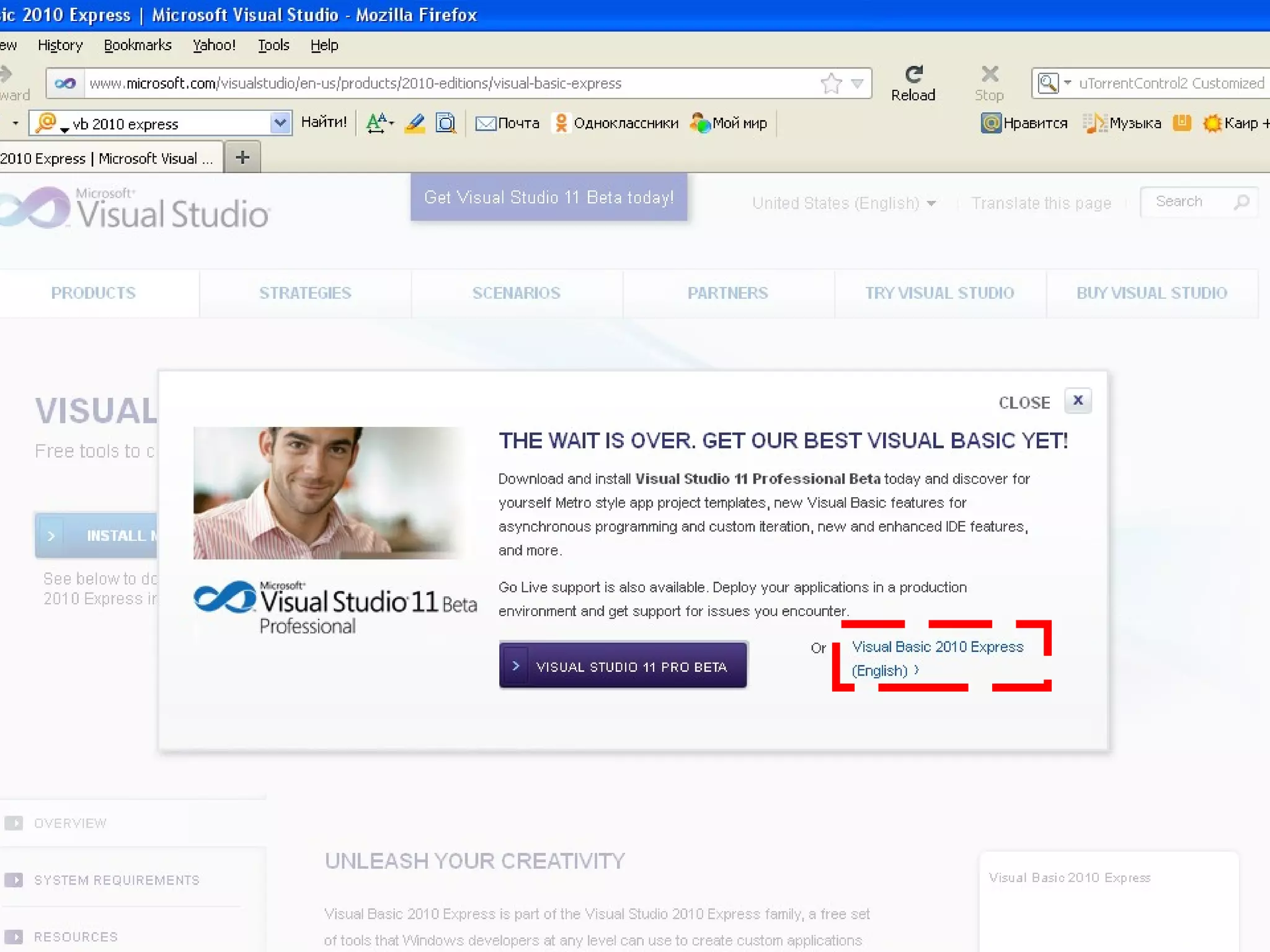
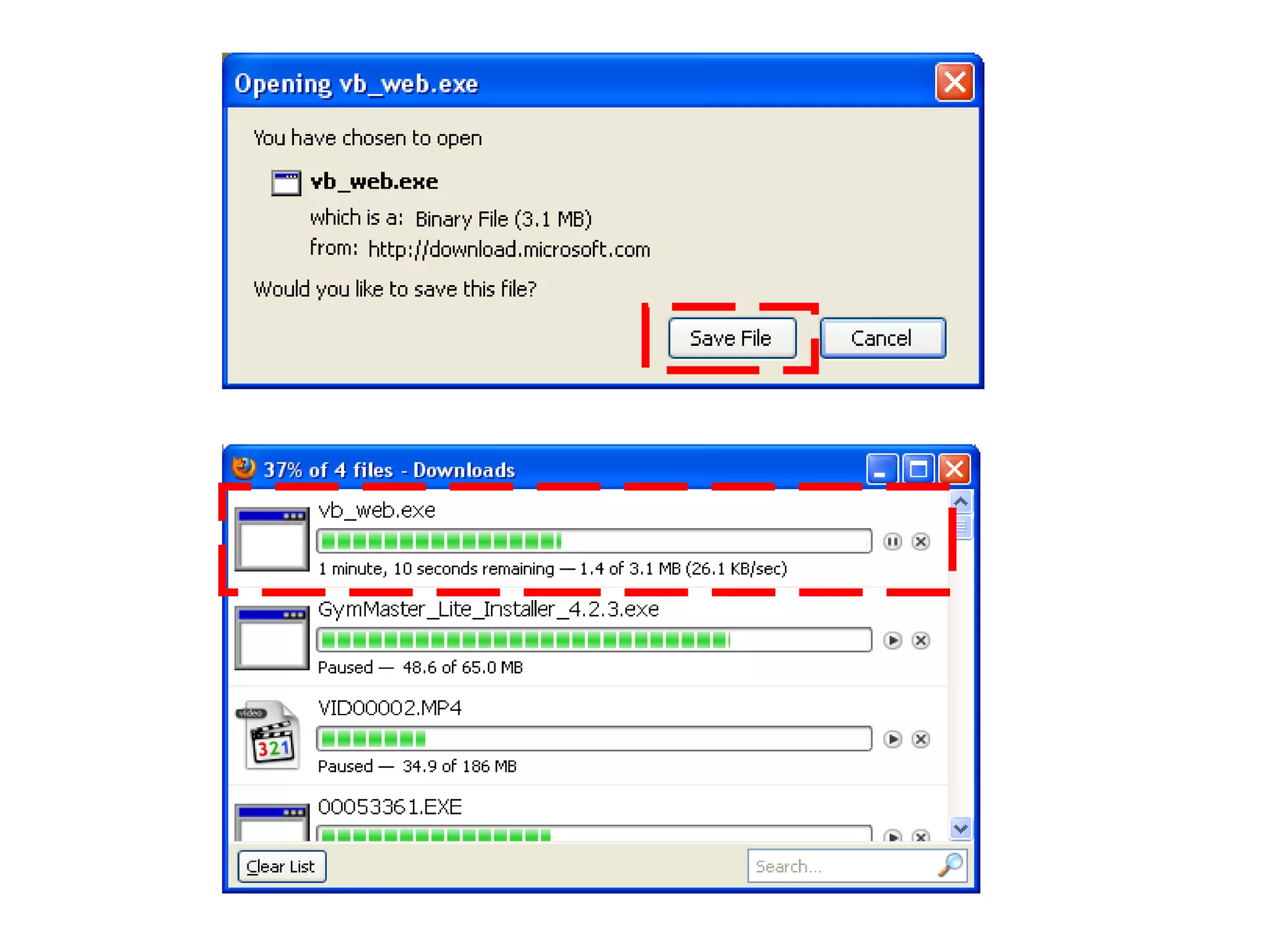
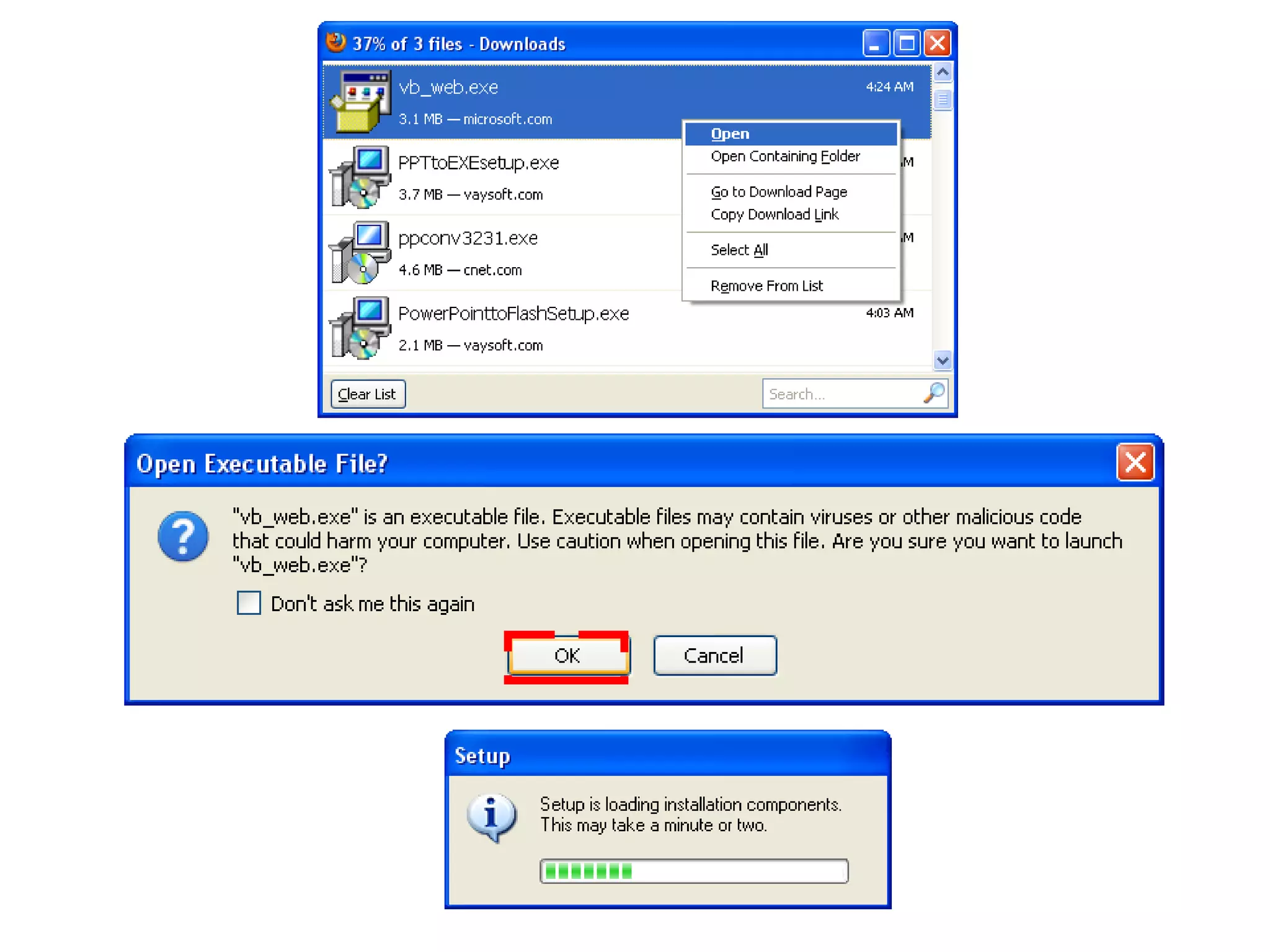
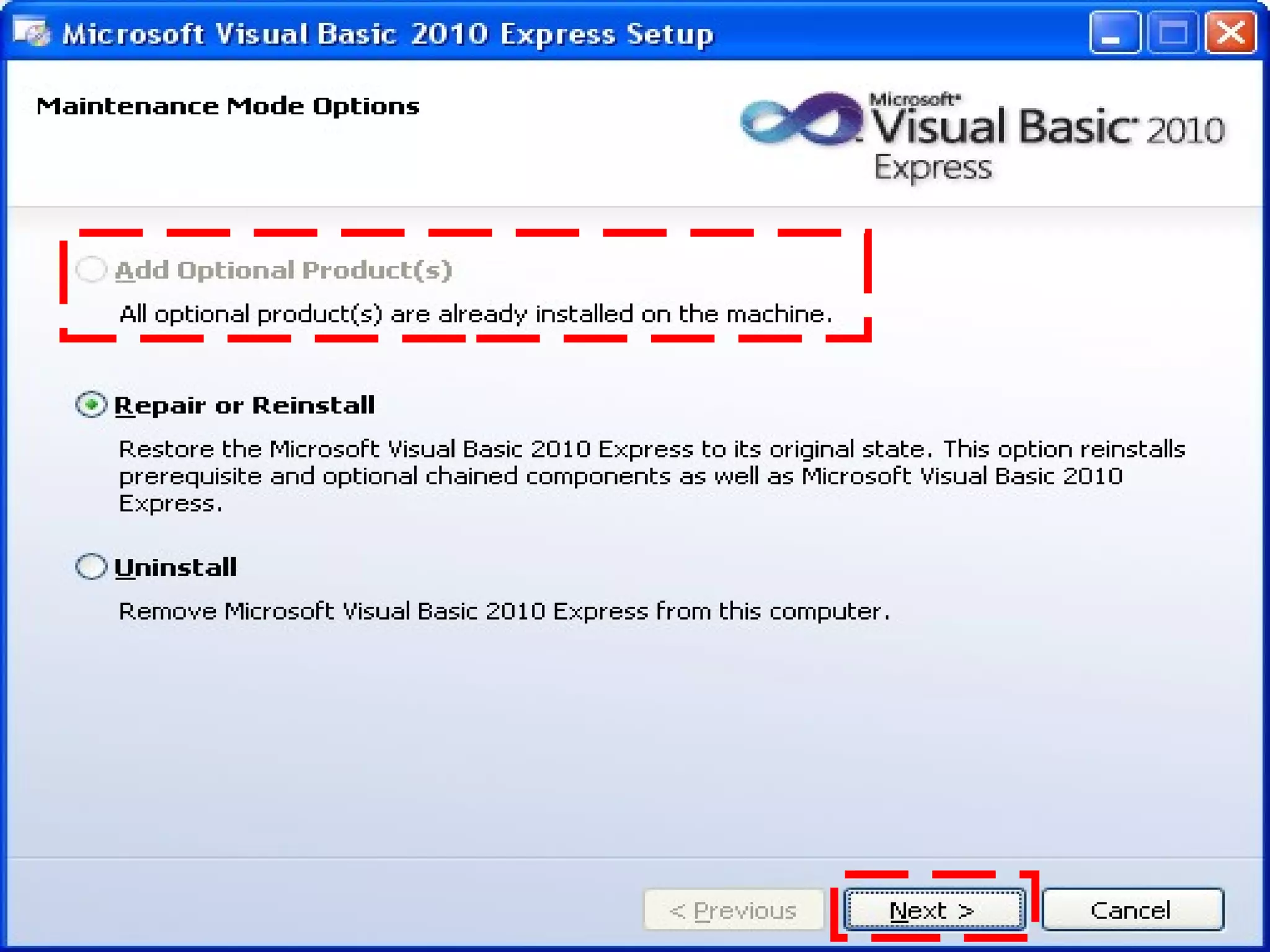
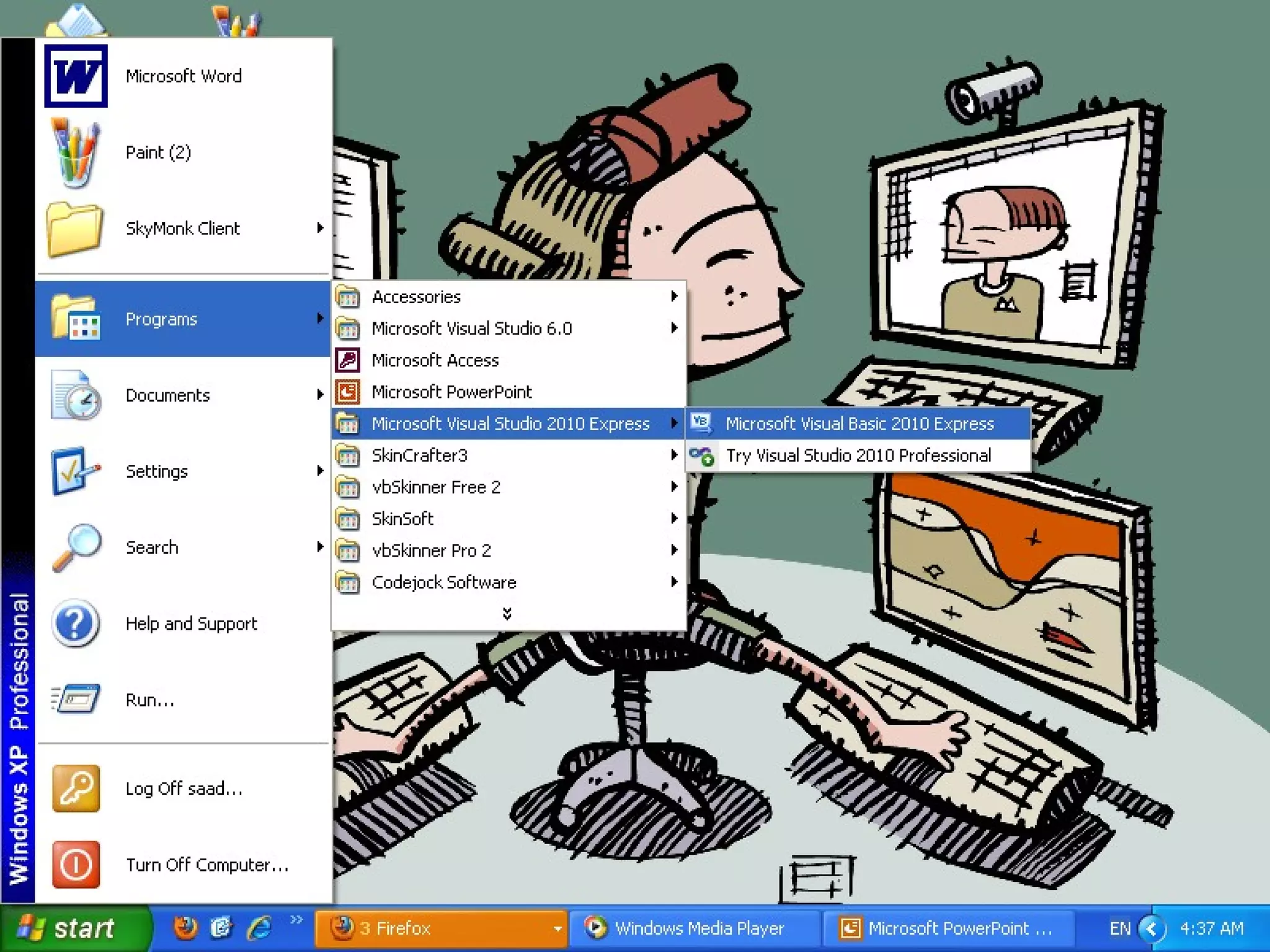
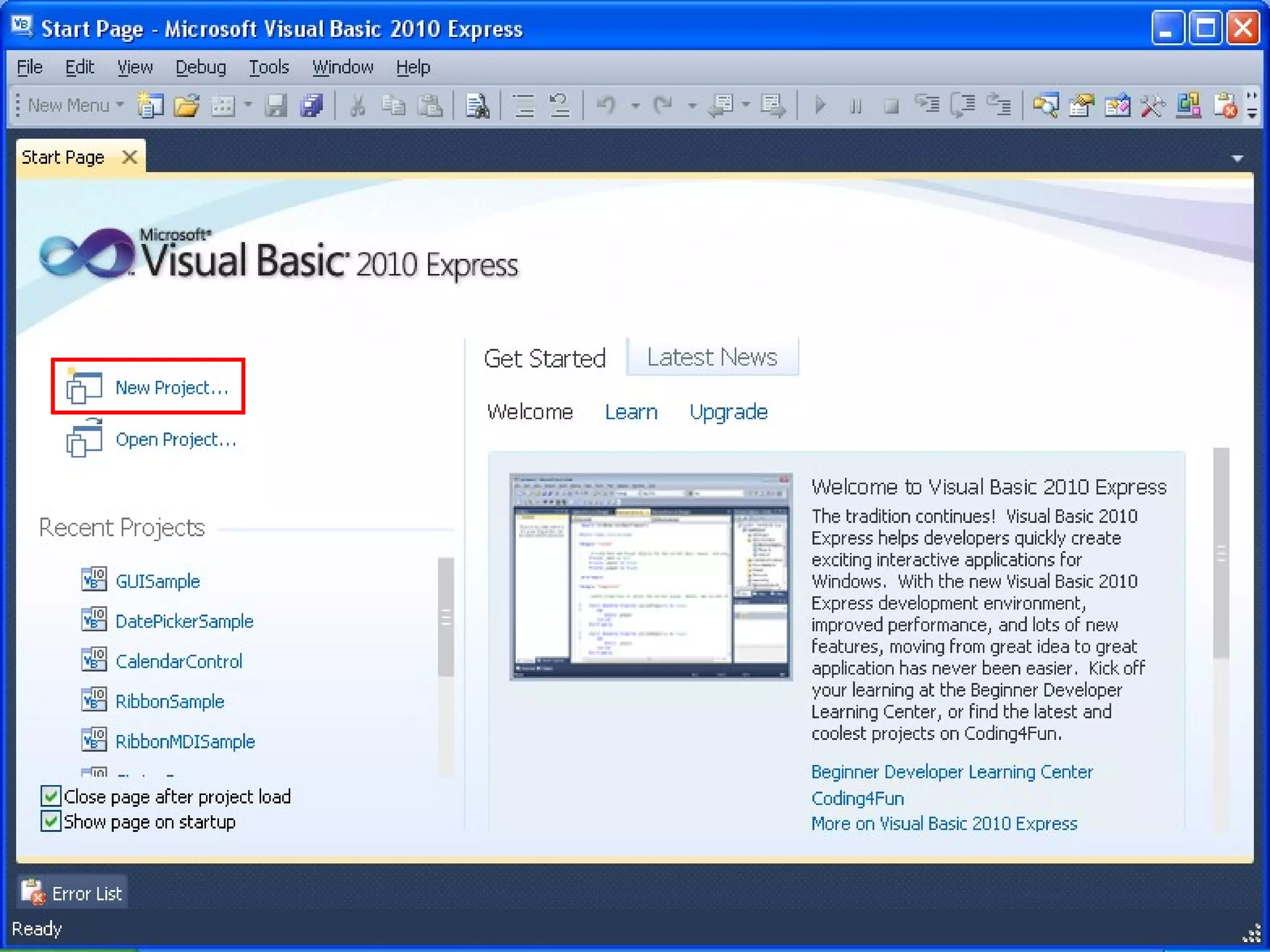
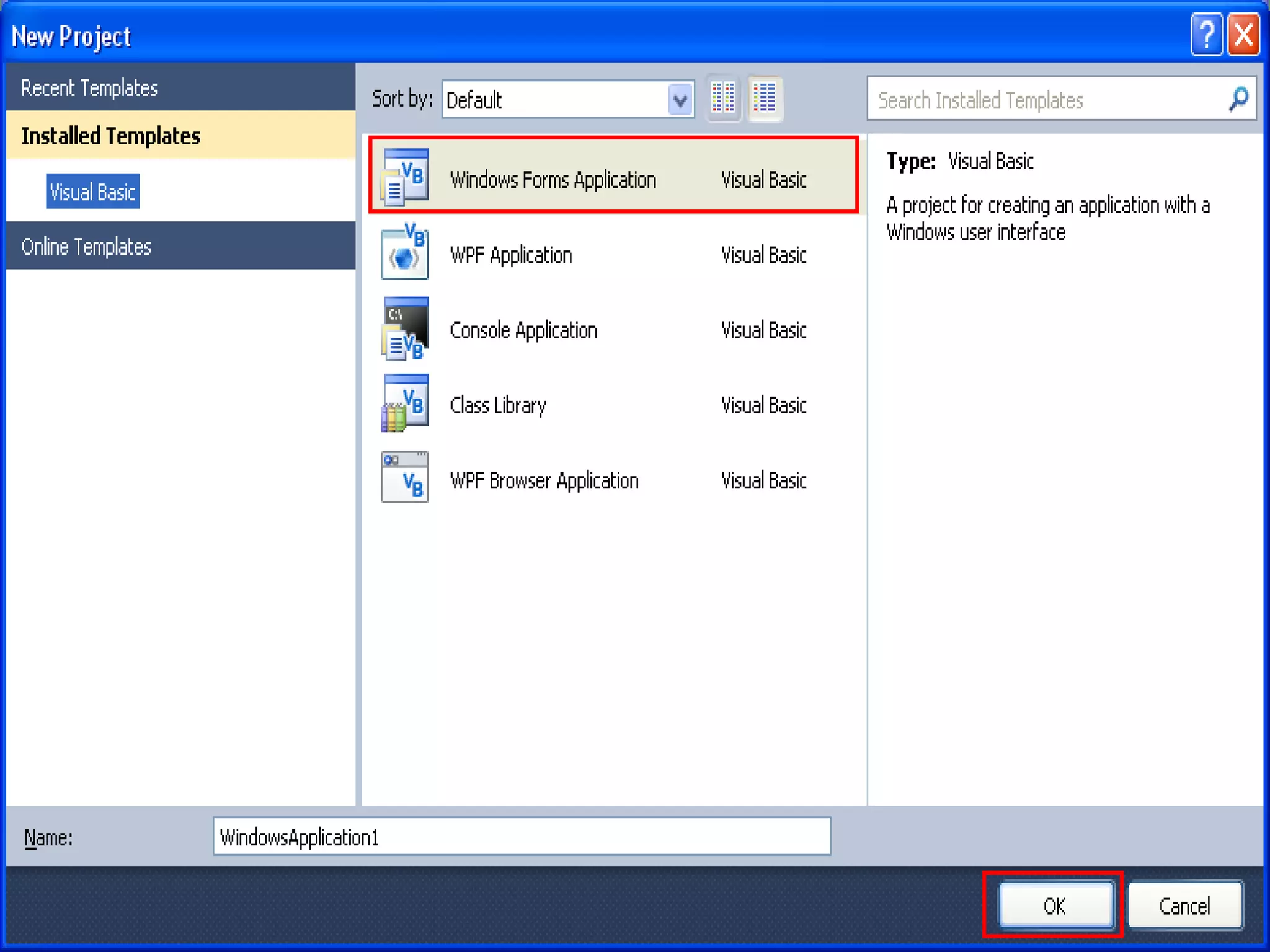
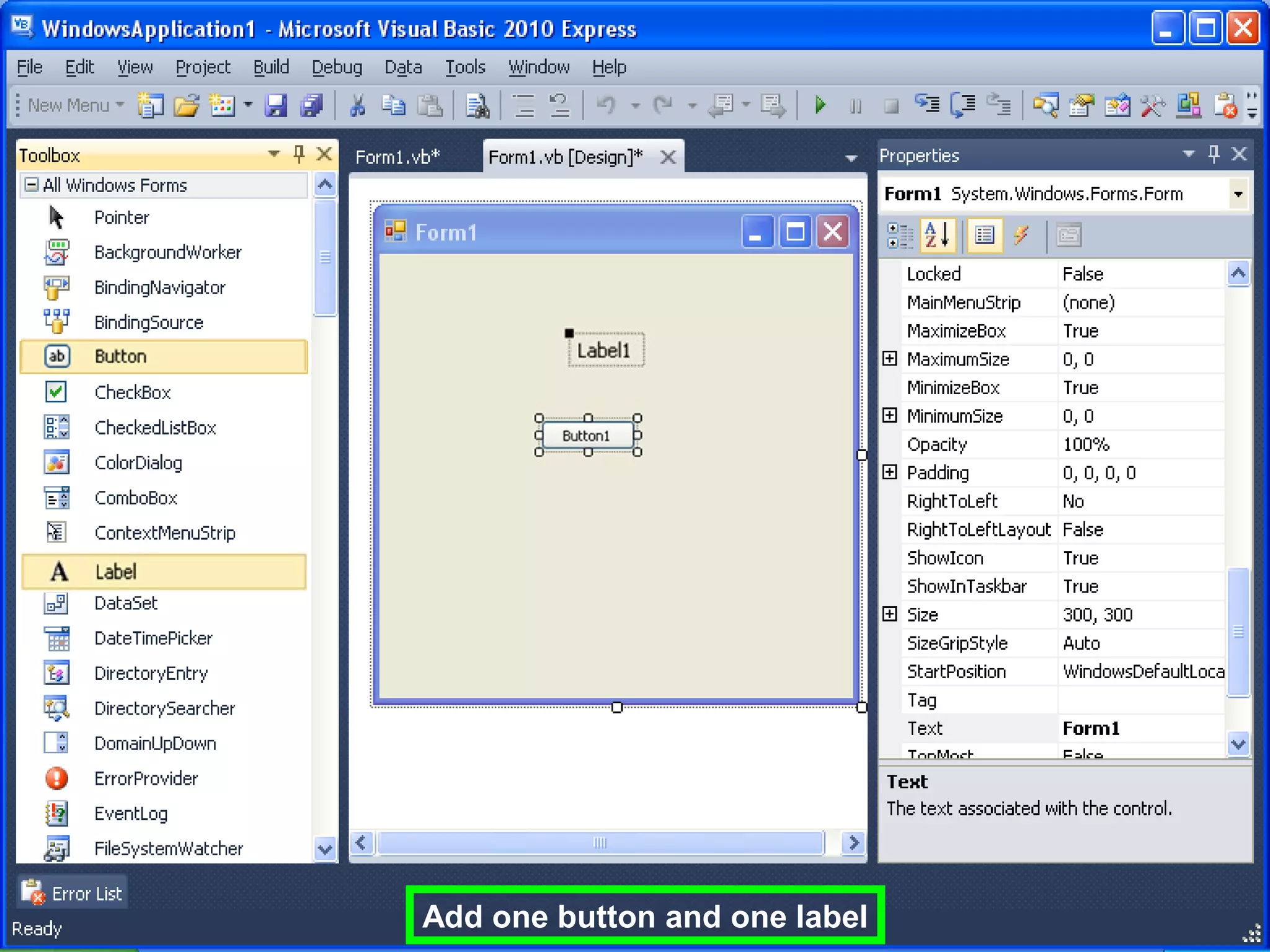
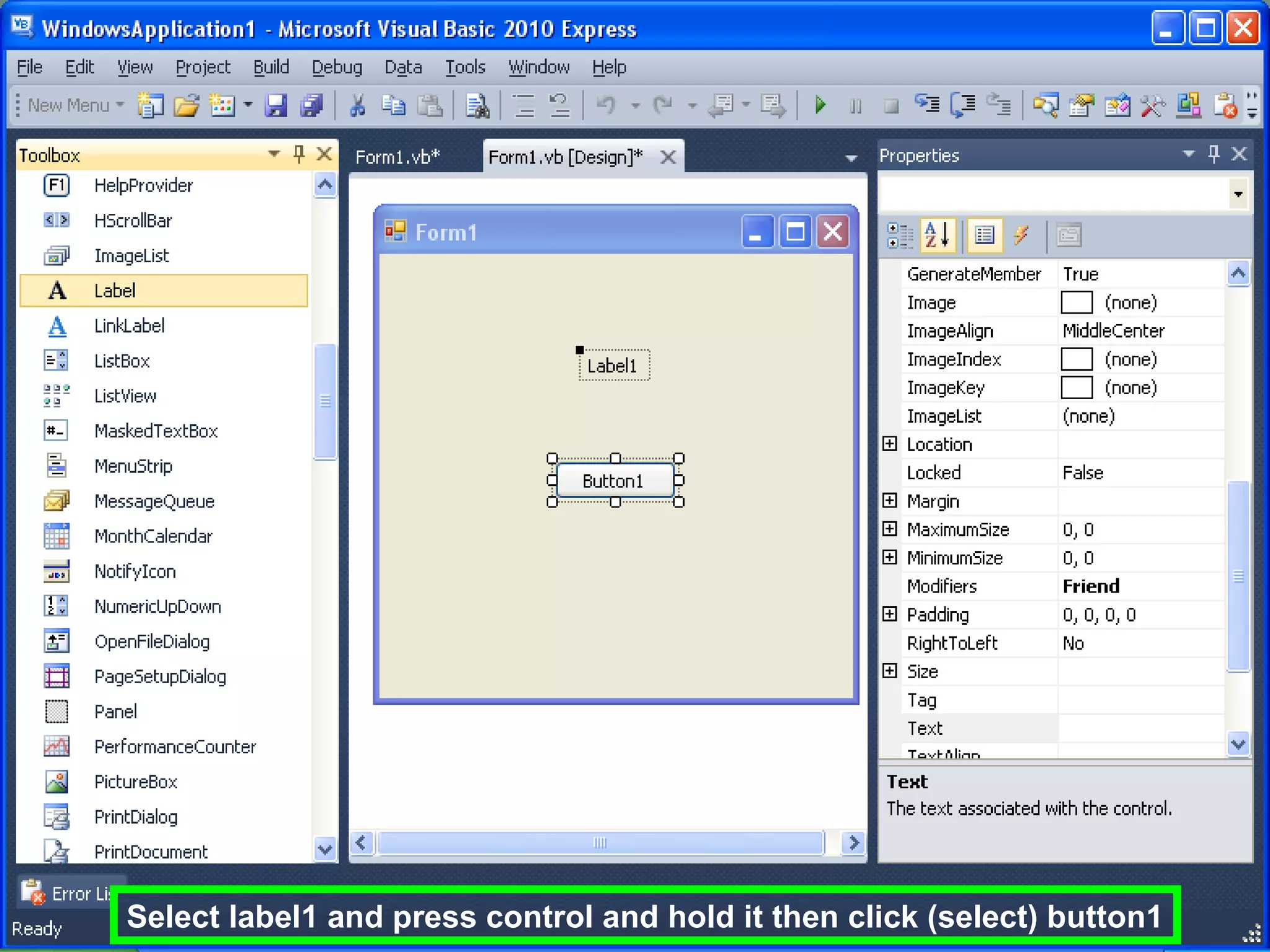
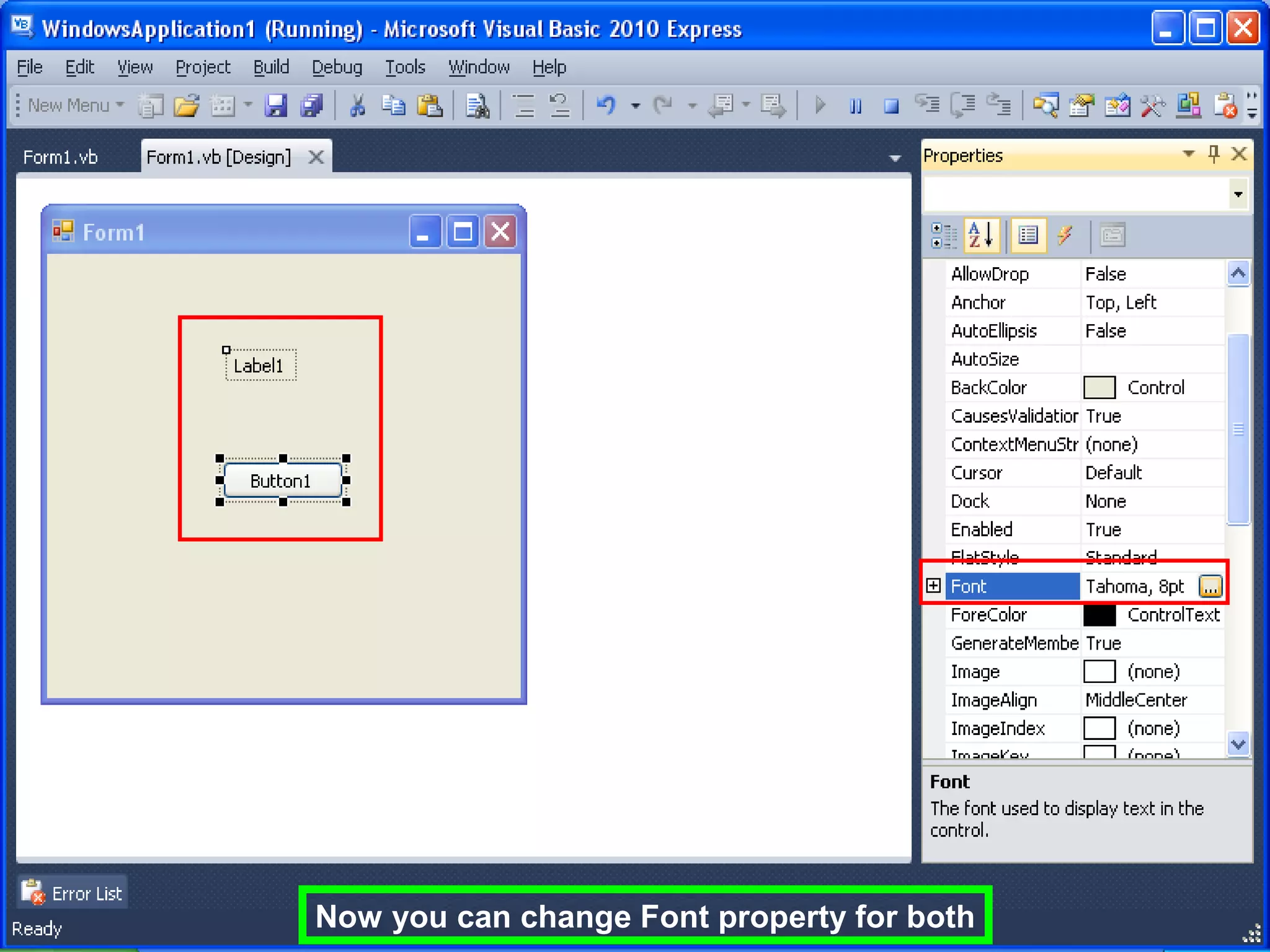
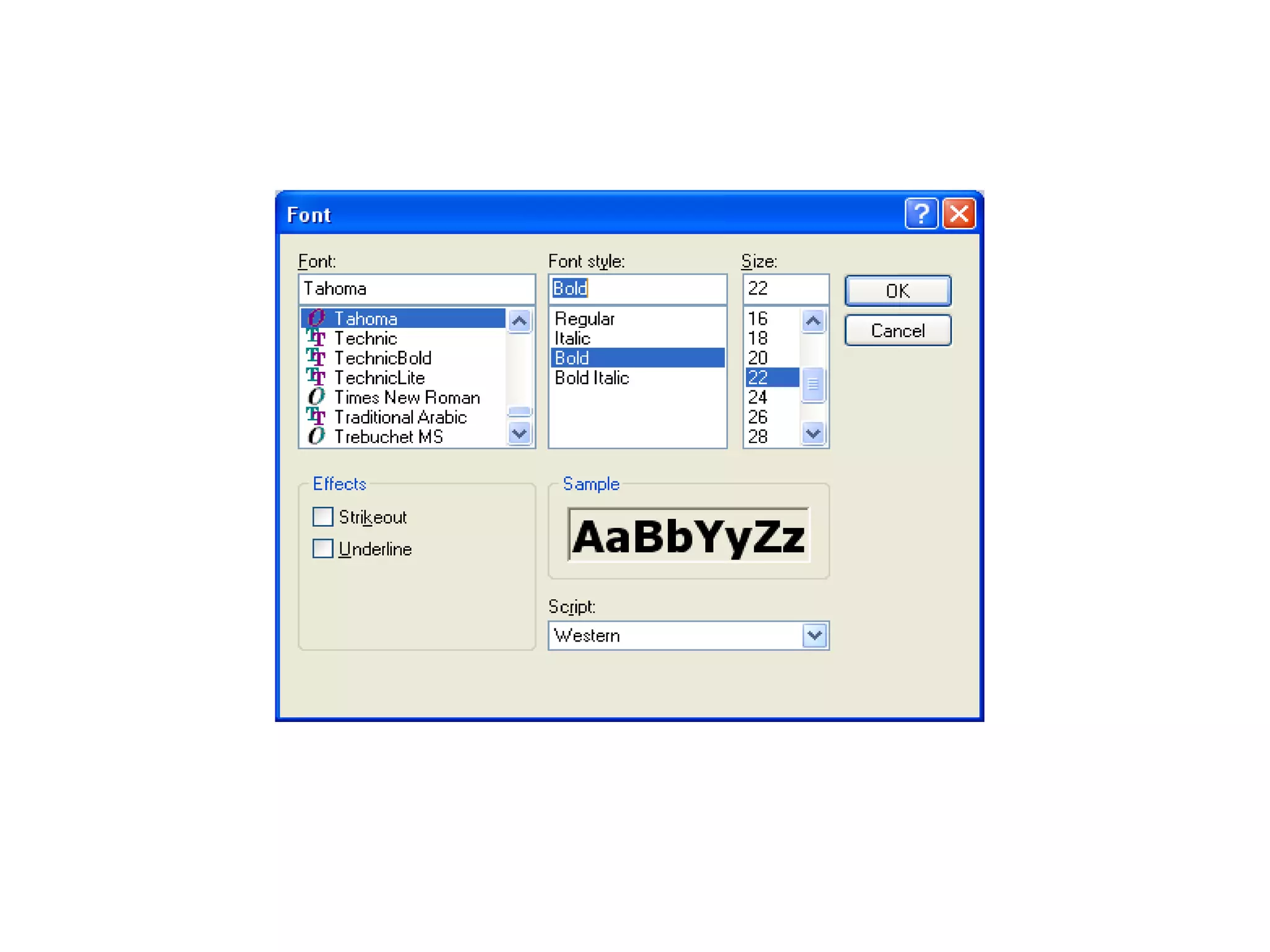
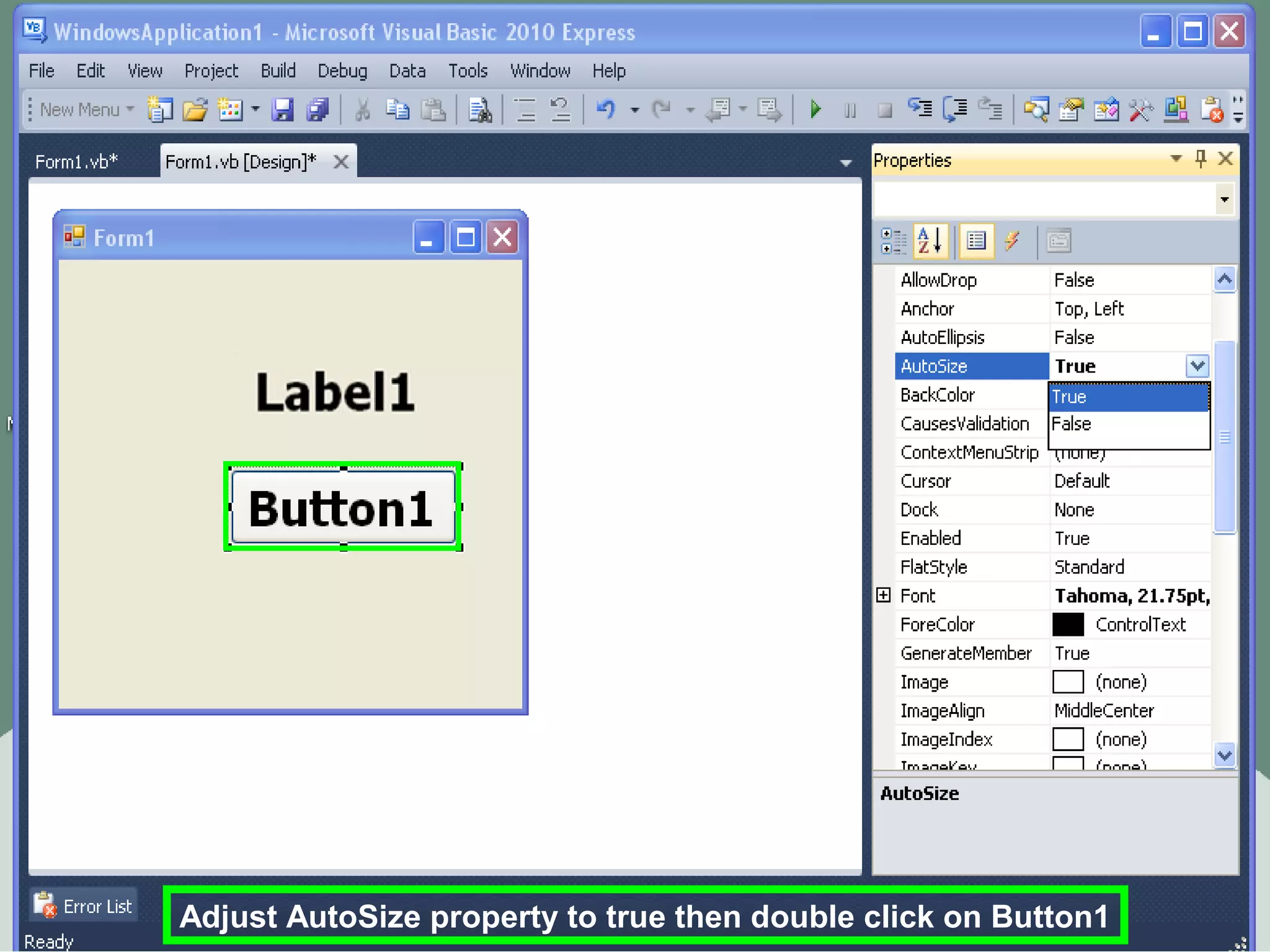
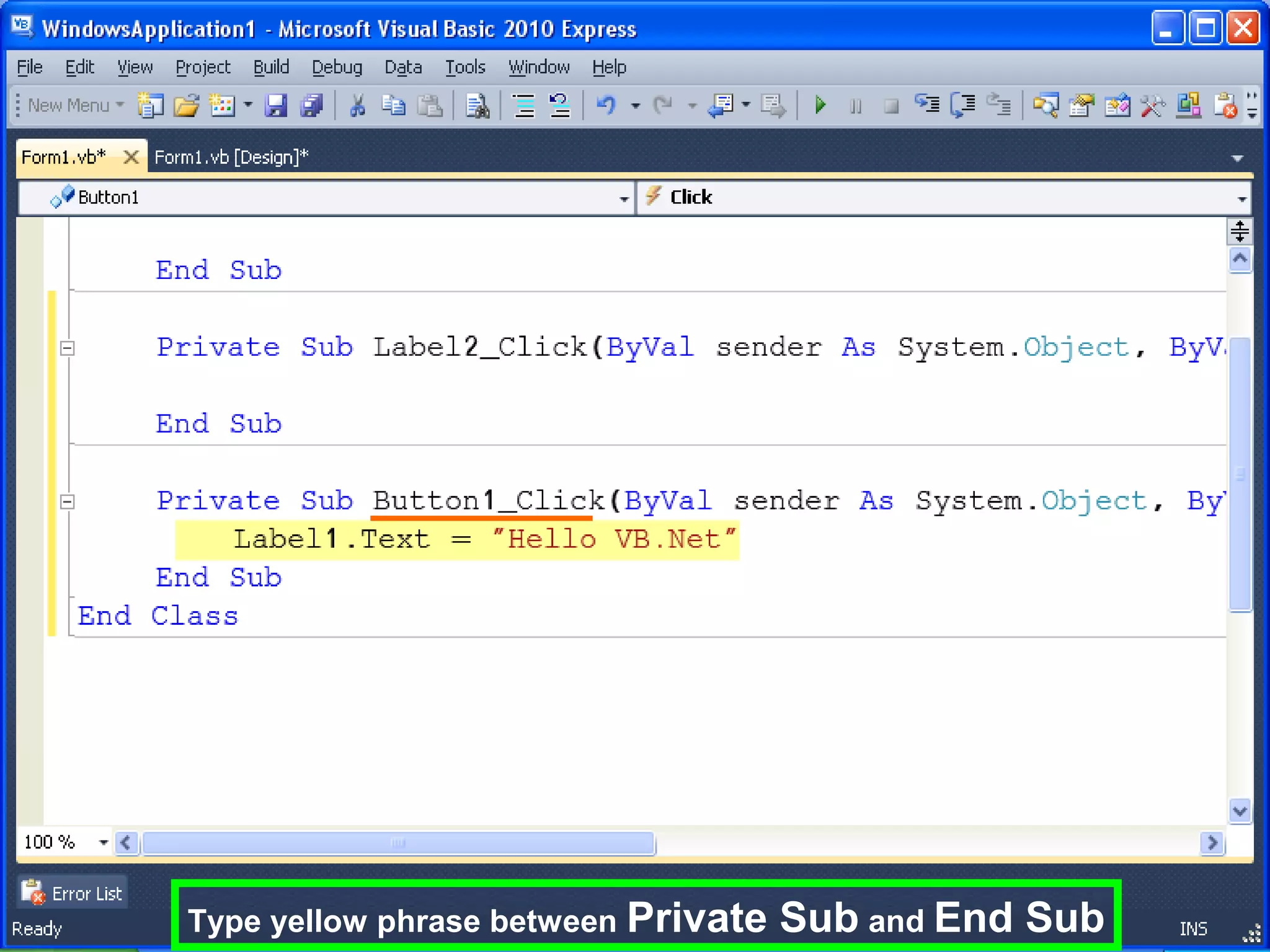
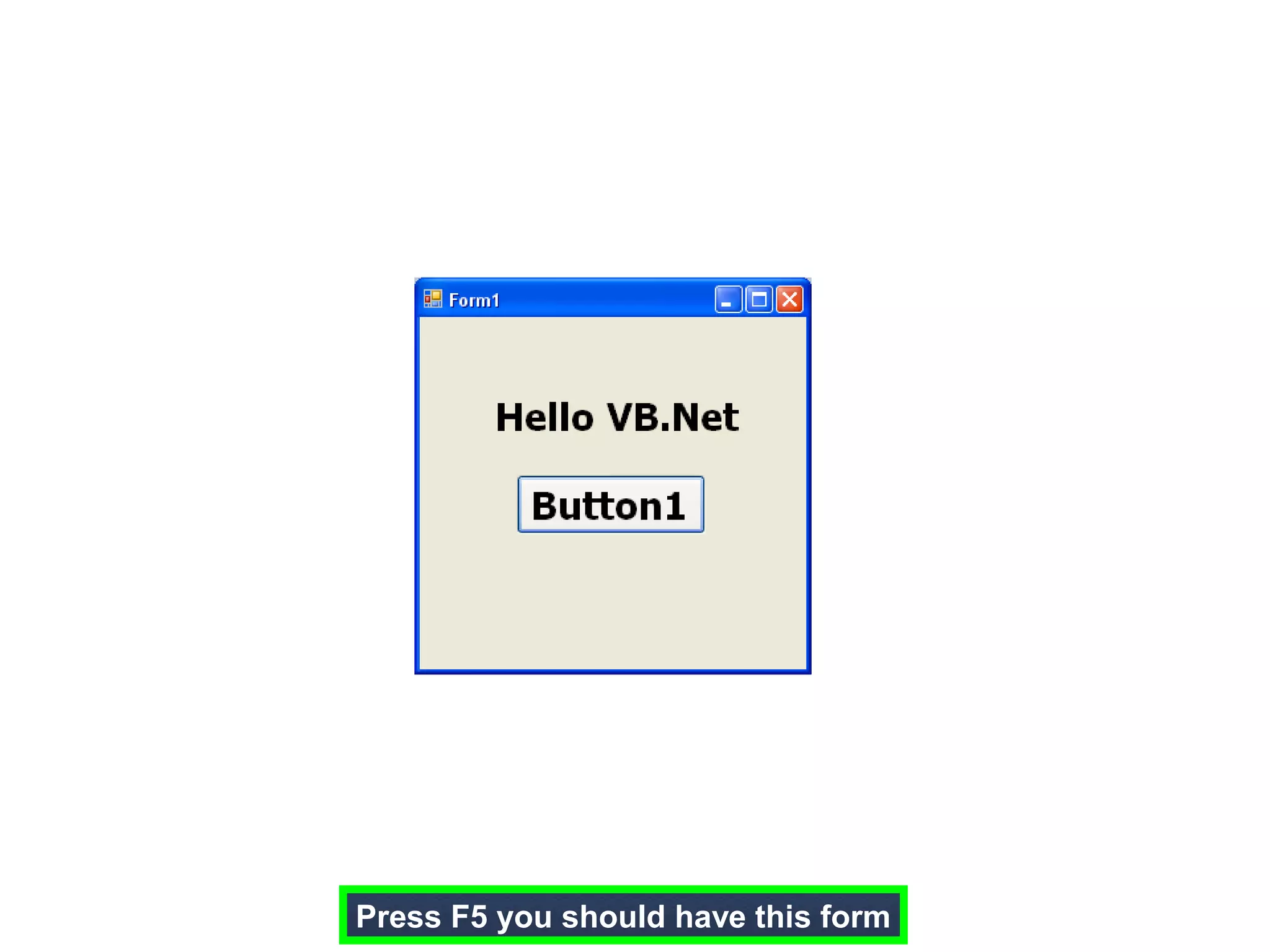
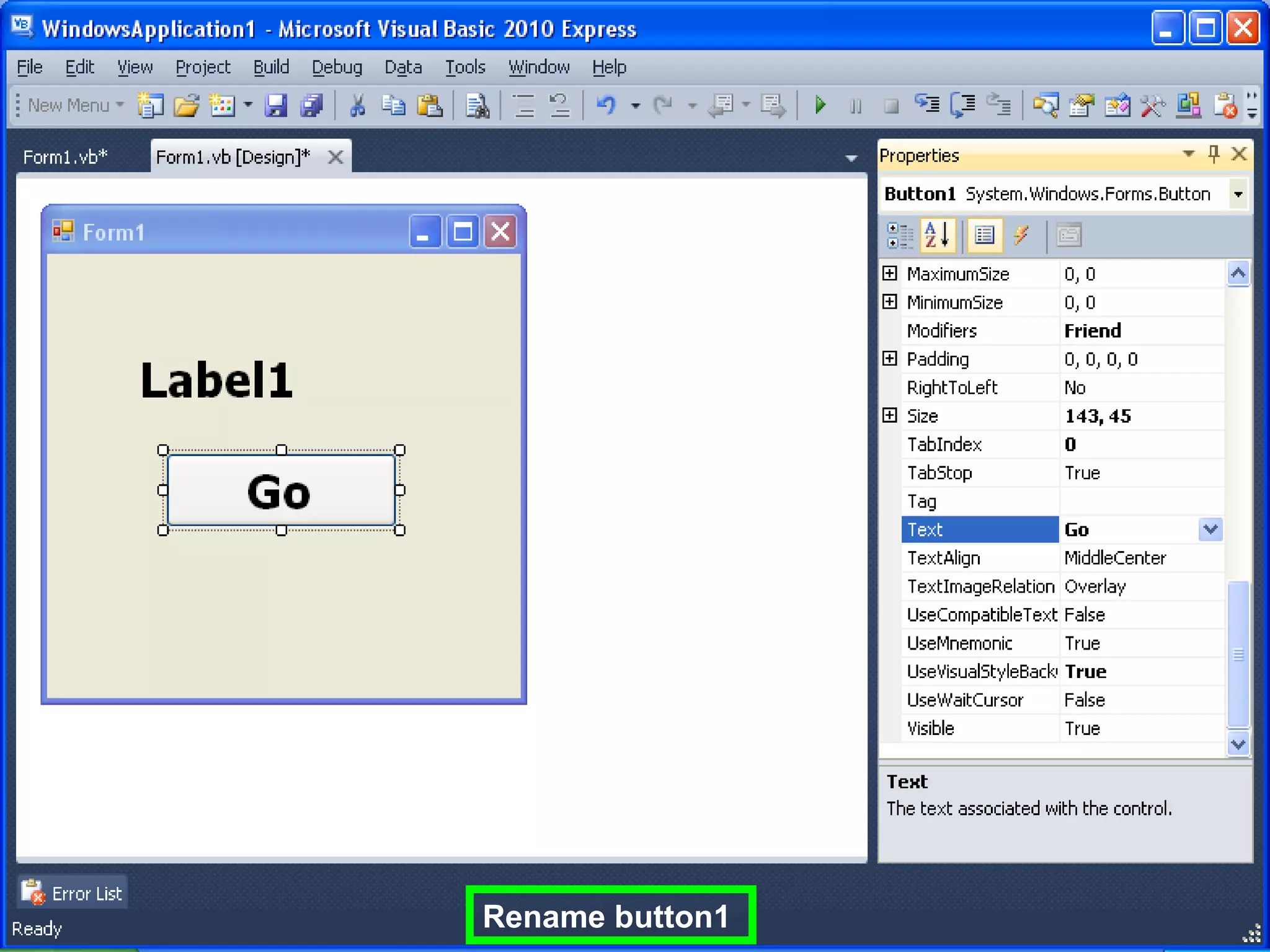
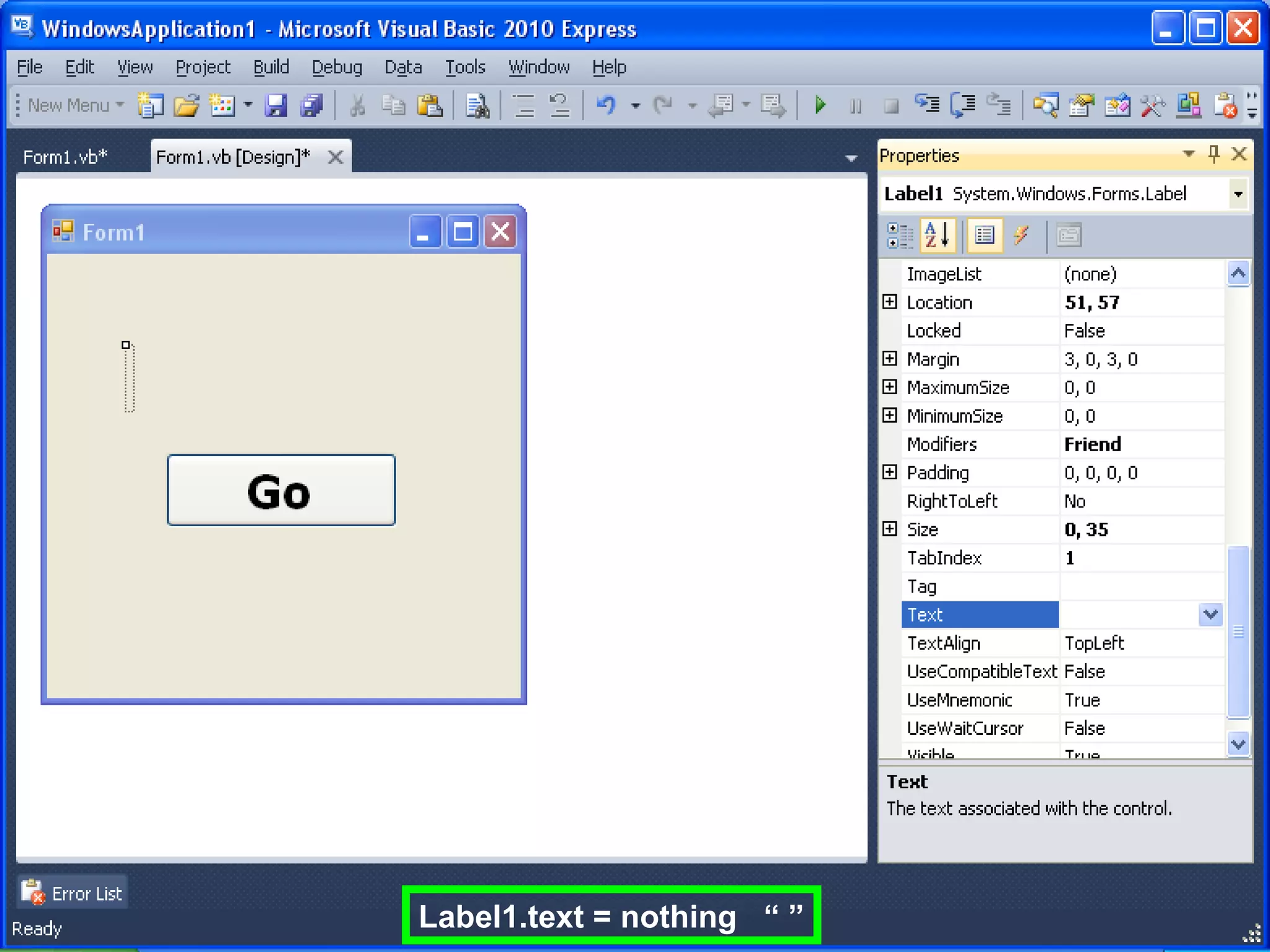
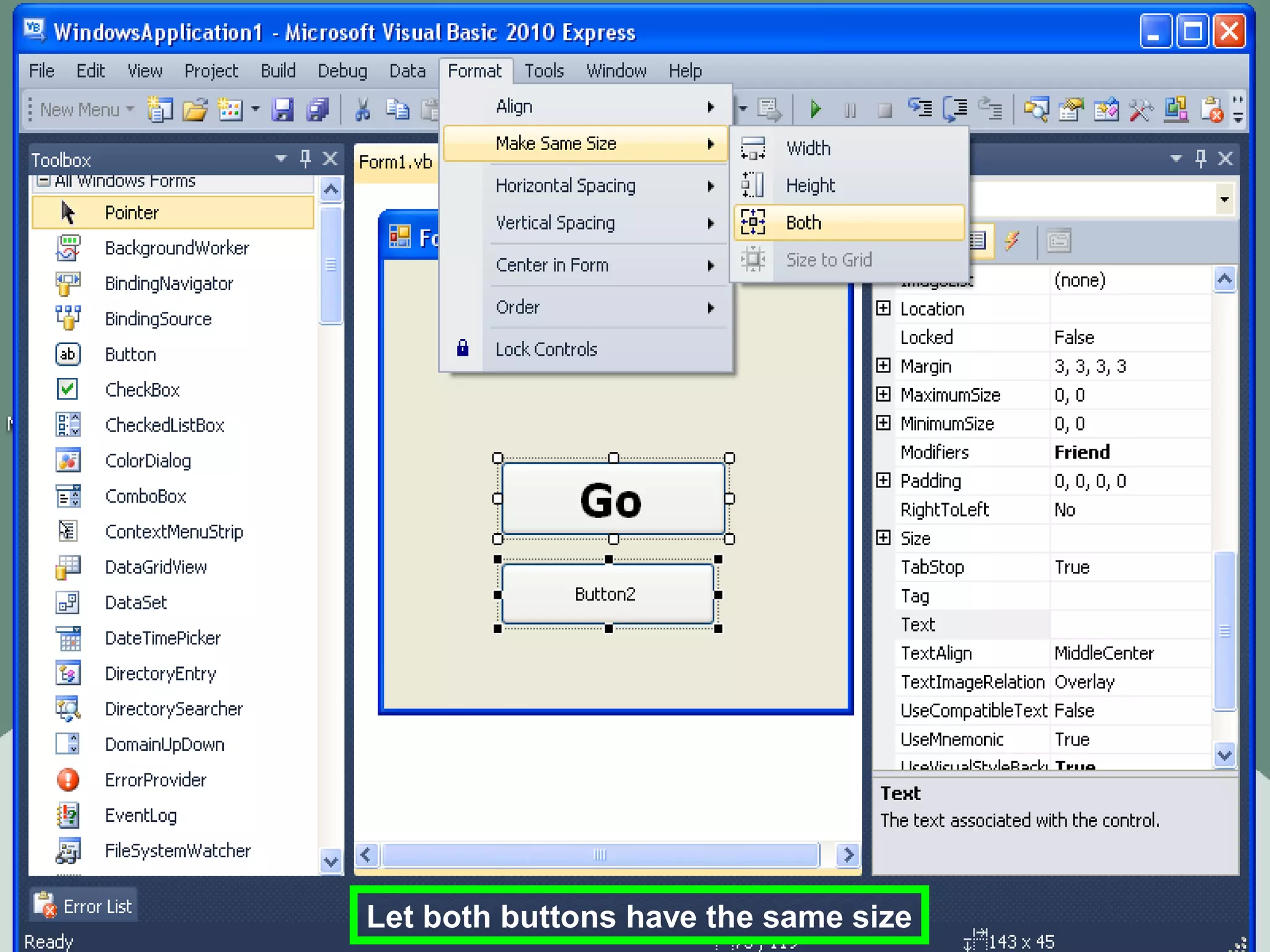
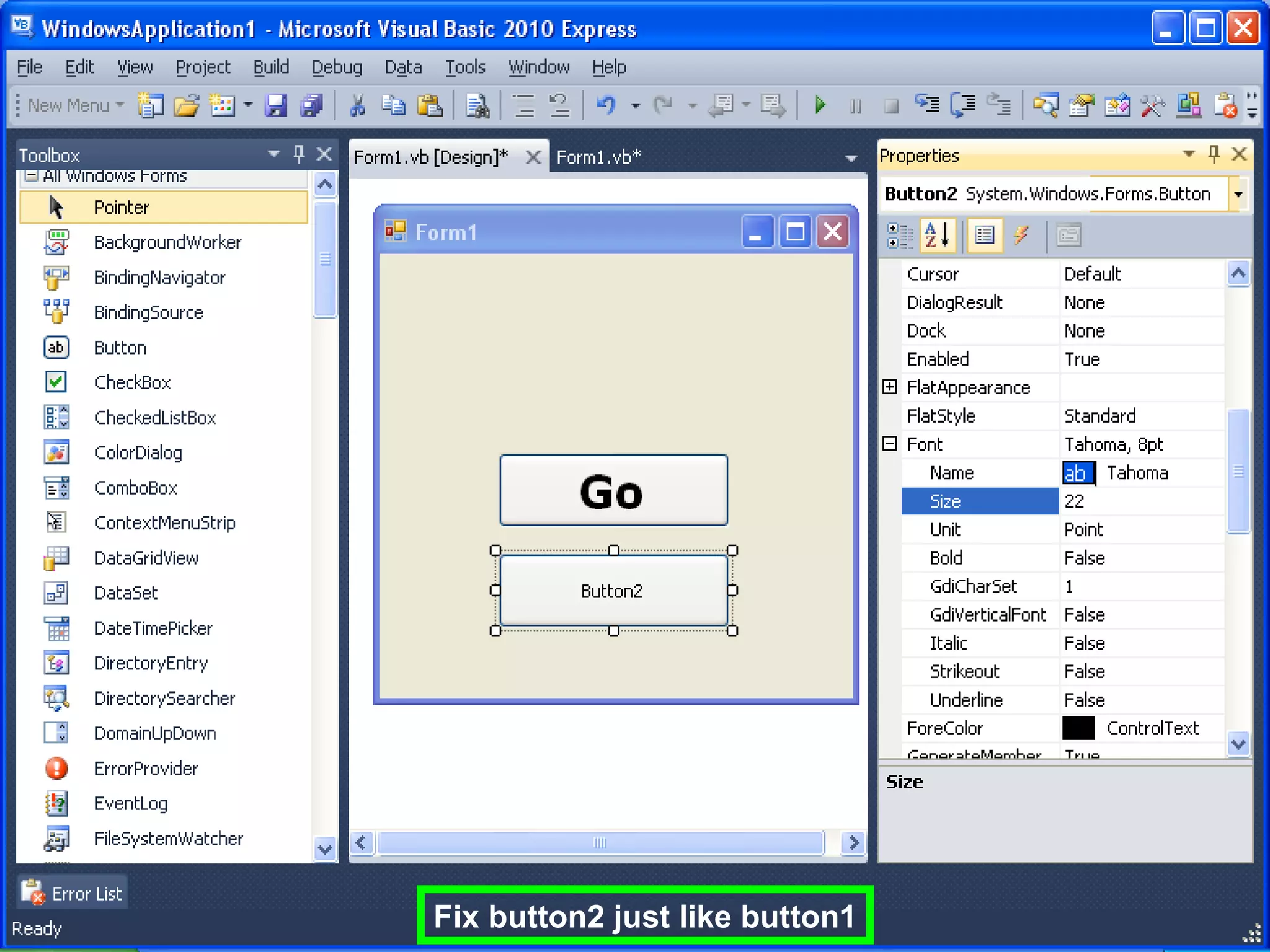
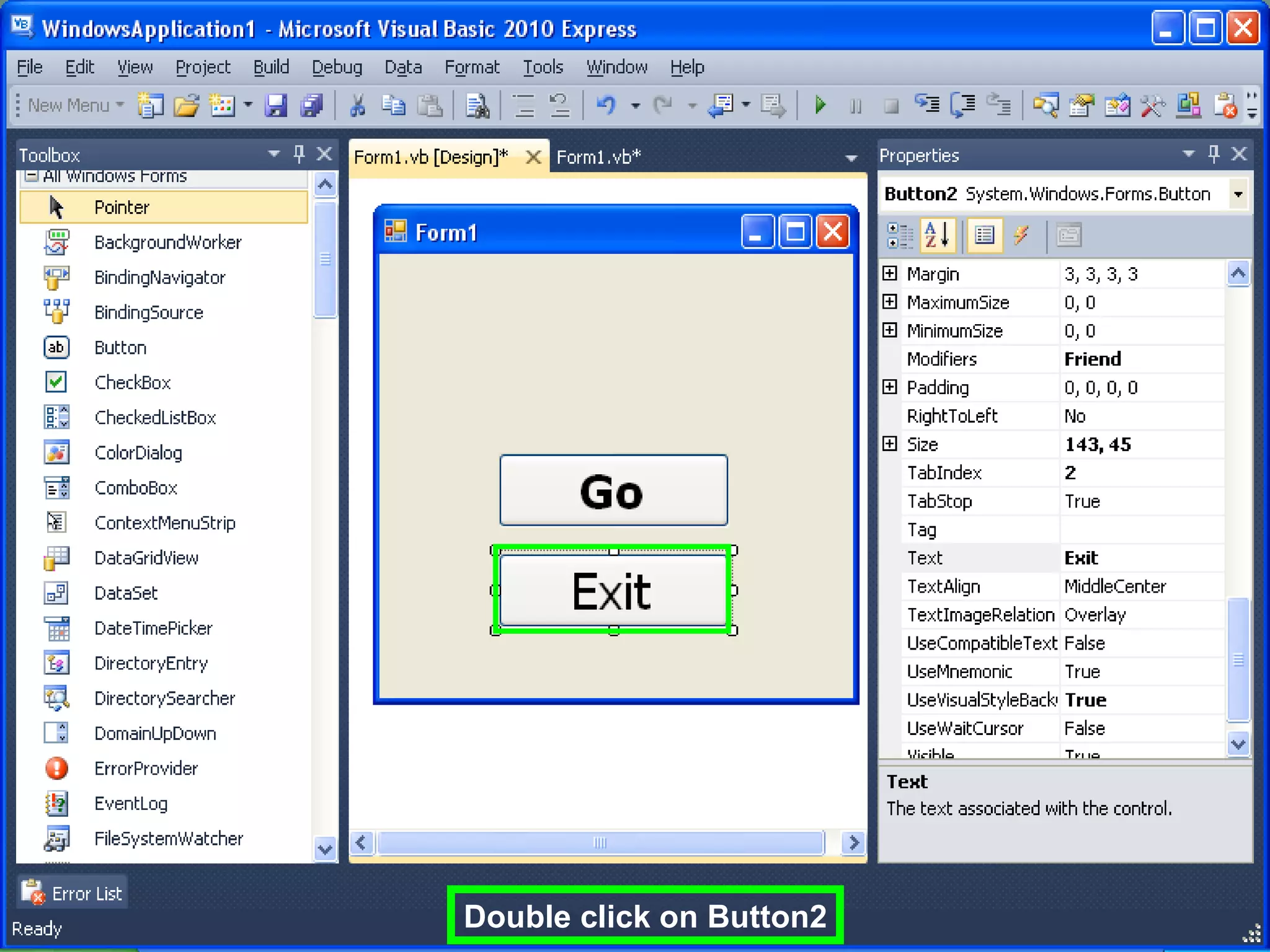
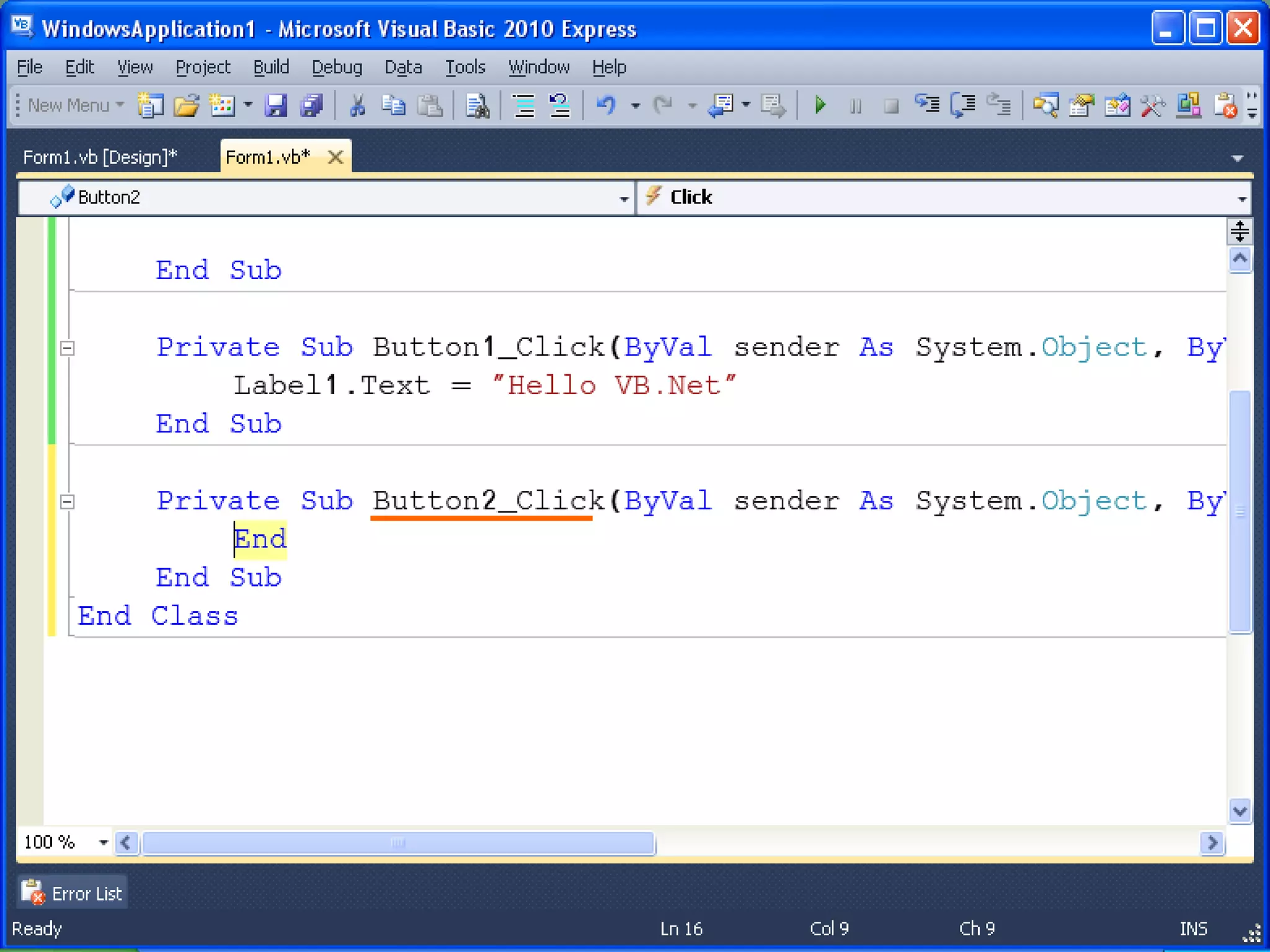
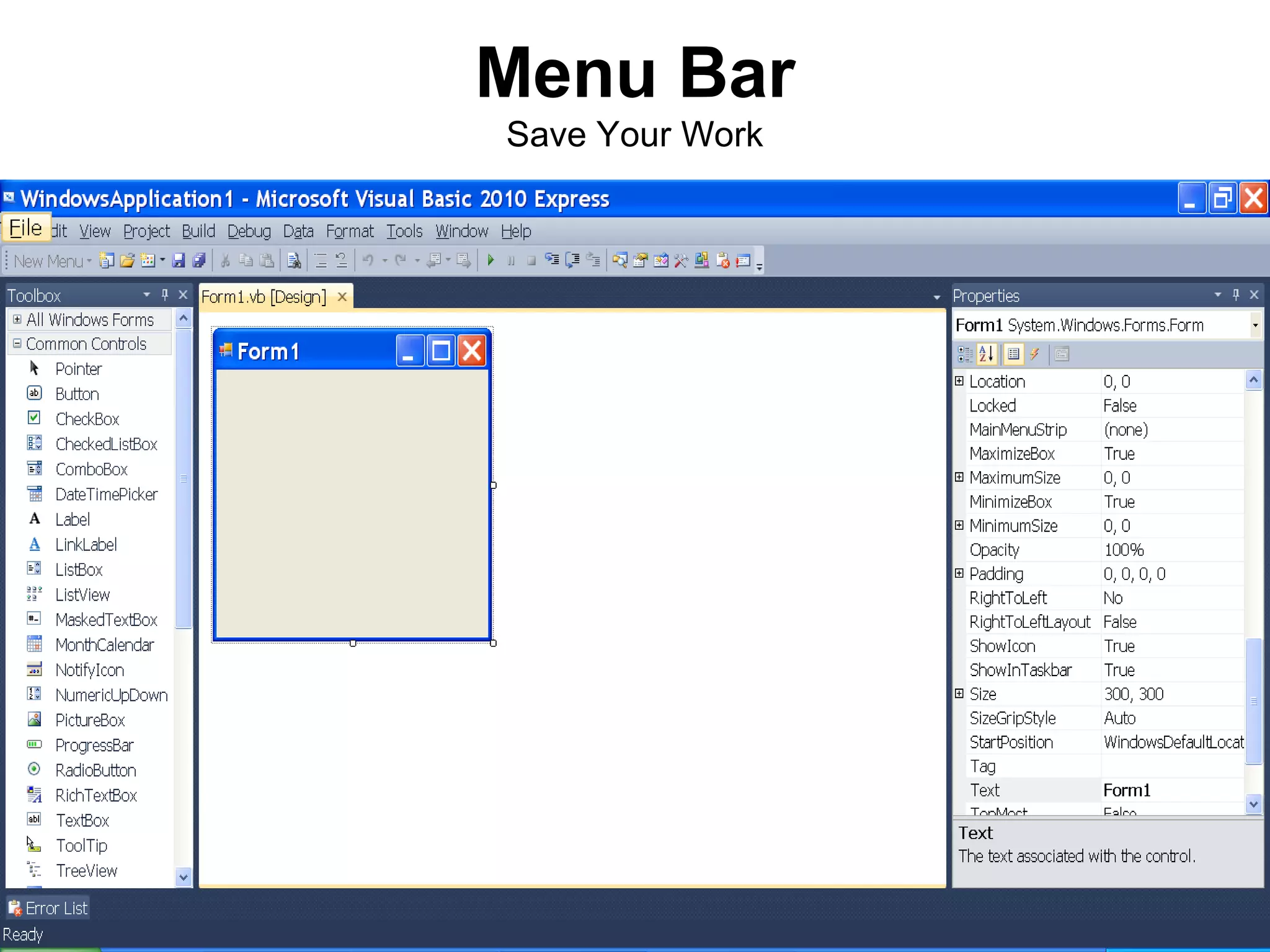
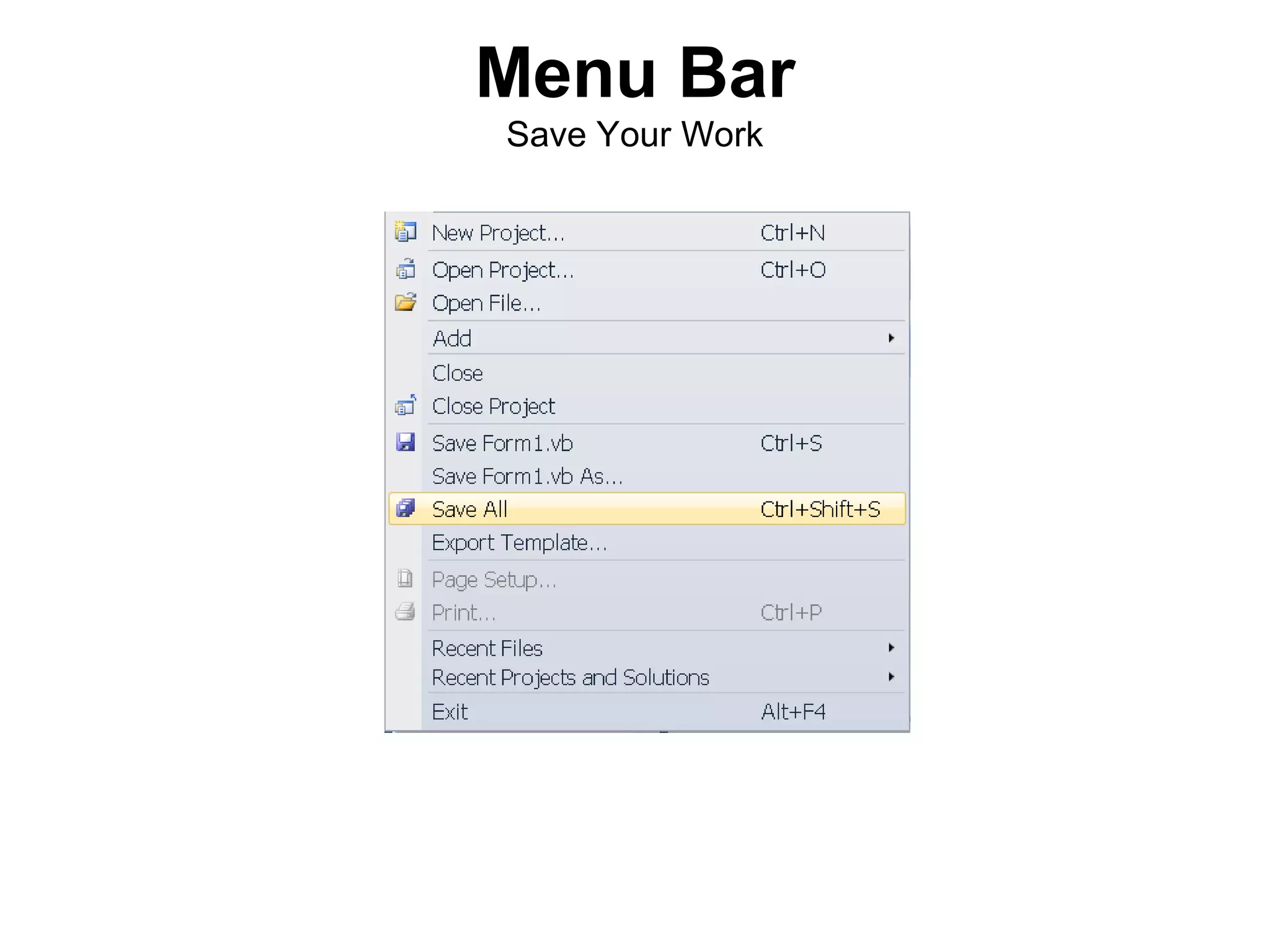
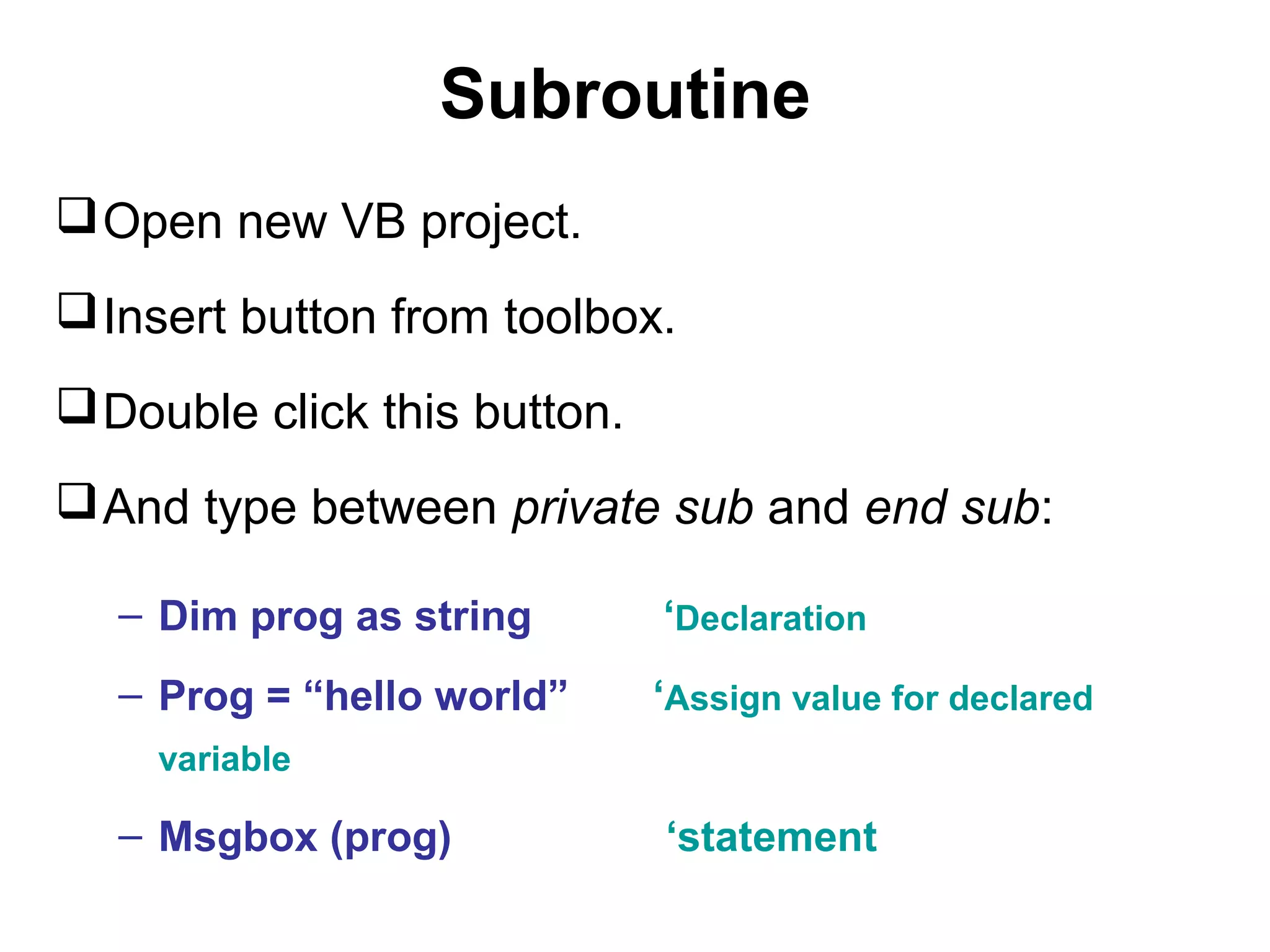
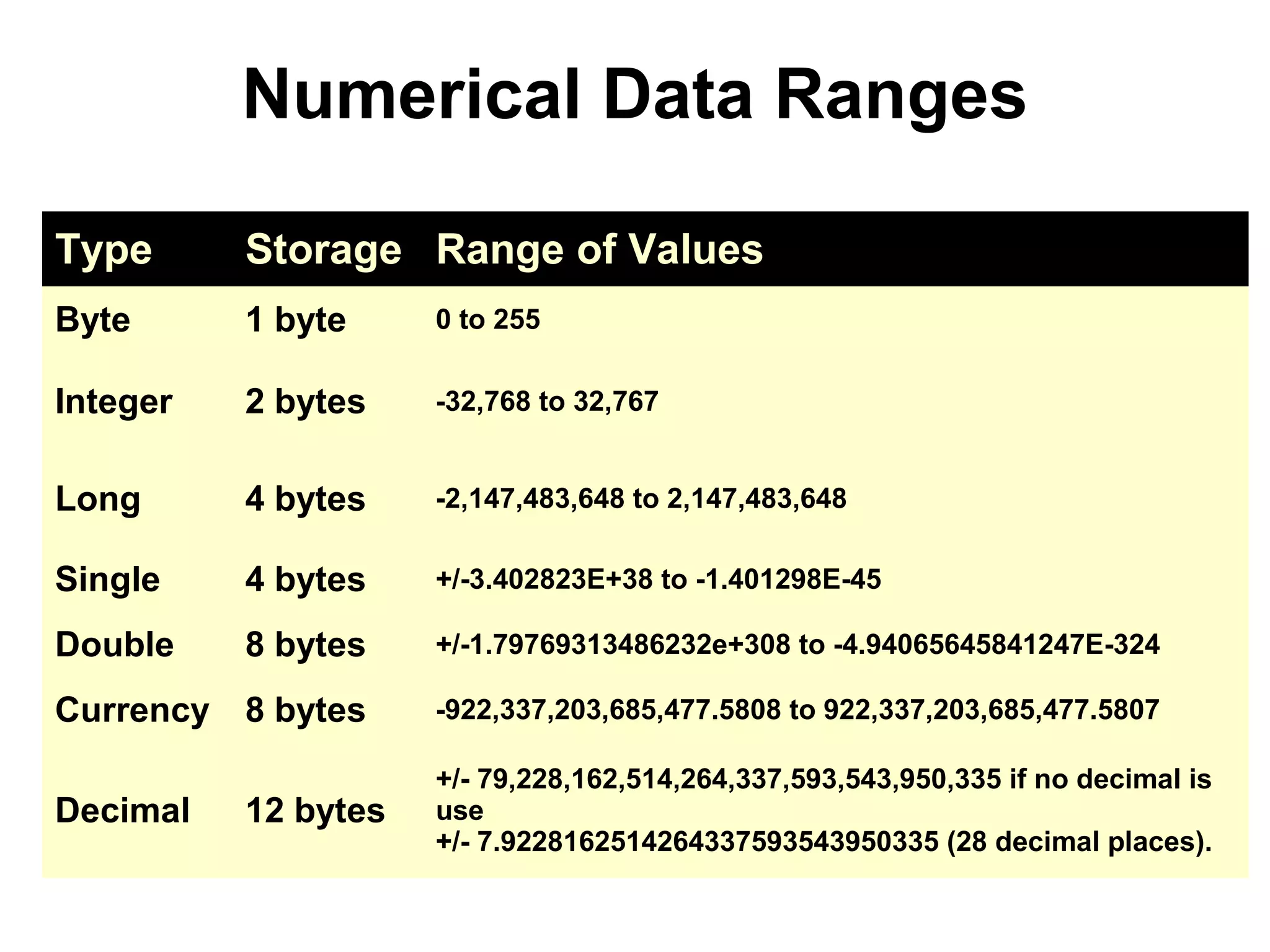
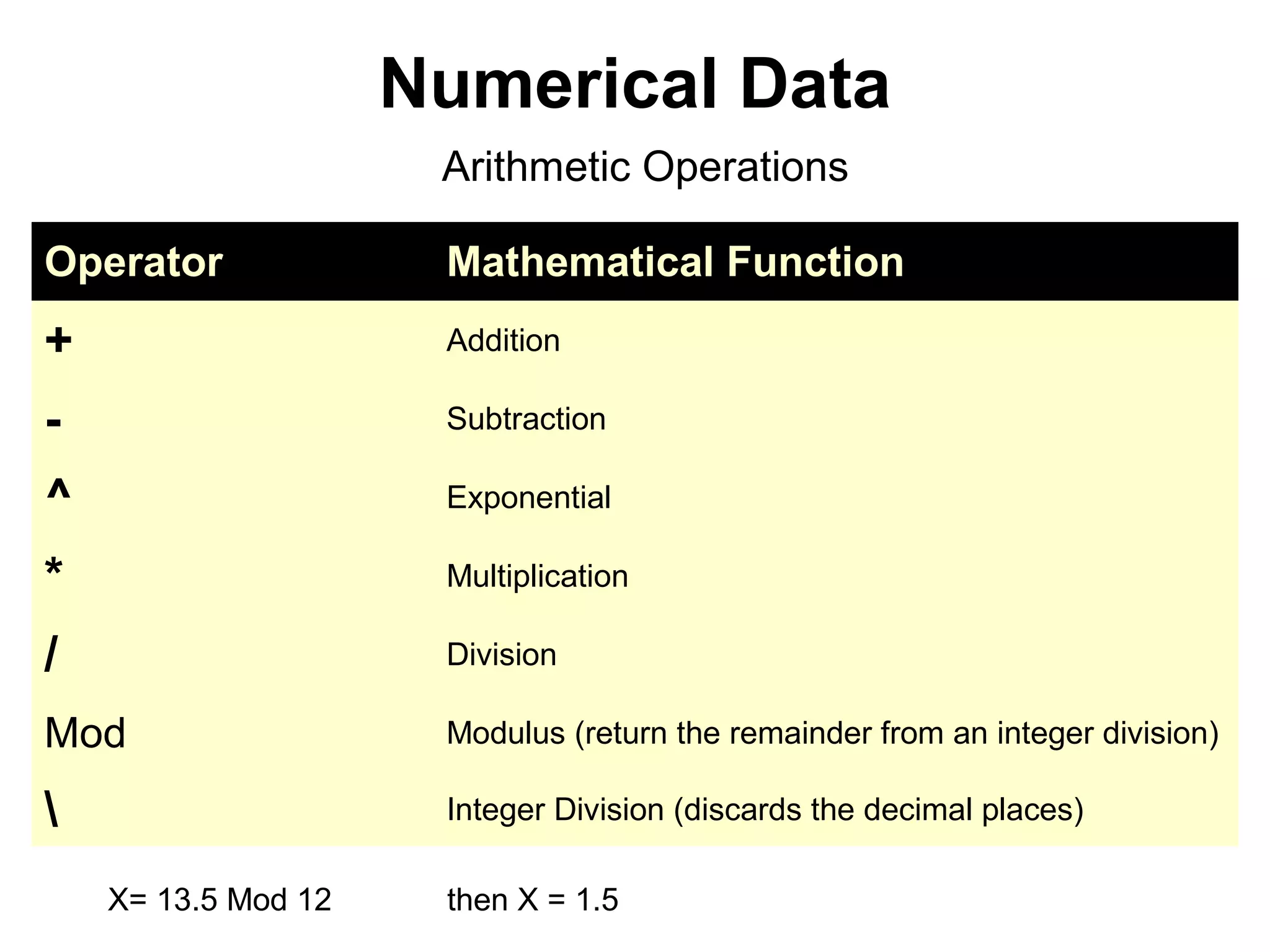
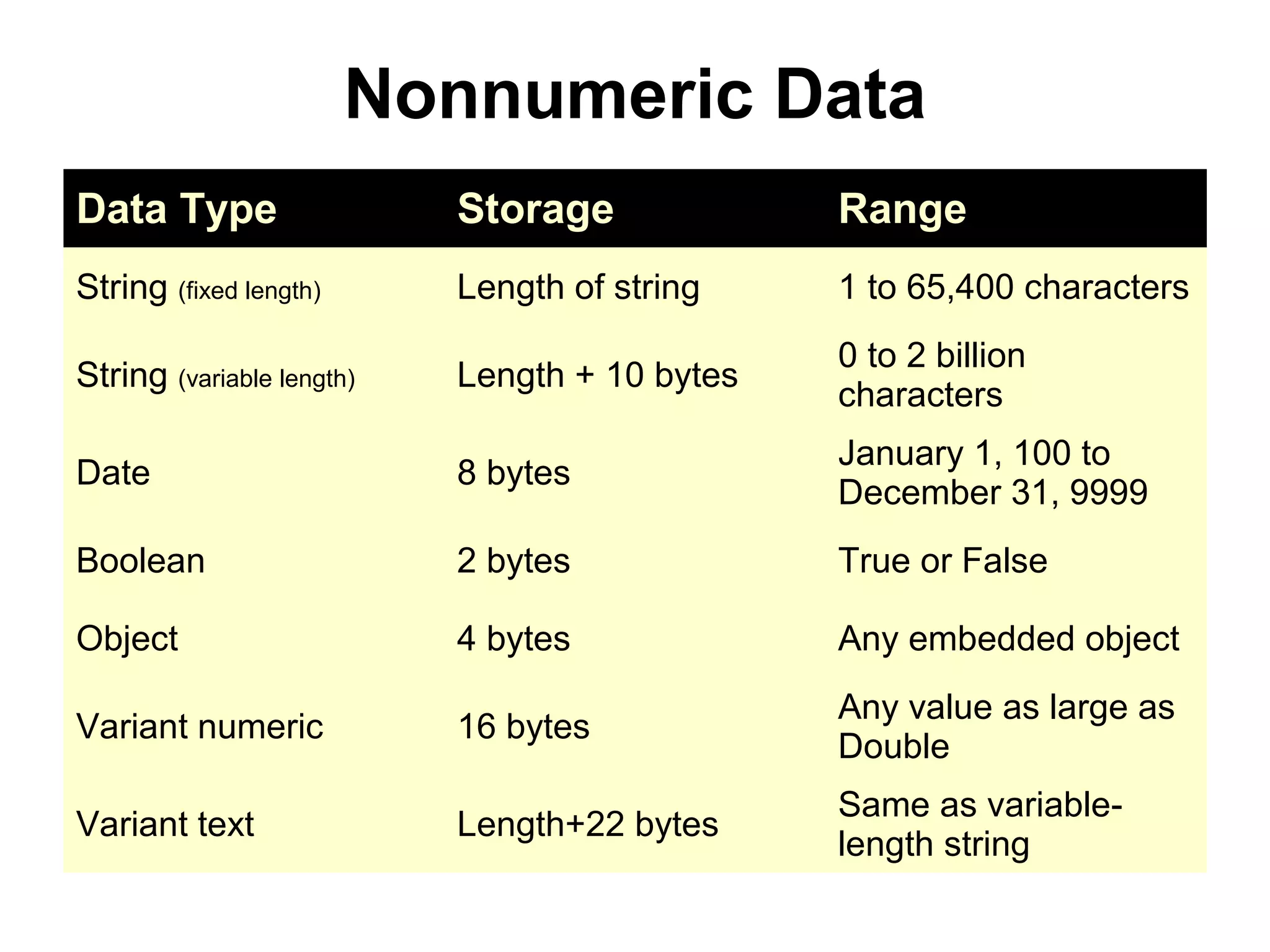
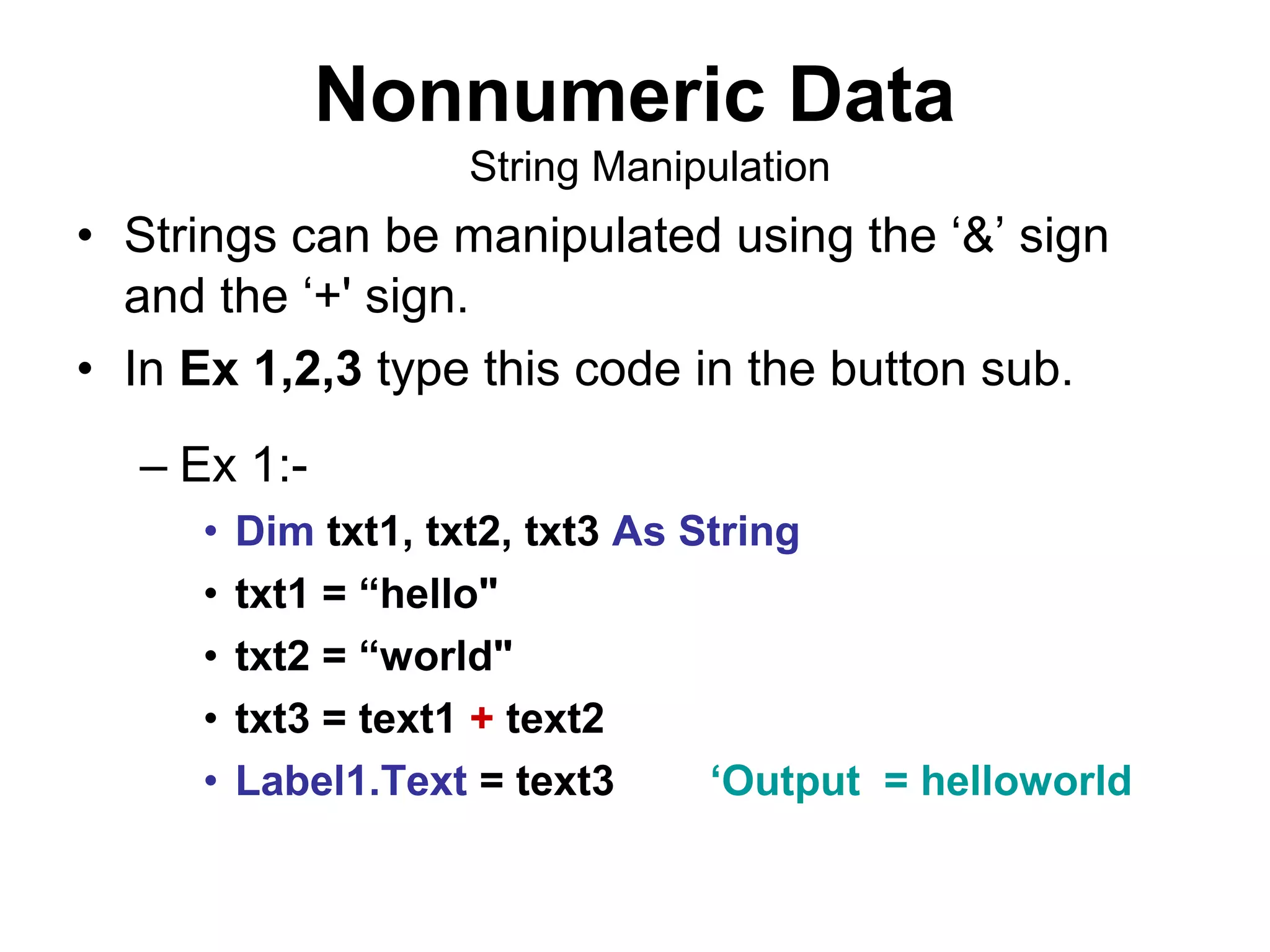
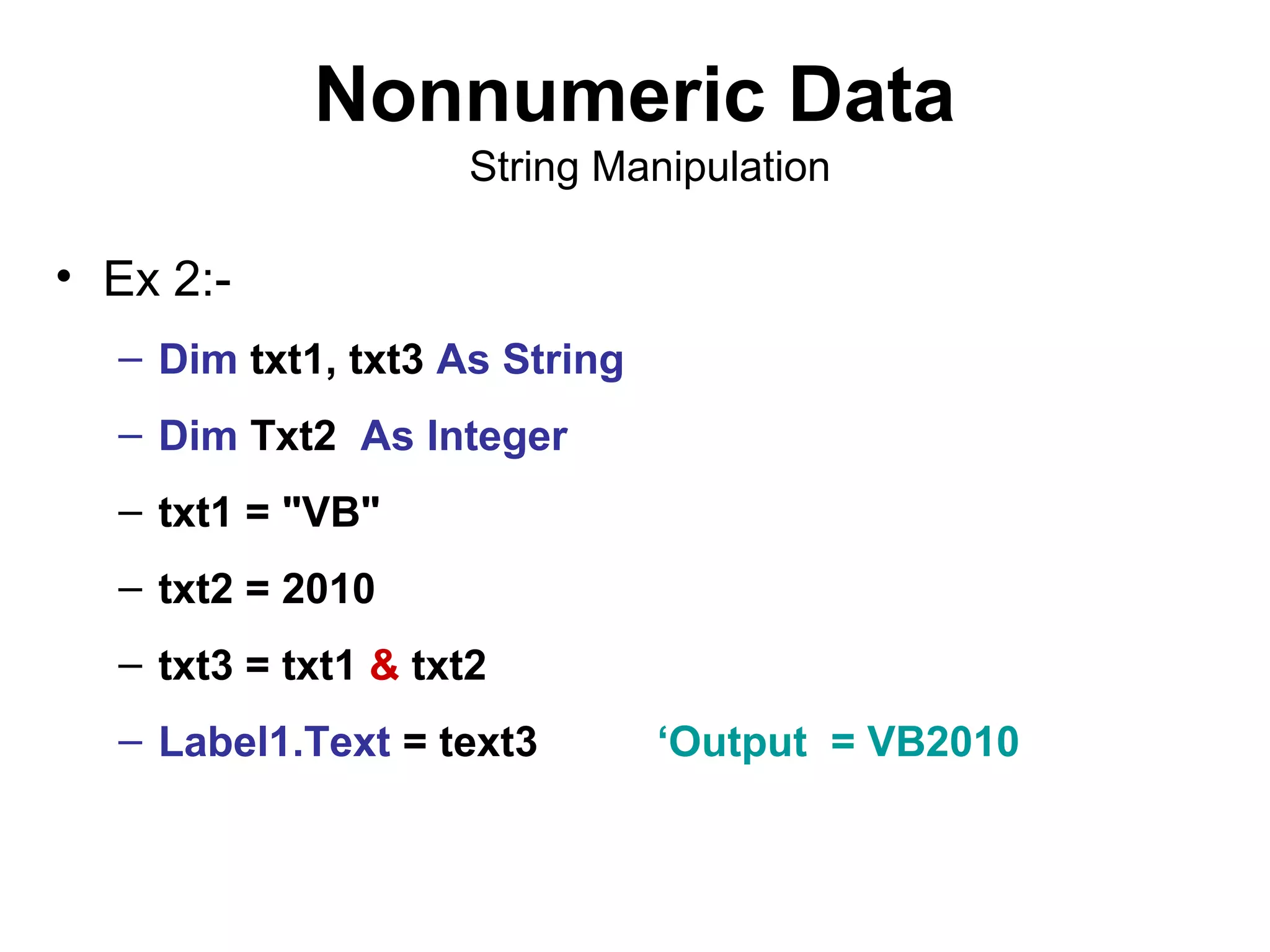
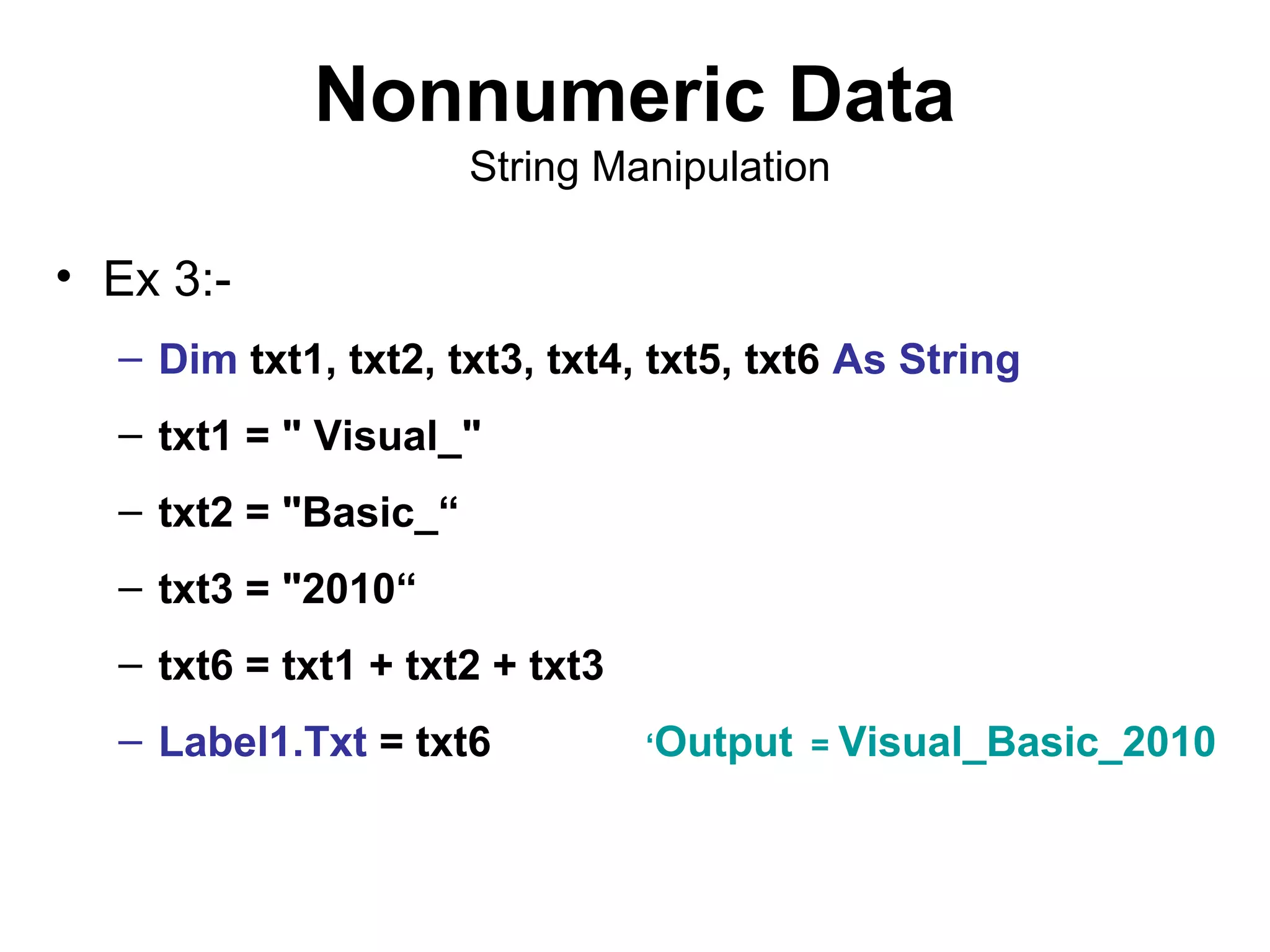
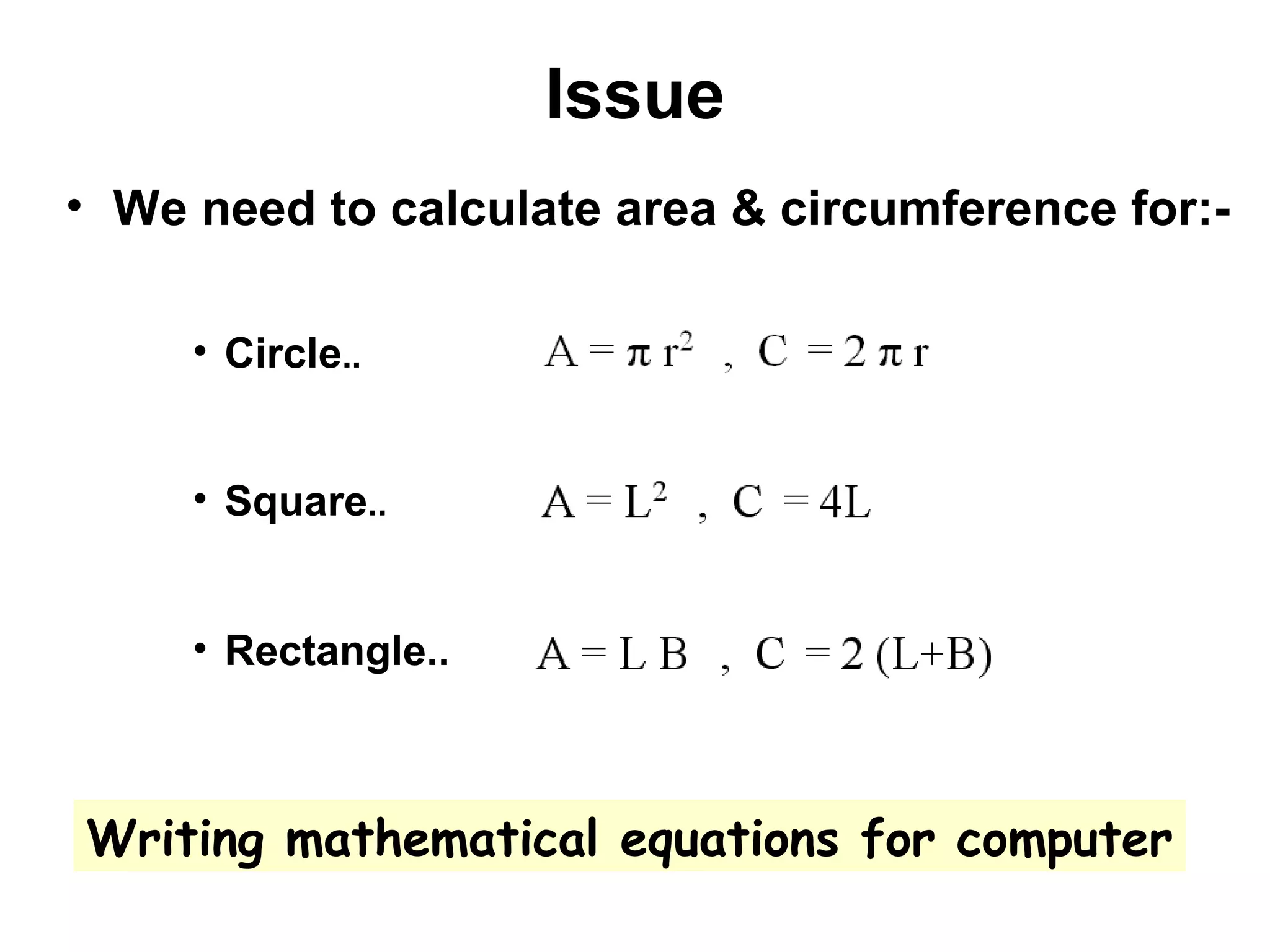
The document discusses Visual Basic 2010 and object-oriented programming concepts. It covers the system development cycle, programming languages, object-oriented principles like encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism. It also discusses programming concepts like classes and objects, events and actions, integrated development environments, and tools like buttons, checkboxes and listboxes. The document provides instructions on installing VB 2010 Express and creating basic programs to learn Visual Basic.