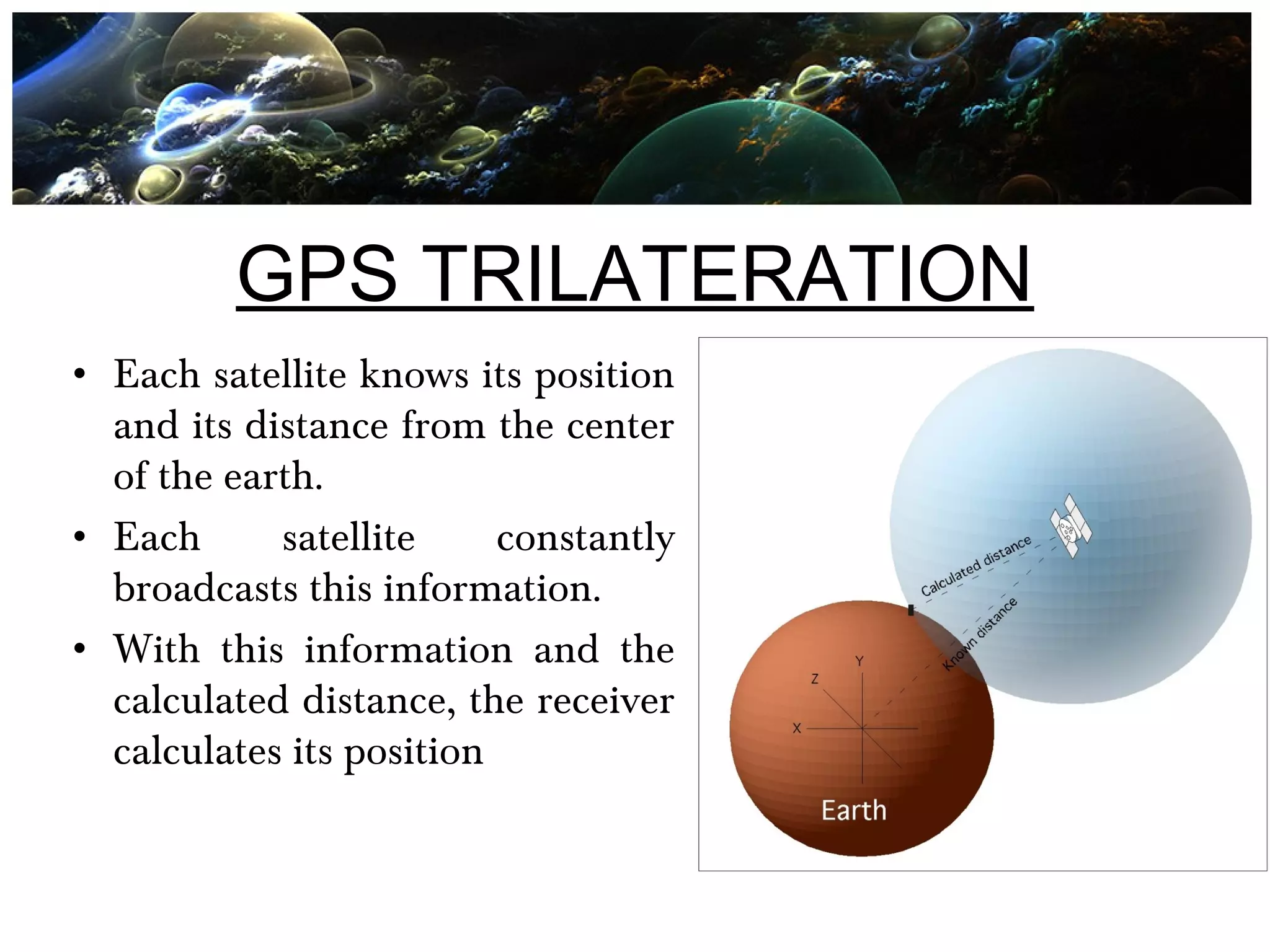
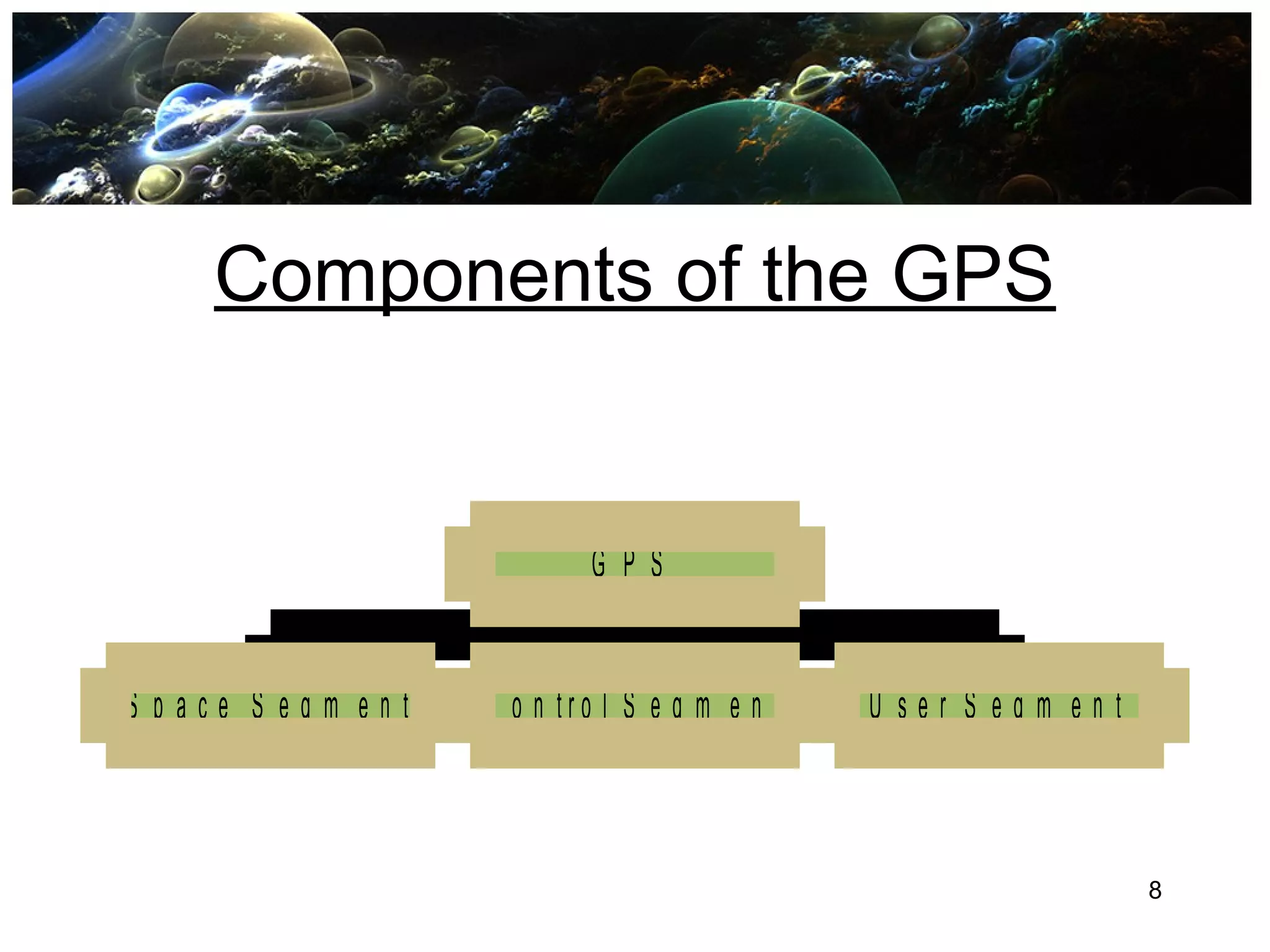
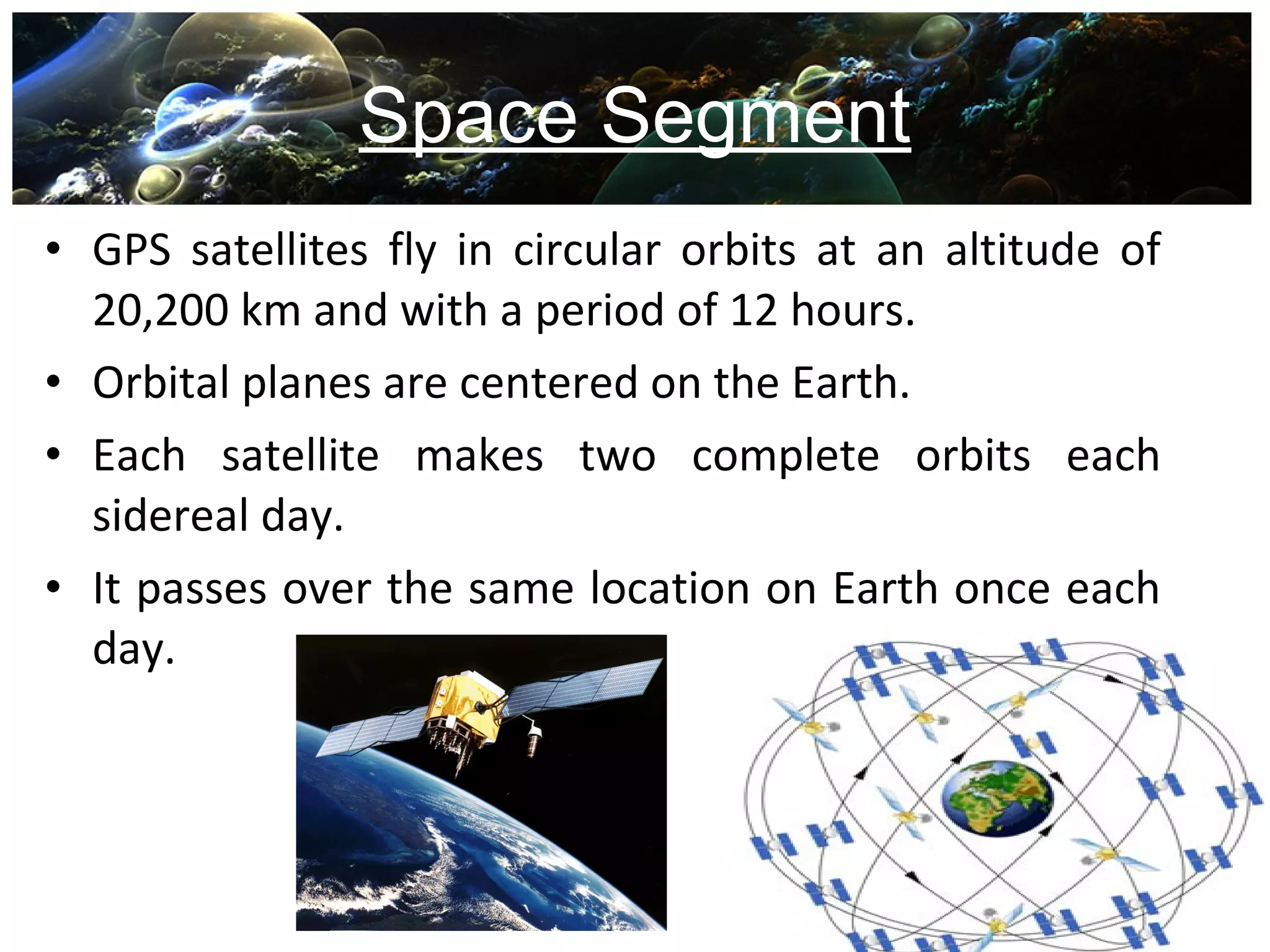
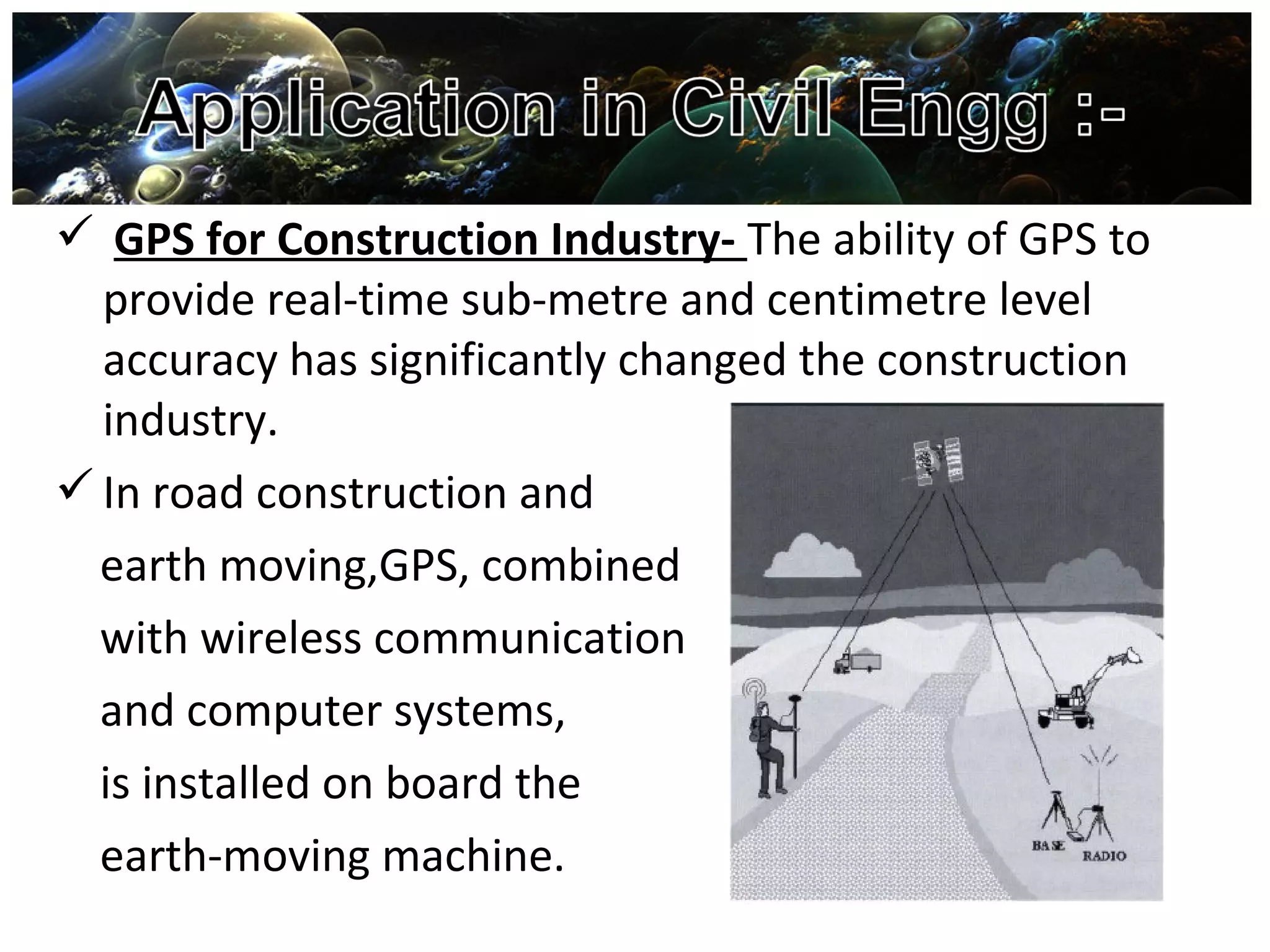
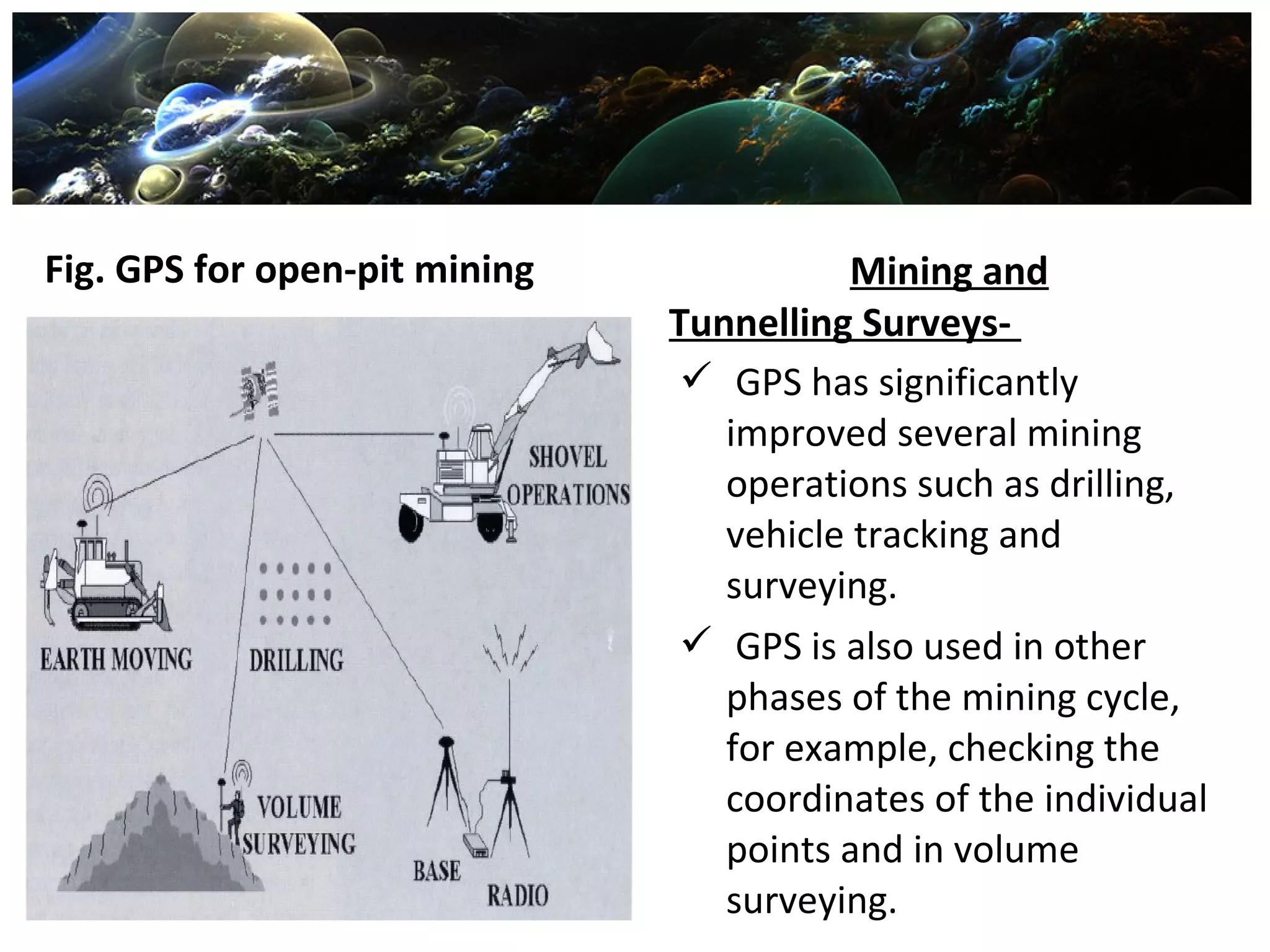
Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system consisting of a network of 24 satellites placed into orbit by the U.S. Department of Defense. GPS allows land, sea, and airborne users to determine their exact location, velocity, and time 24 hours a day, in all weather conditions, anywhere in the world. The GPS uses trilateration to calculate a user's position by comparing times from at least three satellites, and it provides accuracy to within a few meters. GPS has many applications including navigation, construction, mining, military uses, and everyday uses on phones and in cars.