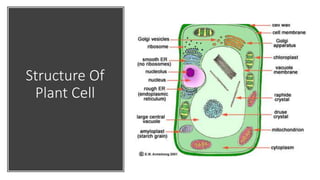
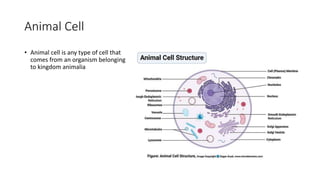
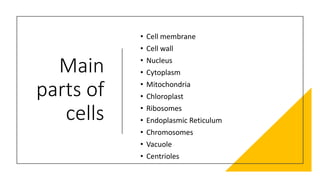
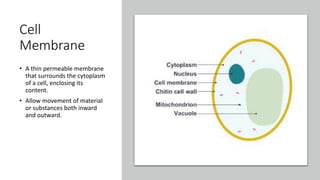
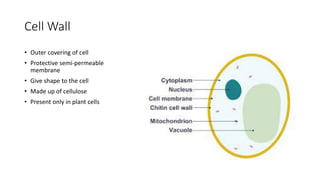
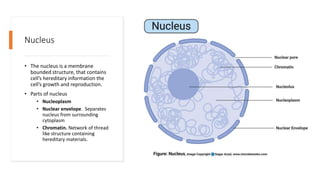
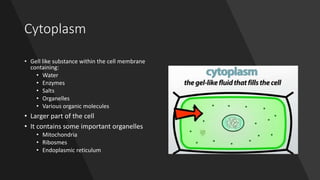
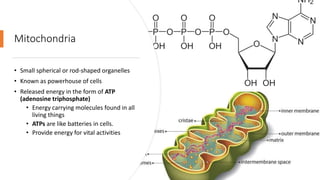
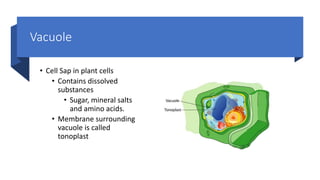
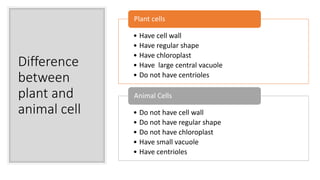
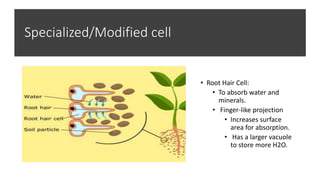
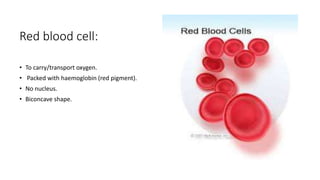
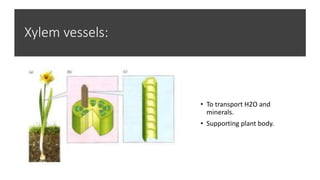
The document explains the structure and functions of plant and animal cells, highlighting key components such as the cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. It details the differences between plant and animal cells, including the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells and centrioles in animal cells. Additionally, it describes specialized cells, such as root hair cells and red blood cells, and their specific functions in their respective organisms.