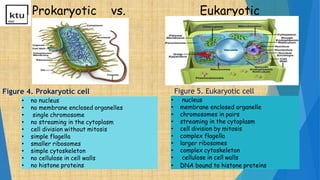
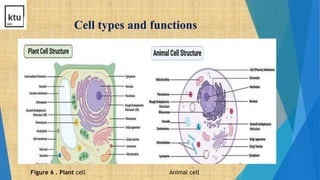
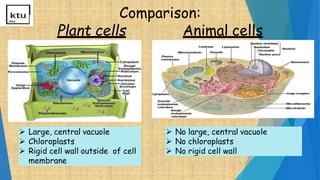
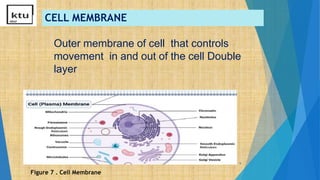
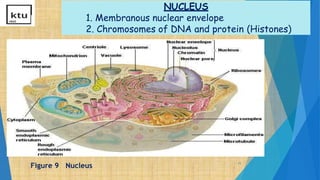
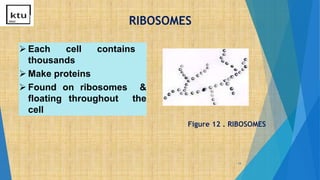
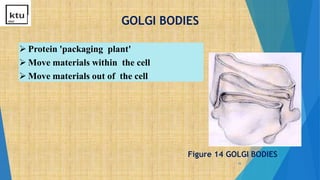
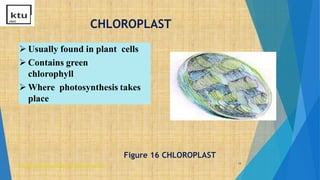
This document provides an overview of cell types, structures, and functions. It begins by outlining the cell theory and defining cells. It then distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as plant and animal cells. The document proceeds to describe various cellular structures such as the cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, nuclear membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, and chloroplasts. It concludes by emphasizing the important and extraordinary functions performed by the various cellular organelles.