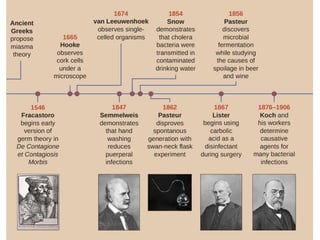
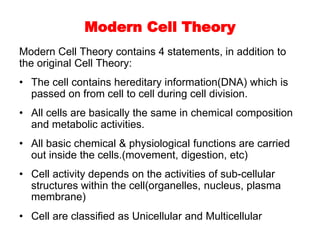
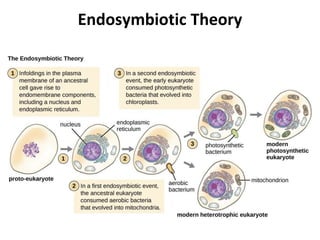
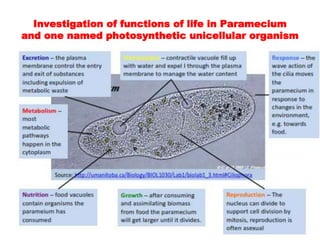
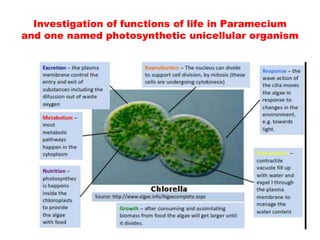
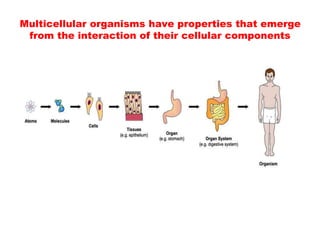
Cell theory, developed in the 19th century by scientists Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow, states that all living organisms are made of cells, which are the basic units of life that arise from preexisting cells. Modern cell theory extends this by including that cells carry hereditary information, are chemically similar, and perform essential life functions within cells. Additionally, the endosymbiotic theory posits that eukaryotic organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from ancestral prokaryotic organisms through a symbiotic relationship.