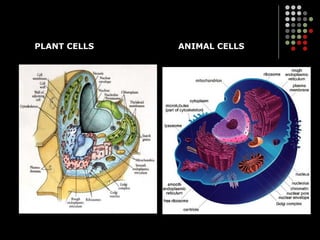
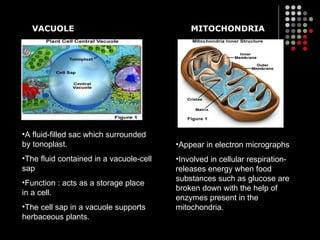
The document discusses the structure and organization of cells. It describes the basic components of plant and animal cells, including the cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, centrioles, and chloroplasts. It compares the key similarities and differences between plant and animal cells, and relates the density of certain organelles to the functions of specific cell types.