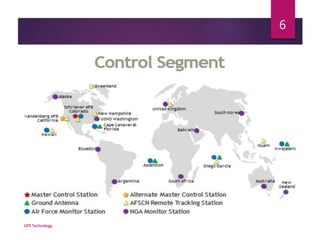
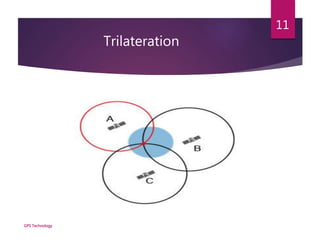
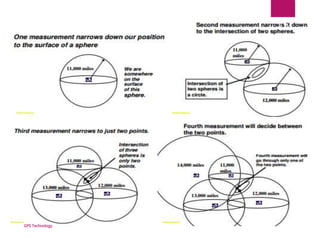
This document provides an overview of GPS technology. It discusses that GPS uses 3 segments - space, control, and user segments. The space segment consists of 32 satellites that orbit 12,000 miles above Earth and transmit timing signals. The control segment monitors the satellites and maintains the constellation. The user segment includes any GPS receiver that can receive and process signals from the satellites to determine location. It then explains how GPS uses trilateration of distances calculated from signal transmission times to pinpoint a user's position.