Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,184 times










The document outlines the significance of linear algebra in computer science, including its applications in graph theory, network models, cryptography, and computer graphics. Linear algebra simplifies complex problems into manageable matrix forms, which are crucial for various scientific fields. The text concludes by emphasizing the diverse applications of linear algebra, ranging from circuit analysis to advanced algorithms.













Introduction to the applications of Linear Algebra in various fields of computer science.
Overview of the key topics: importance, graph theory, network models, cryptography, and computer graphics.
Linear algebra simplifies issues in science, enabling numerous complex problems to be solved via matrices.
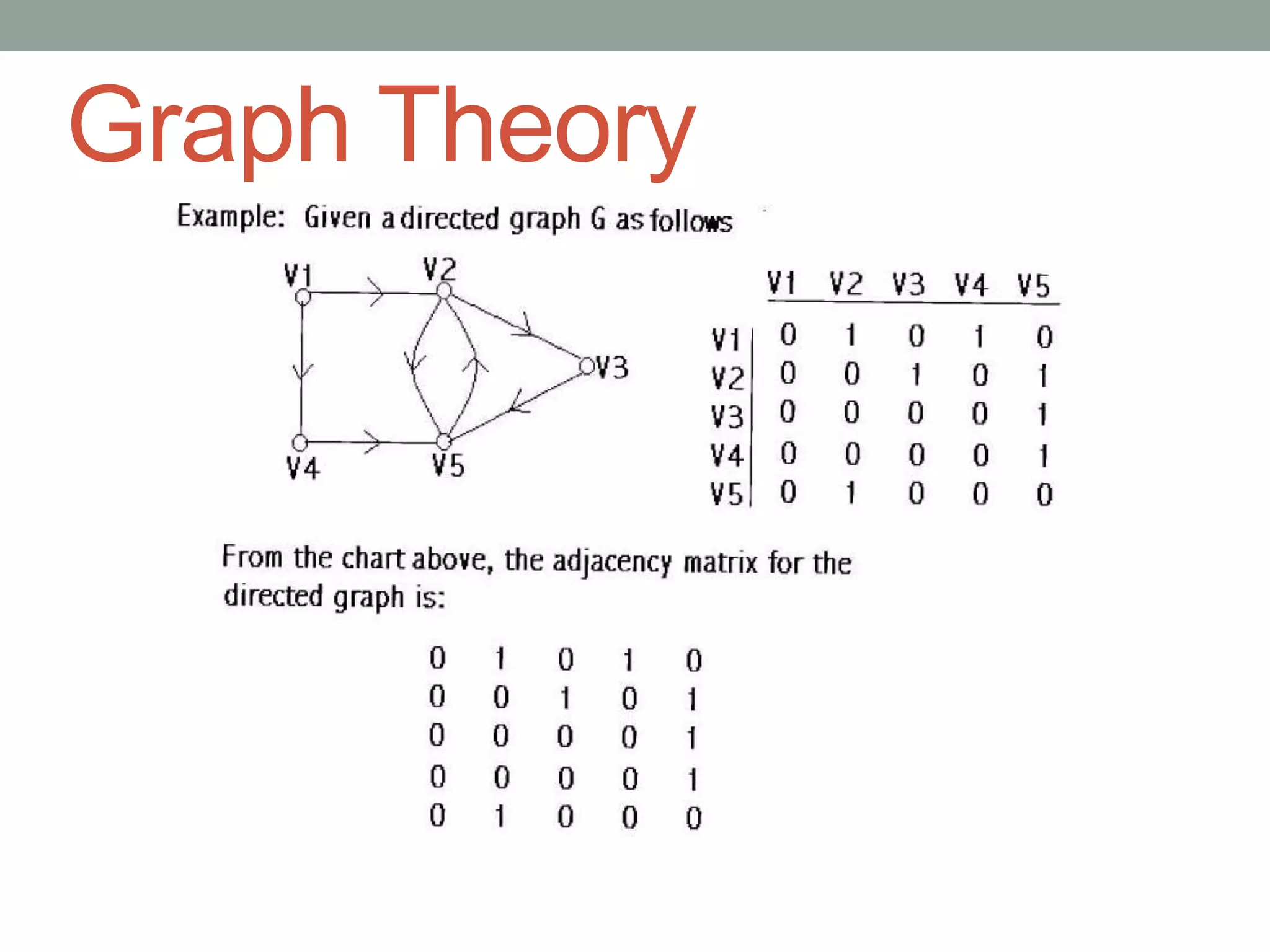
Introduction to graph theory, its principles, and how linear algebra applies to it.
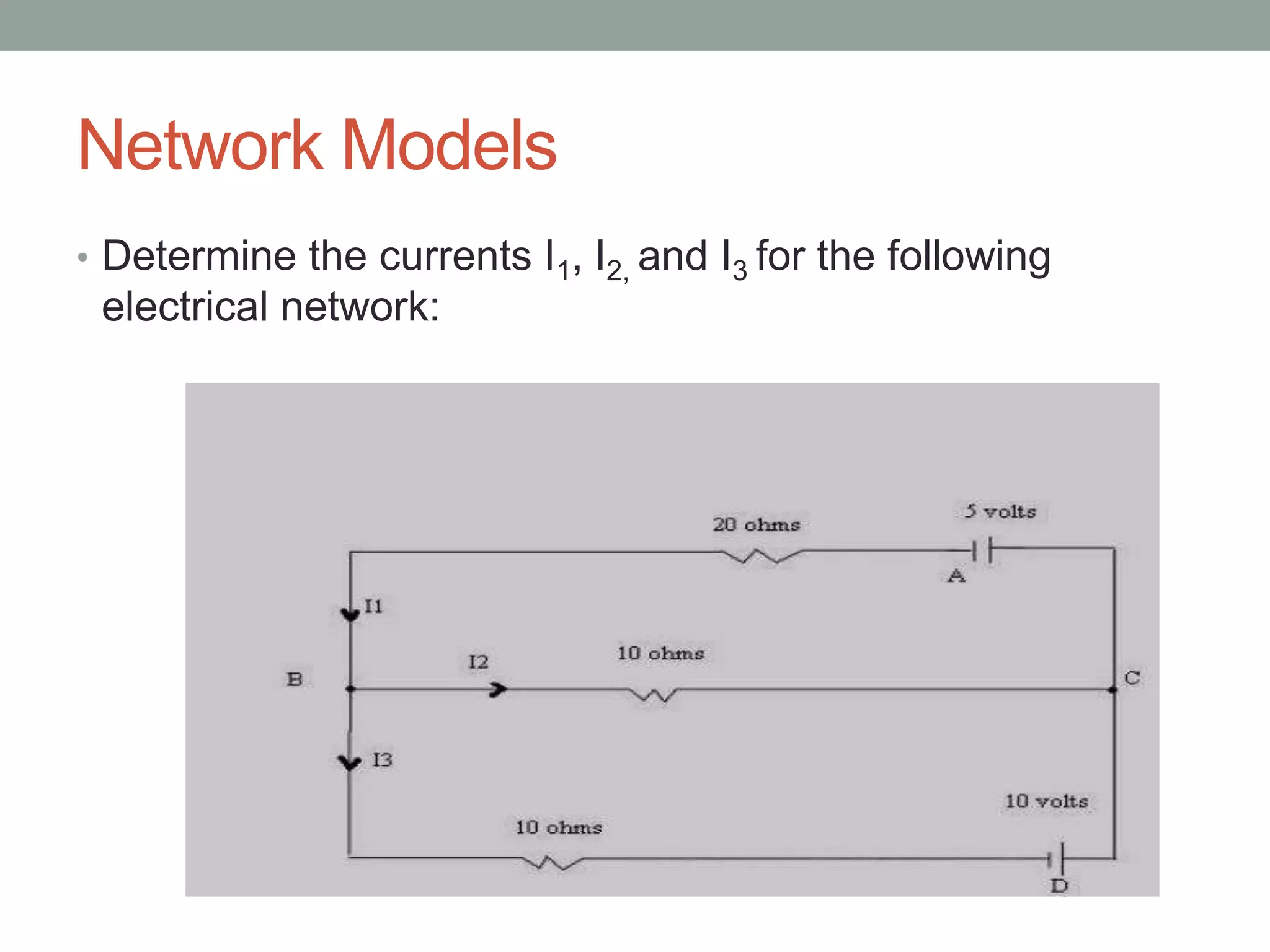
Applying linear algebra to find electrical currents in a given network.
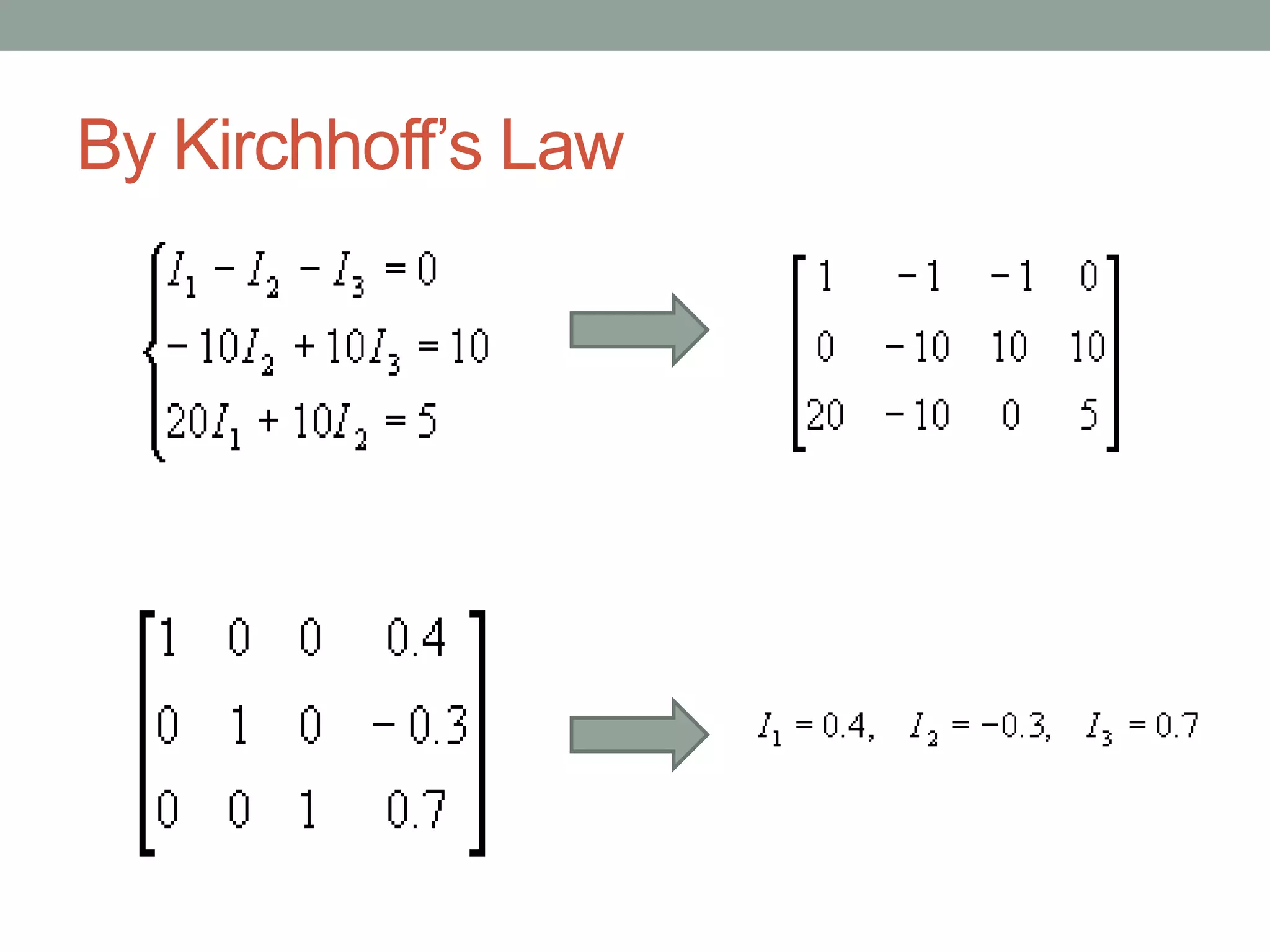
Utilizing Kirchhoff's Law to analyze electrical circuits within the context of linear algebra.
The role of linear algebra in encryption and decryption processes, highlighting the use of keys.
Demonstrating encoding by transforming messages into vectors for encryption using matrices.
Explanation of how to encrypt messages by multiplying with an encoding matrix.
Demonstrating decryption by using the inverse of the encoding matrix to retrieve original messages.
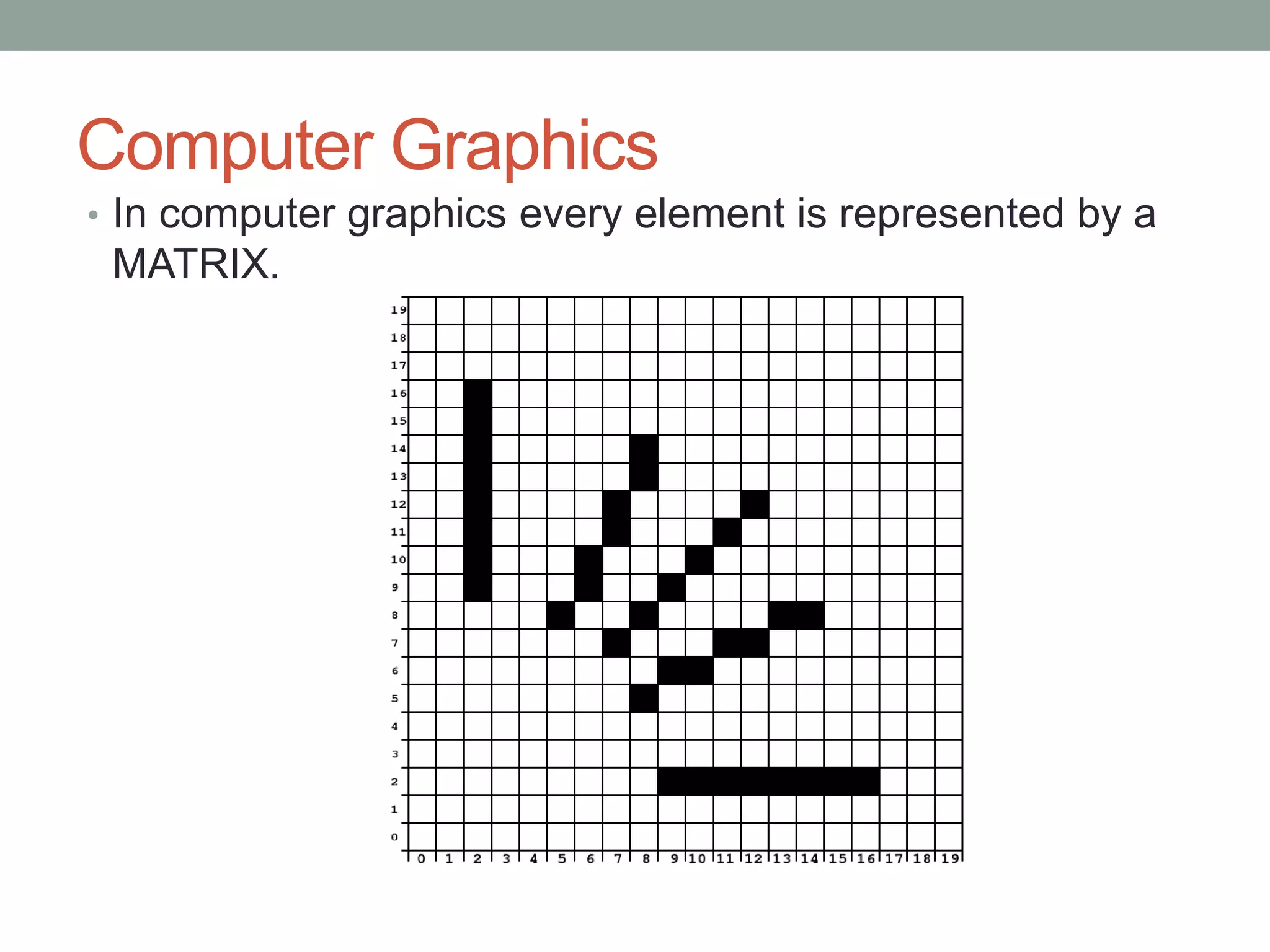
In computer graphics, all visual elements are represented through matrices.
Recap of the extensive applications of linear algebra in computer science, from circuits to algorithms.
Thank you note, concluding the presentation.