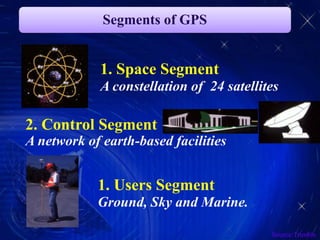
The document discusses the Global Positioning System (GPS). It provides an overview of GPS including that it is a satellite-based navigation system consisting of 24 satellites maintained by the US Department of Defense. GPS is used to determine location, time, and speed. The document describes the key components and principles of how GPS works including its space, control, and user segments. It involves calculating distance via signal travel time from 4 or more satellites to determine a position.