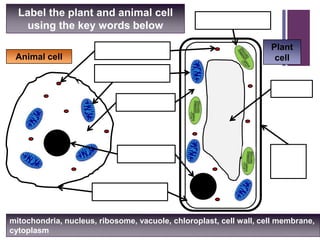
This document provides information about plant and animal cells. It begins with defining a cell and then labels the structures of plant and animal cells such as the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and cell wall. It explains the roles of each structure and compares plant and animal cells in a Venn diagram. The key differences are that plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large permanent vacuole while animal cells do not. The document also discusses cell organization and the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.