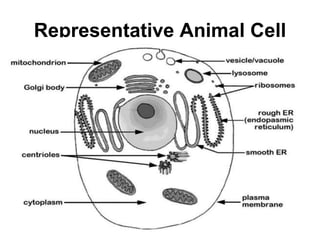
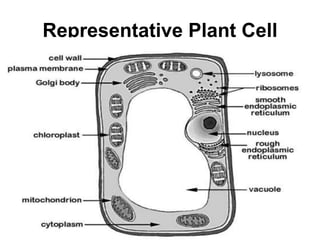
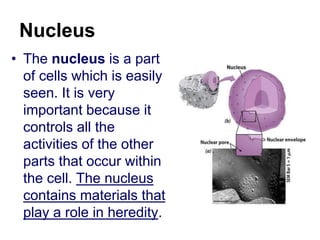
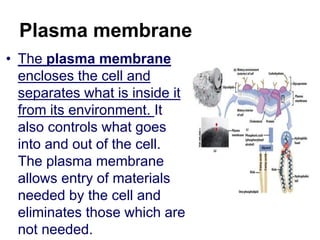
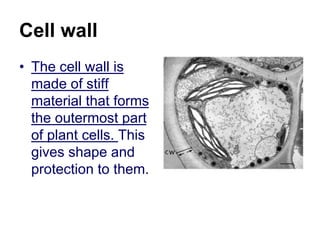
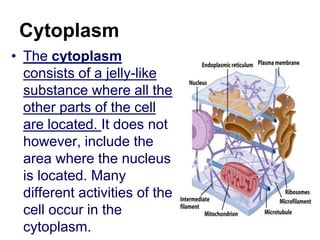
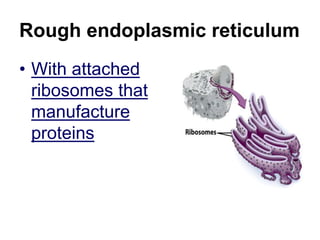
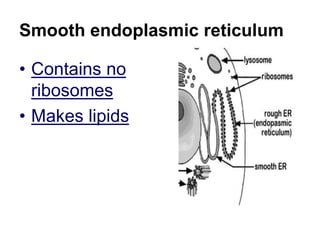
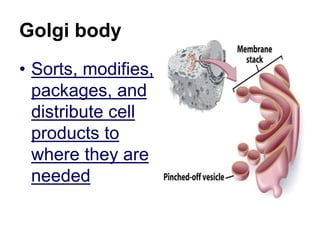
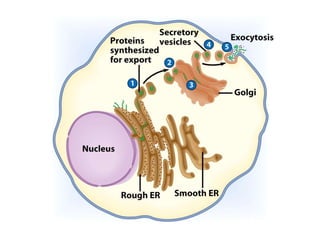
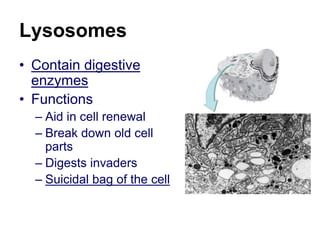
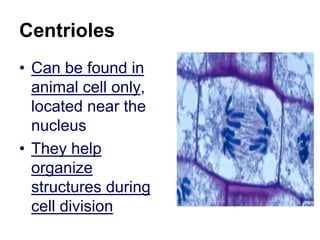
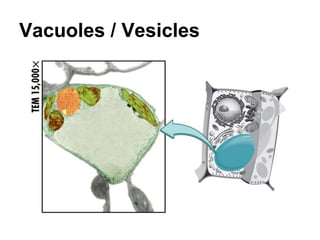
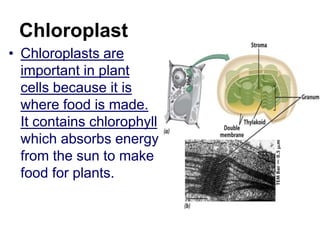
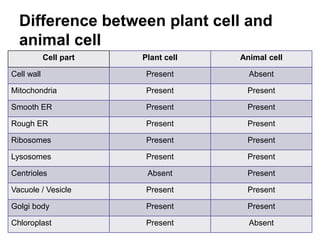
The cell has three basic parts - the nucleus, plasma membrane, and cytoplasm. The nucleus controls the cell's activities and contains hereditary materials. The plasma membrane encloses the cell and regulates what enters and exits. Plant cells also have a cell wall that provides structure and protection. Within the cytoplasm are organelles that carry out specialized functions like mitochondria that generate energy and chloroplasts that perform photosynthesis in plant cells. Key differences between plant and animal cells include the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells.