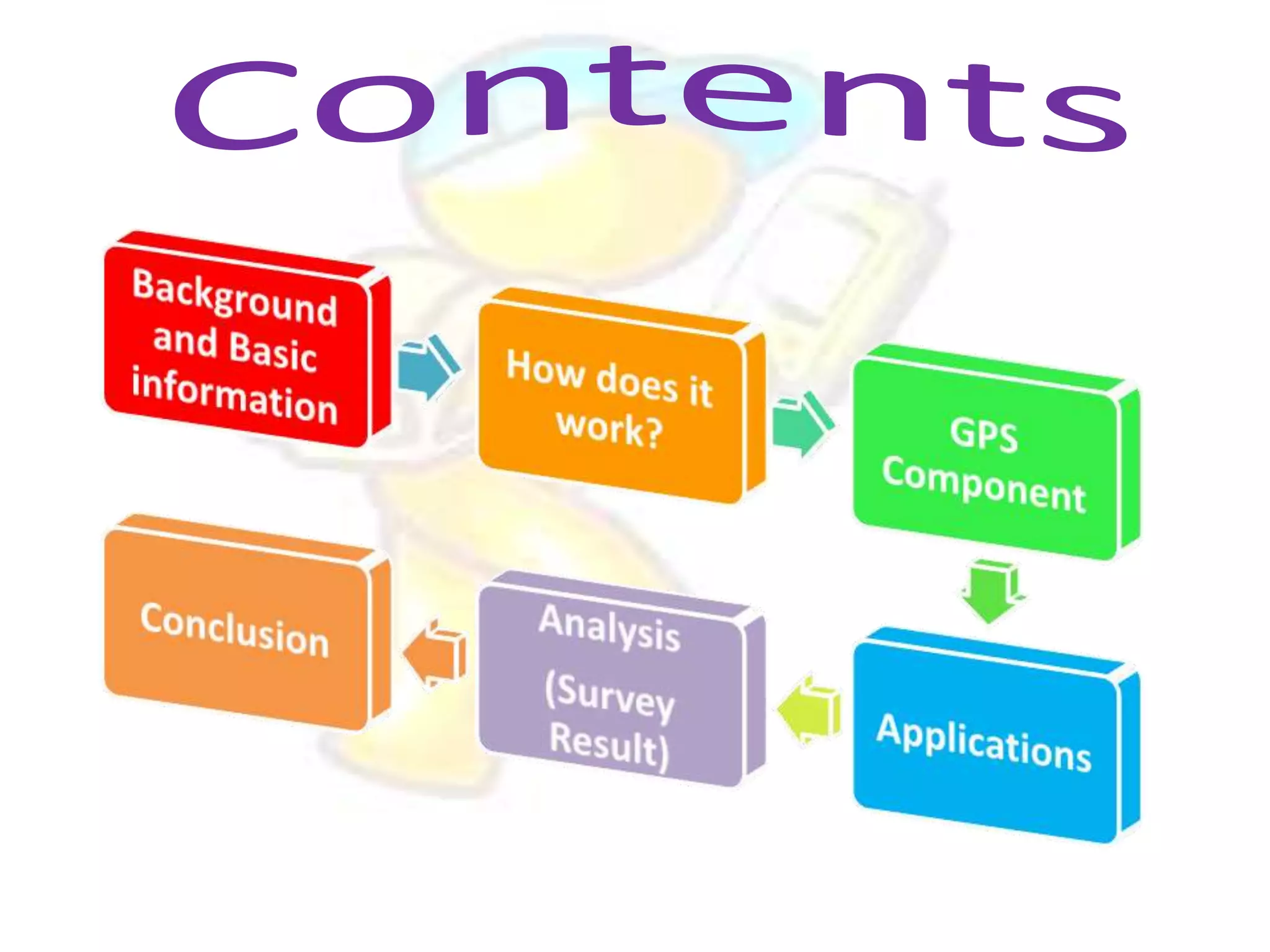
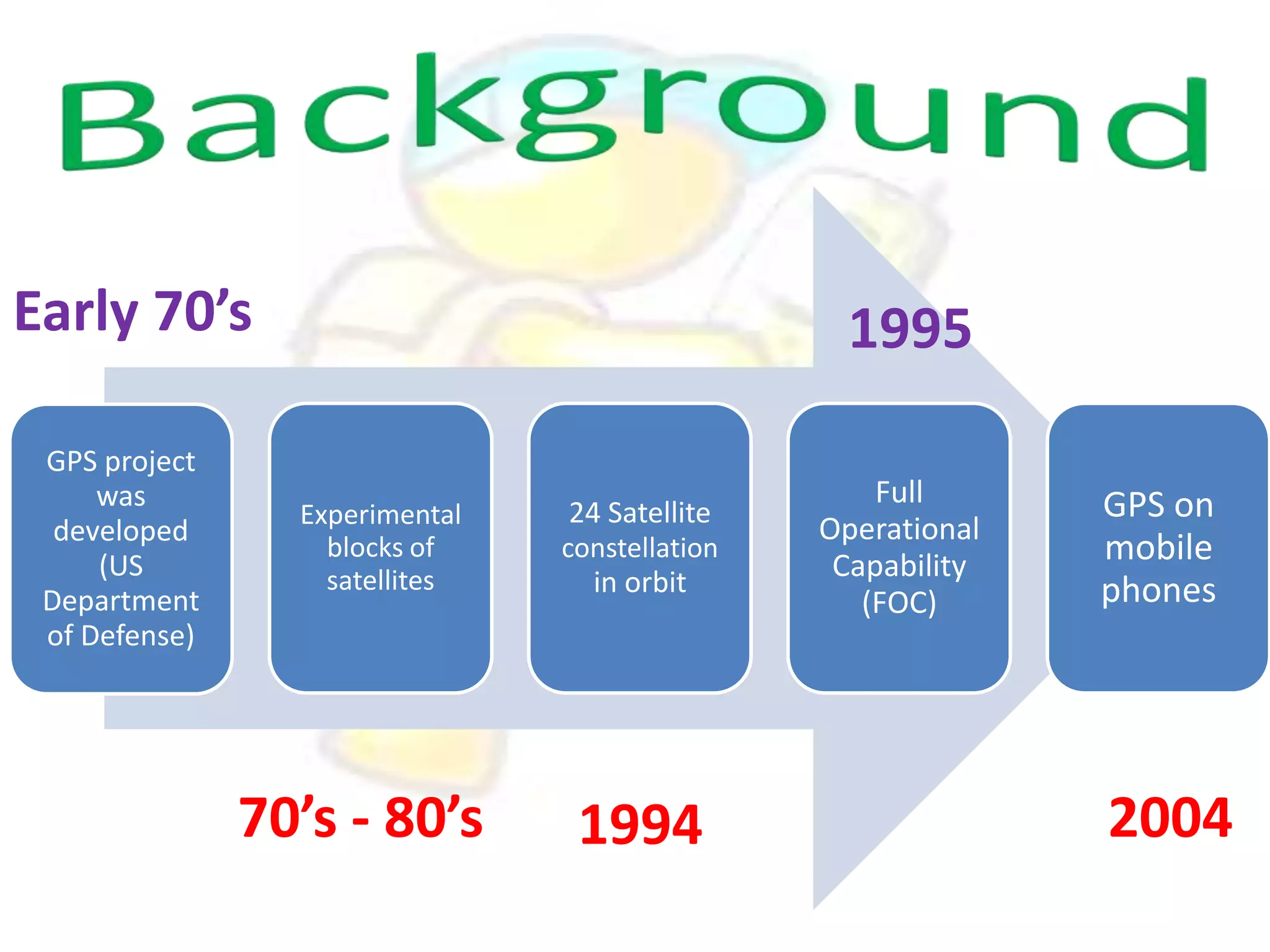
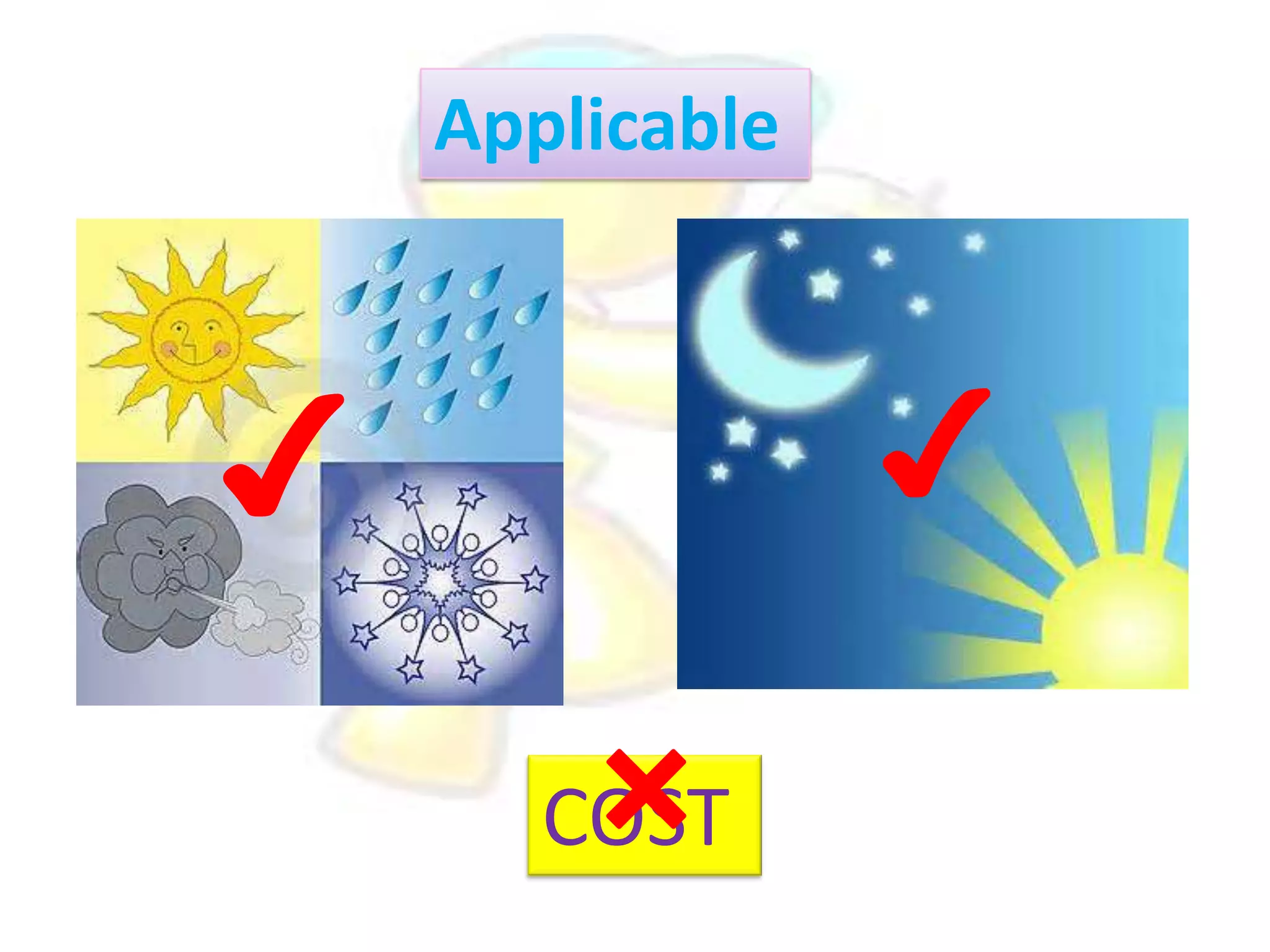
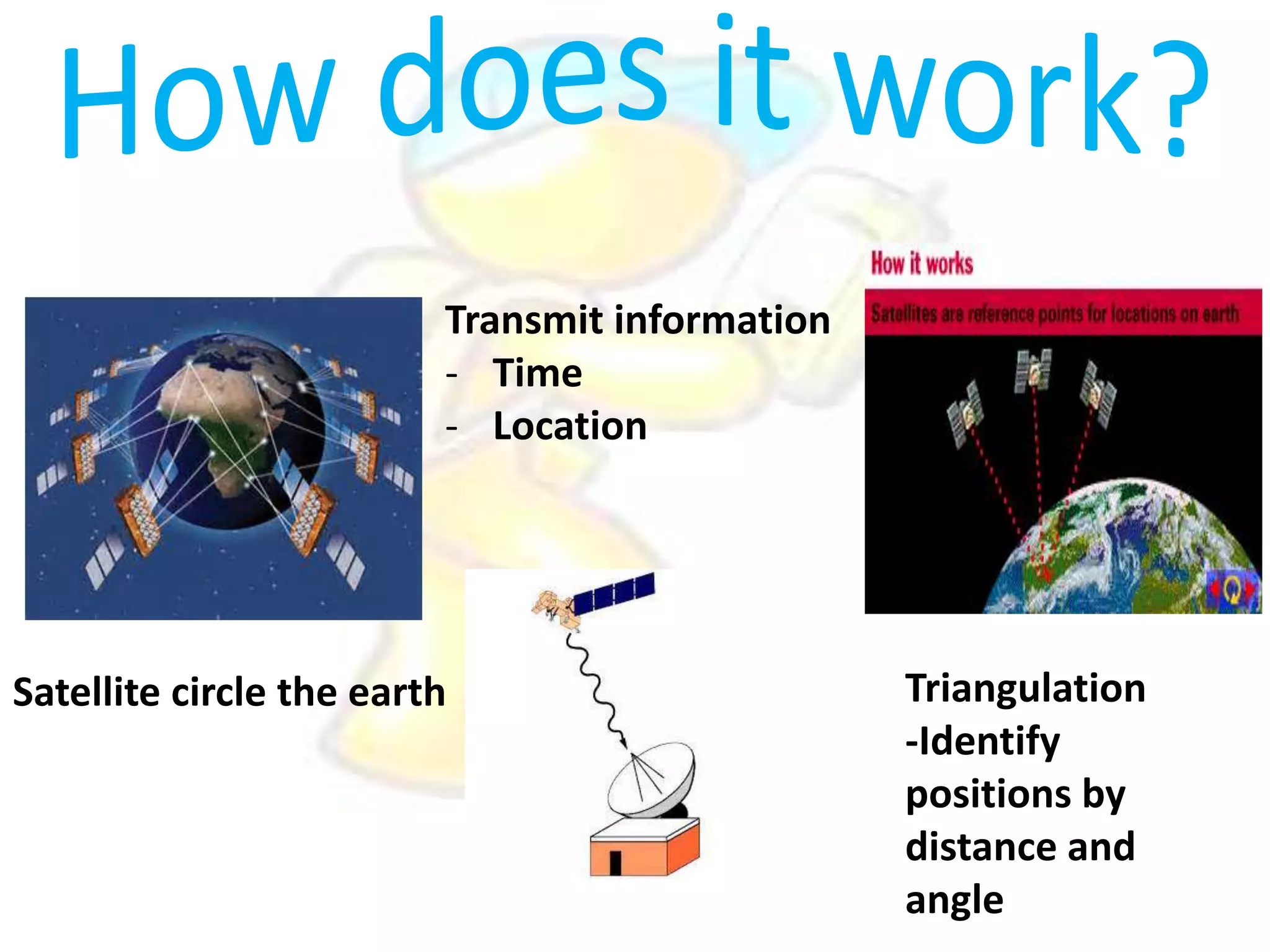
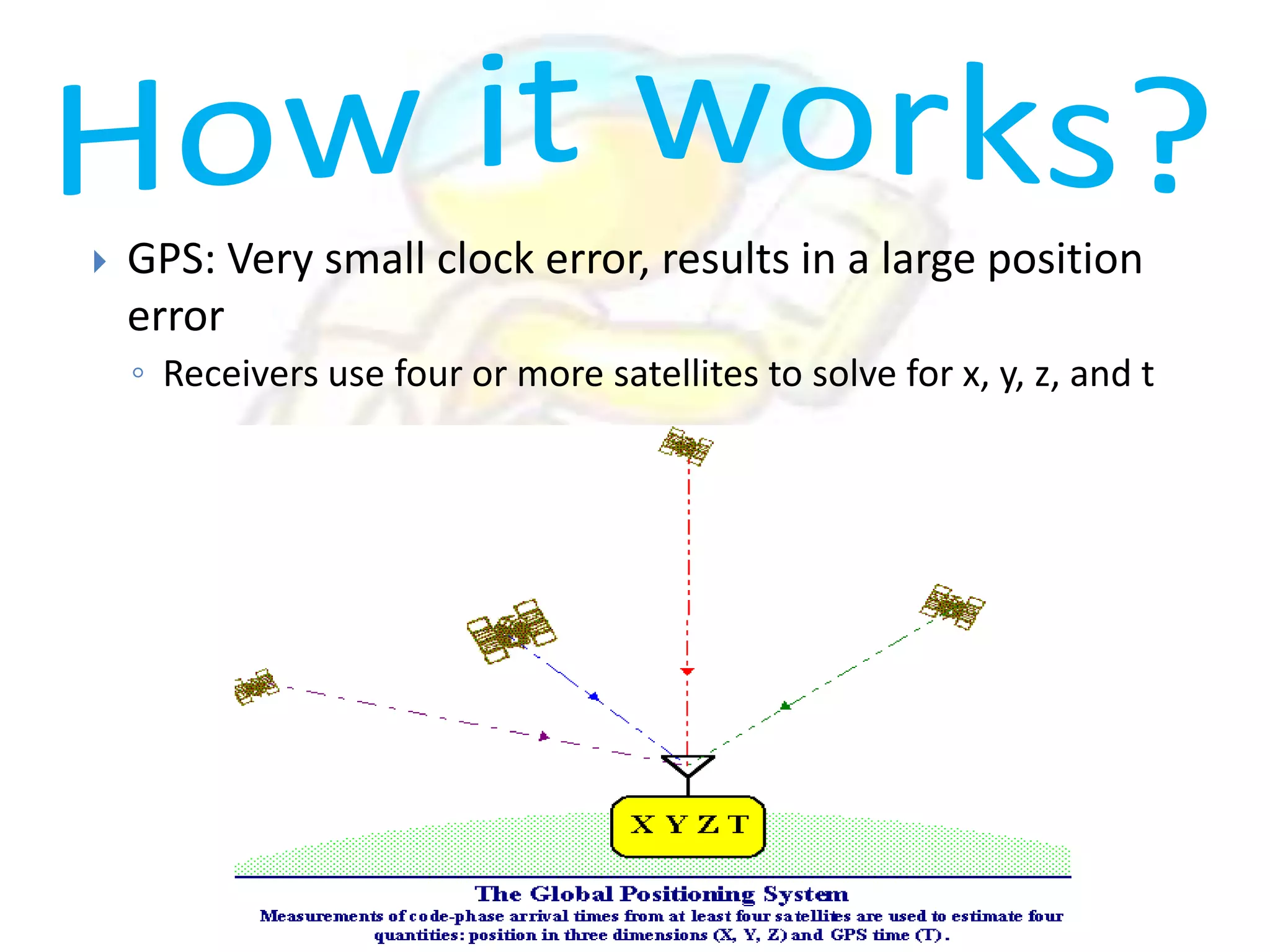
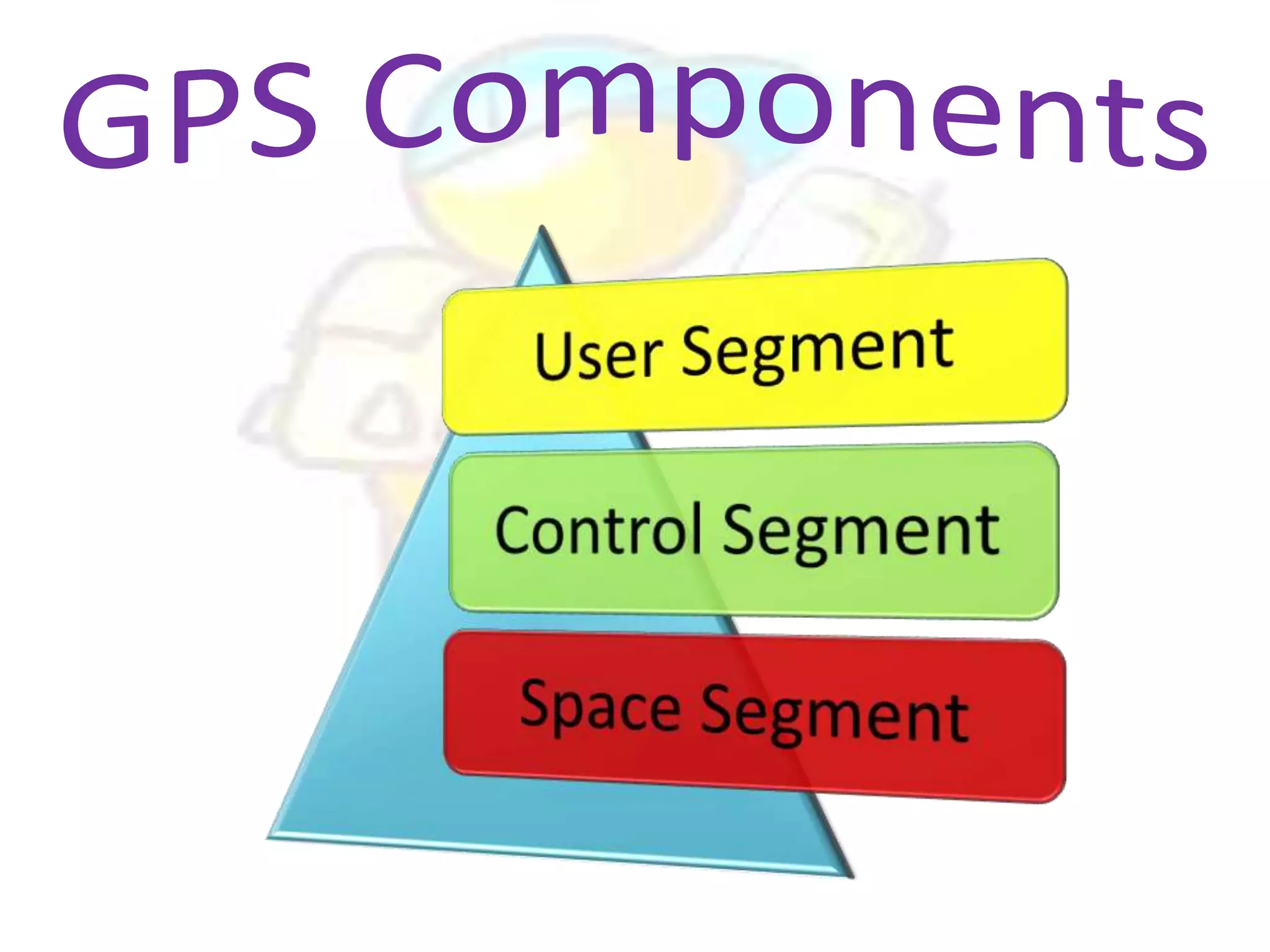
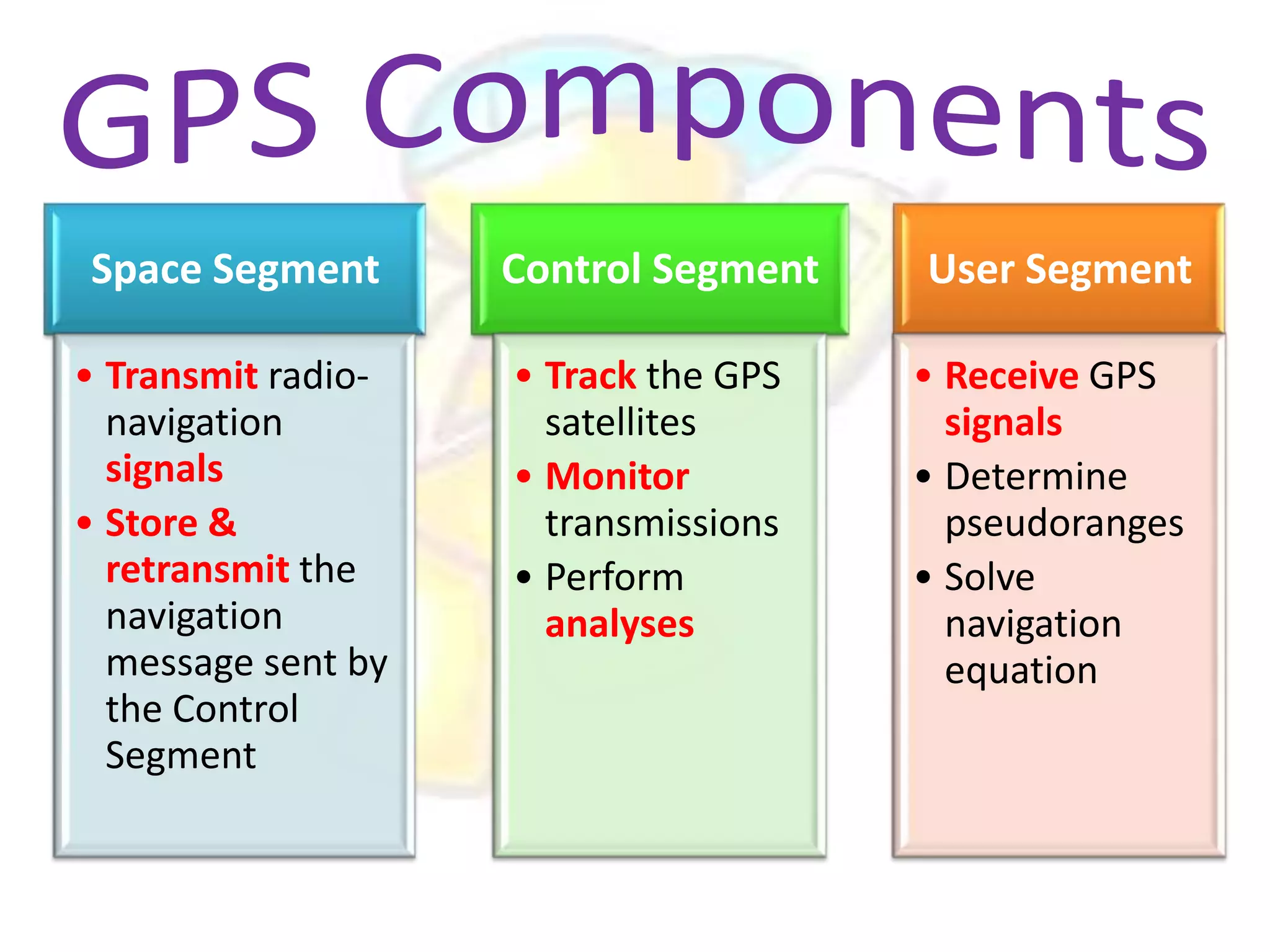
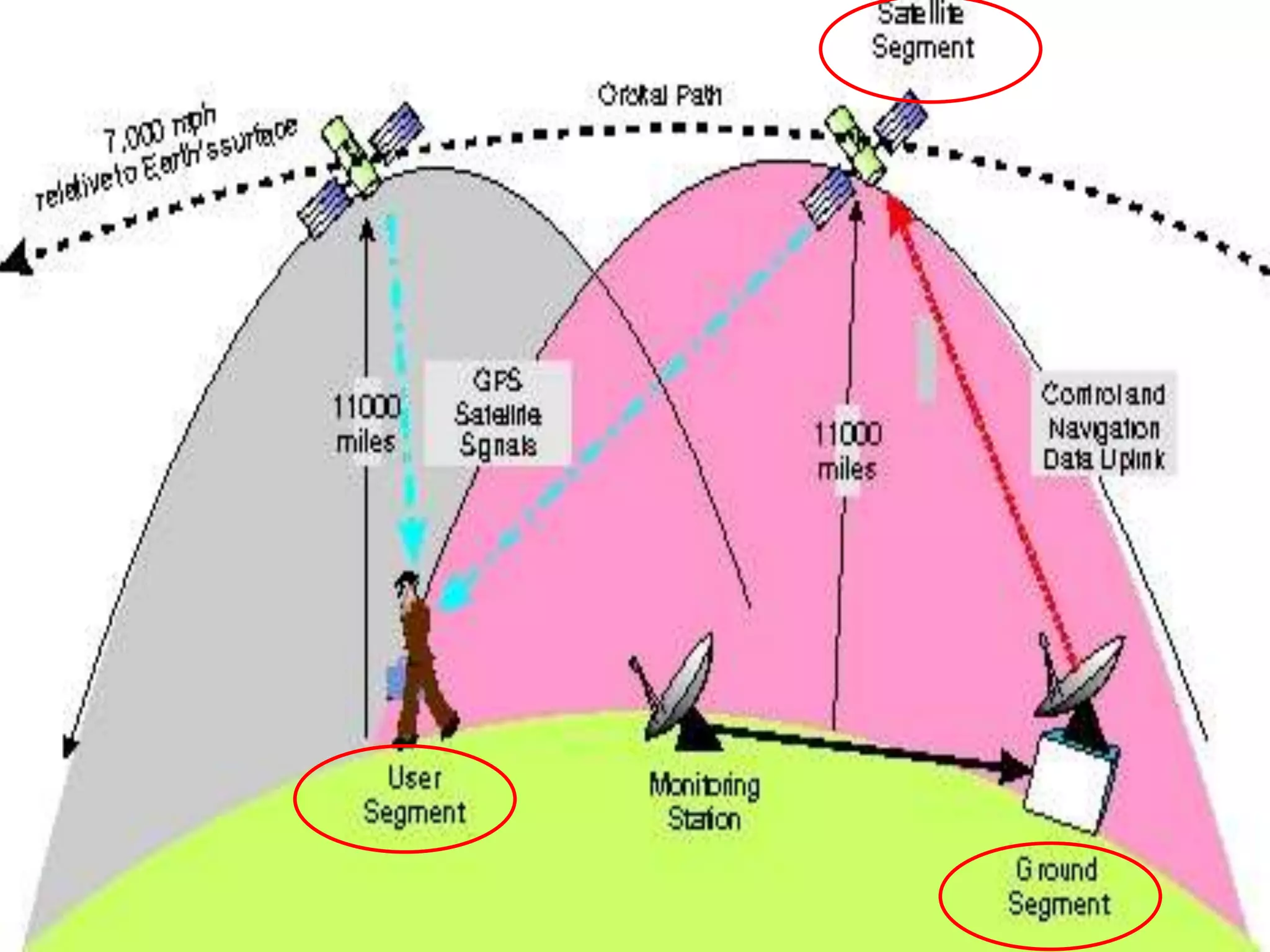
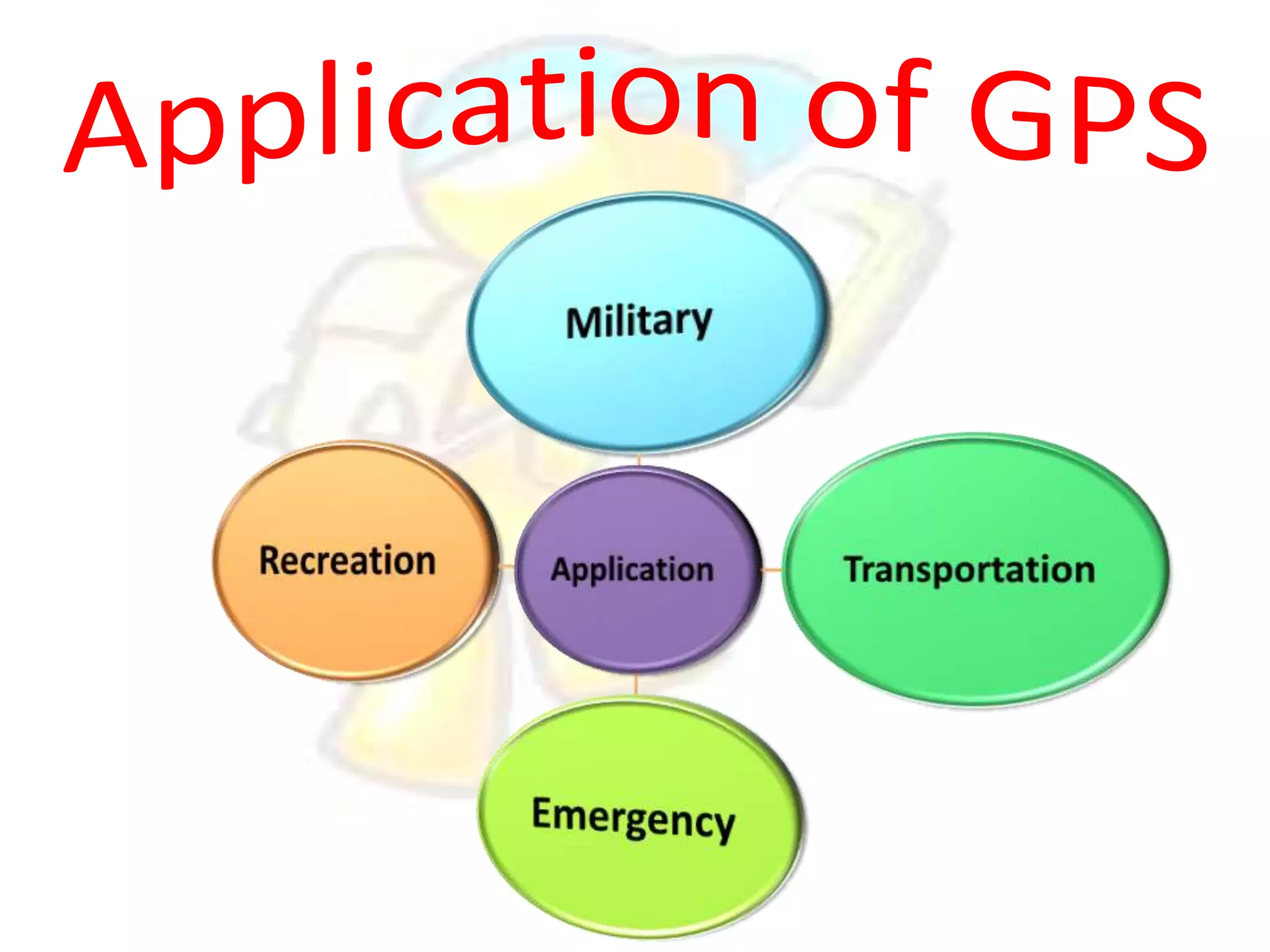
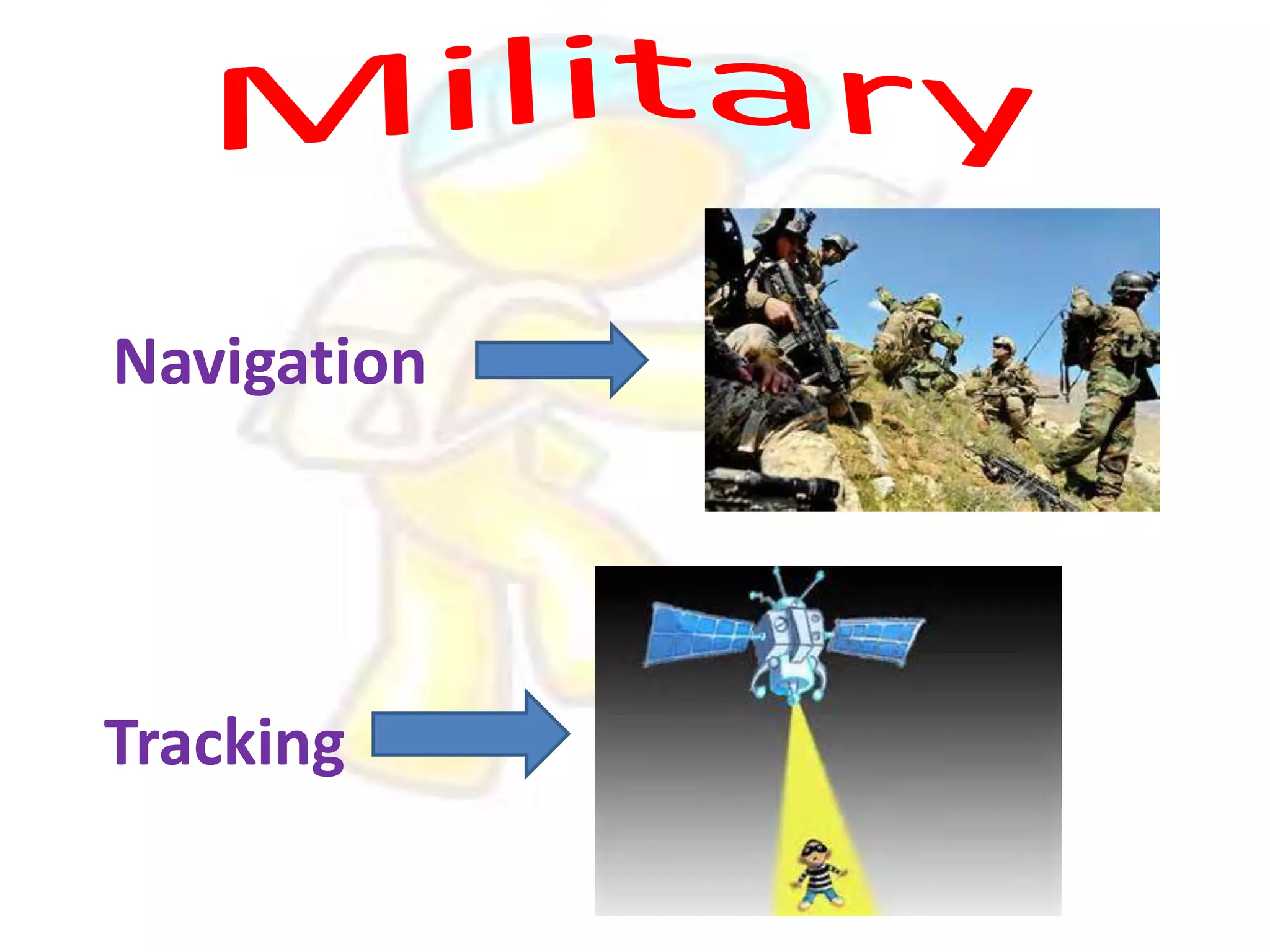
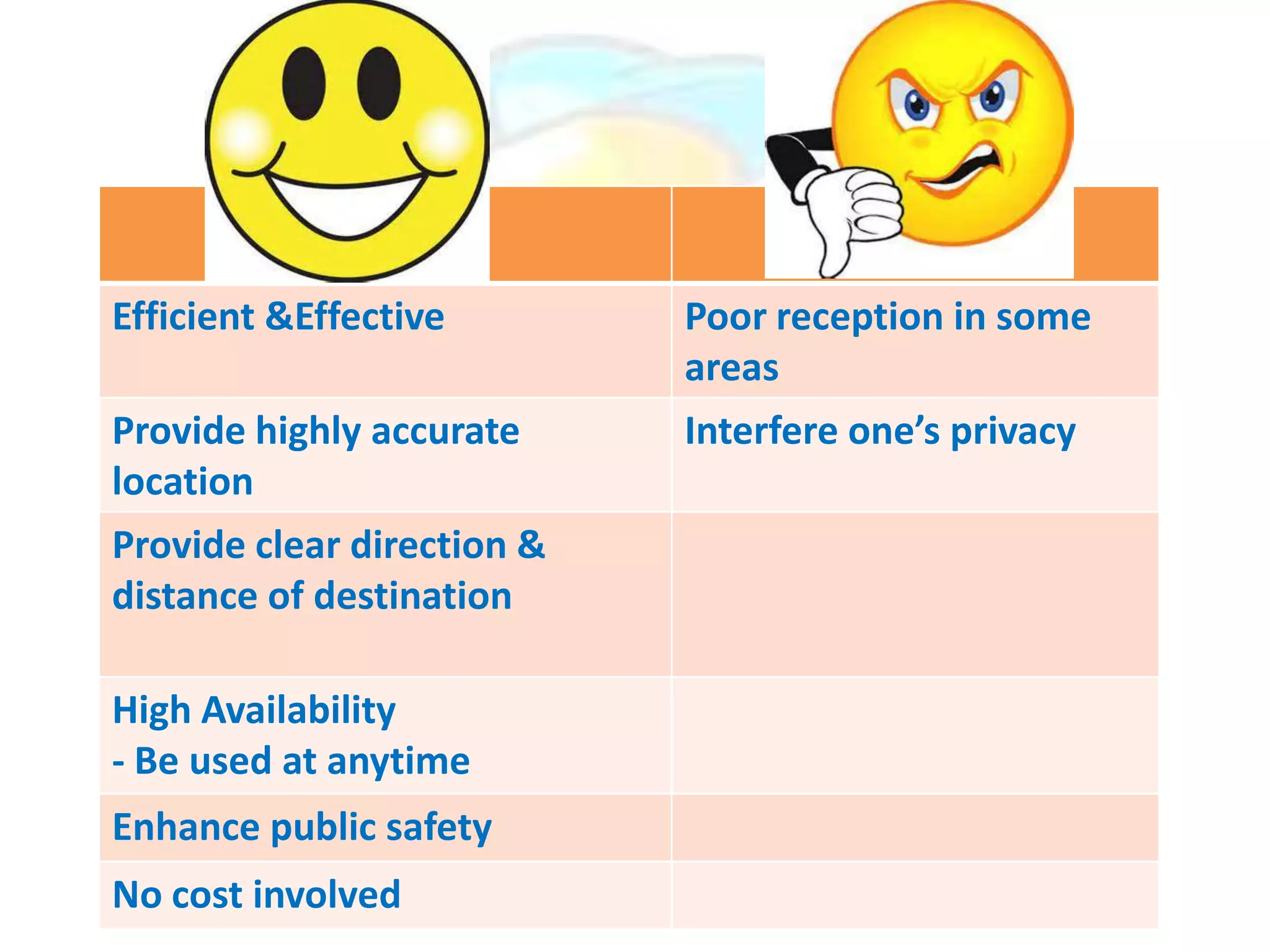
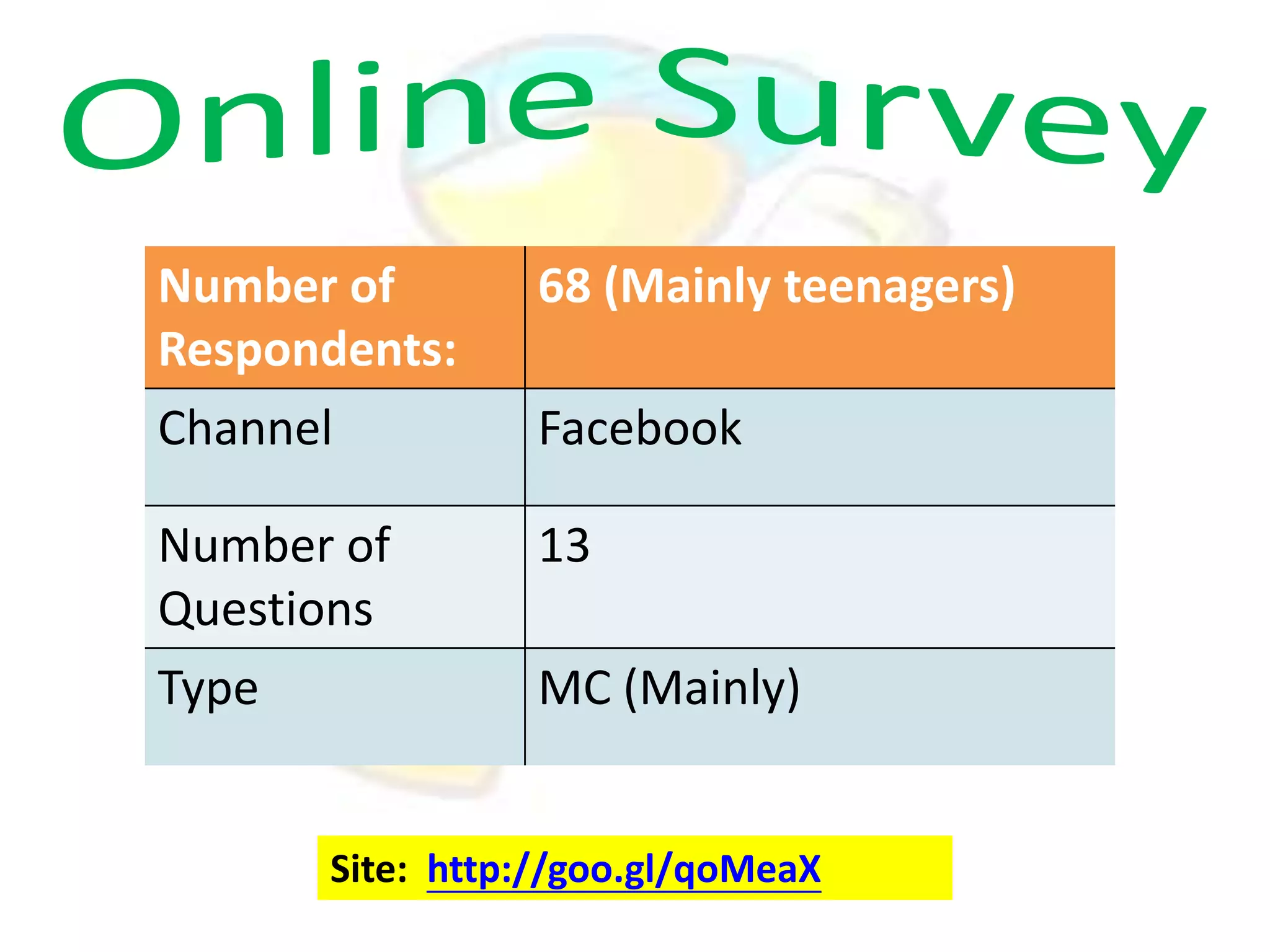
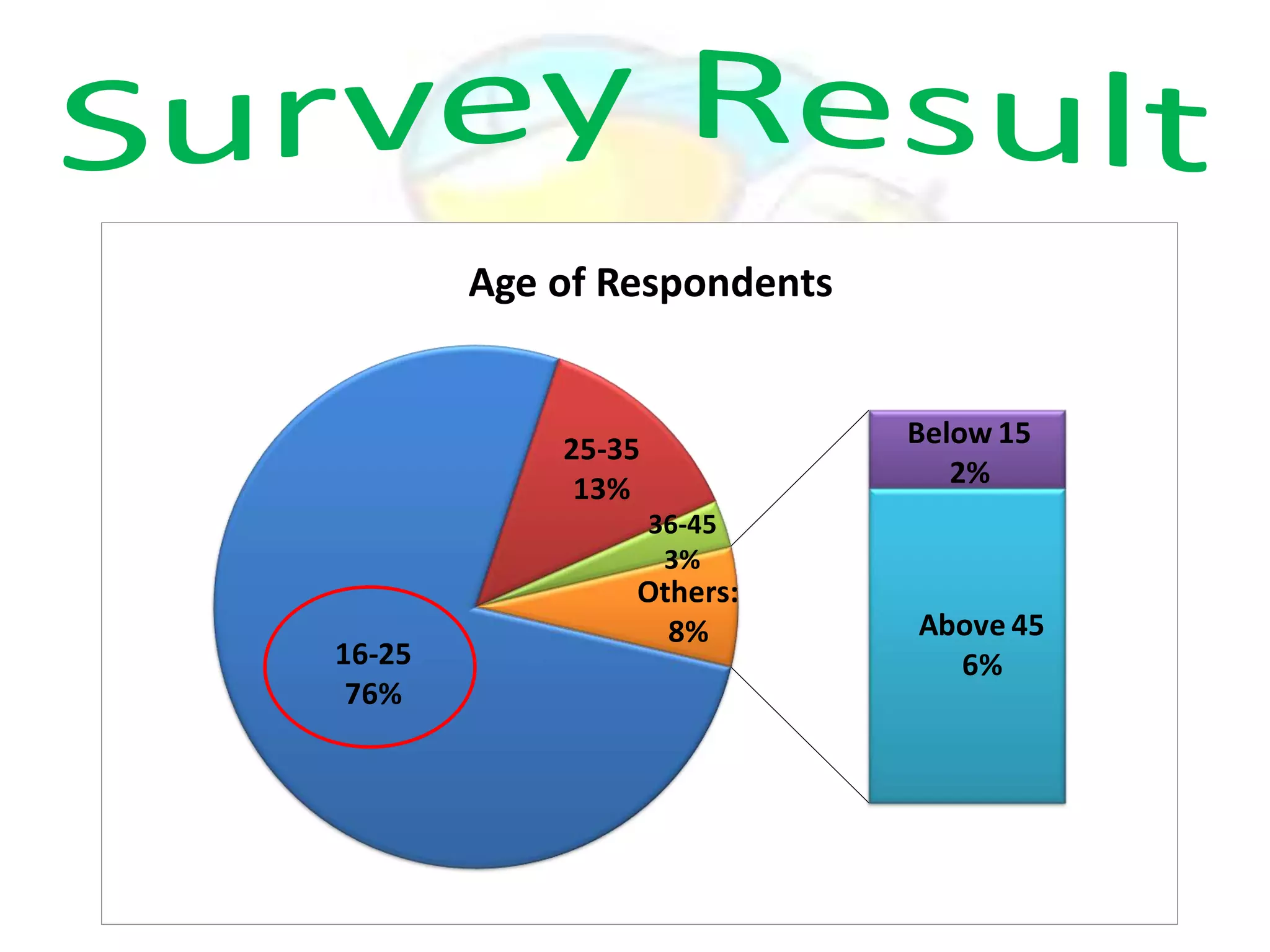
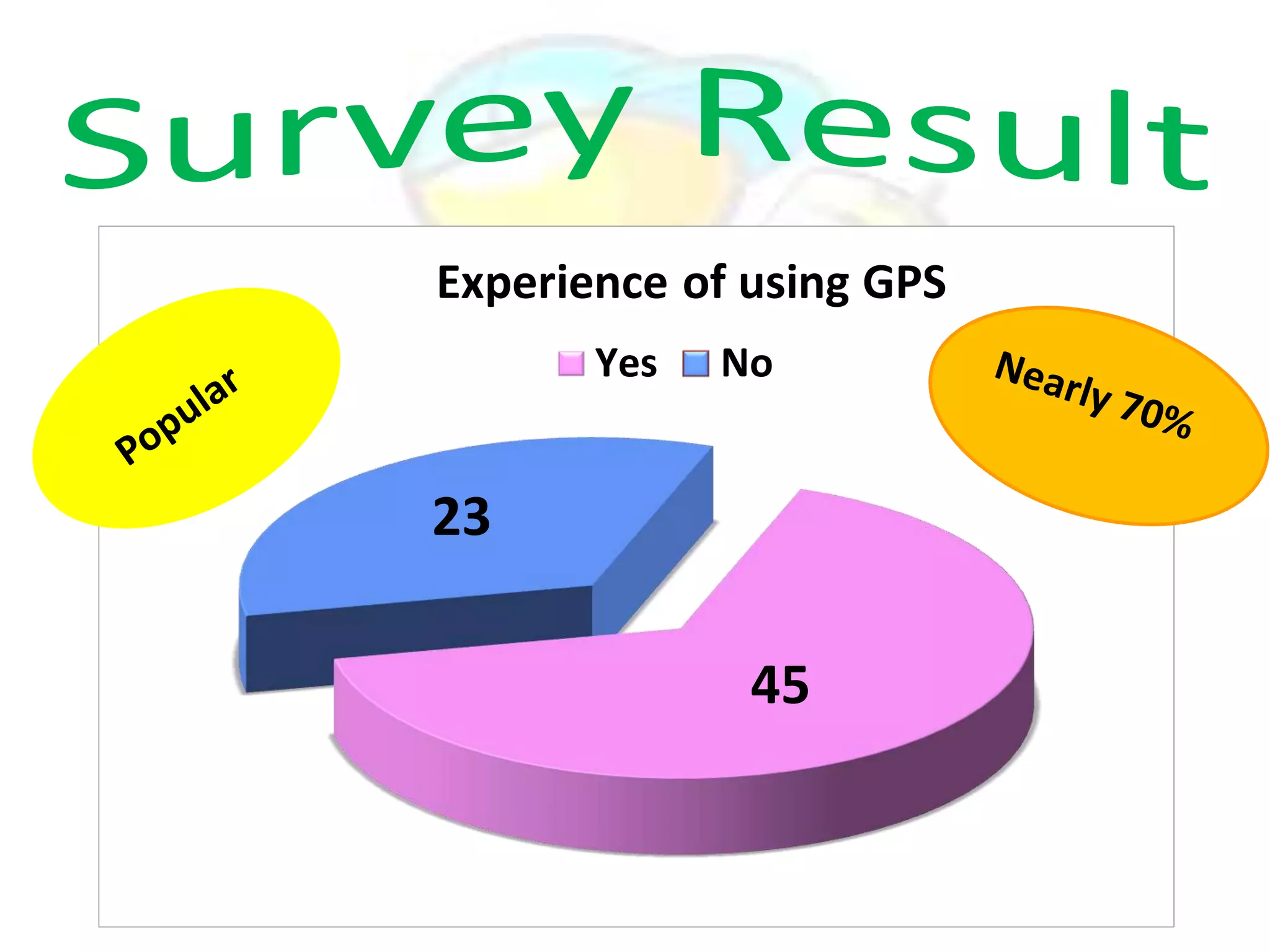
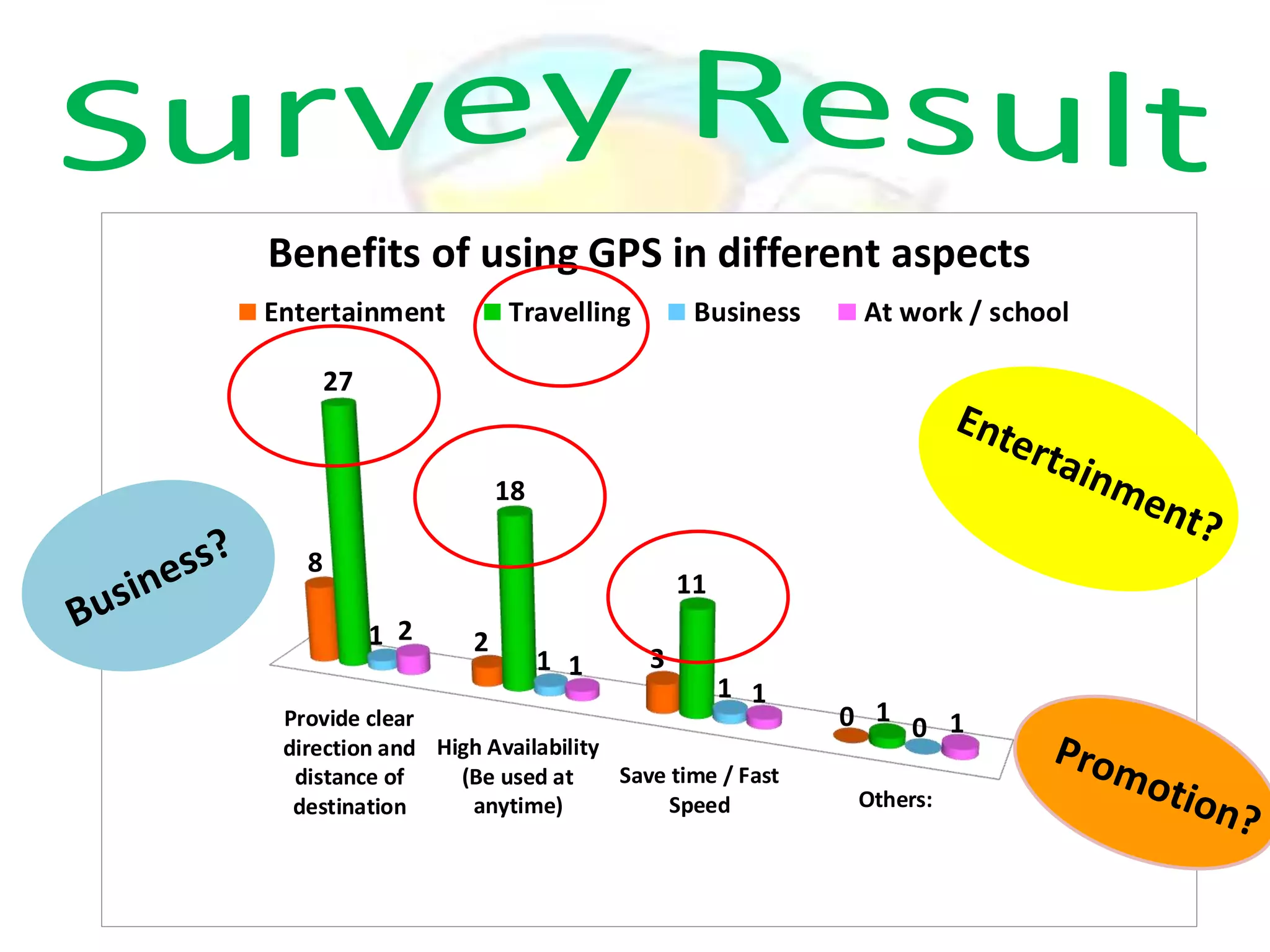
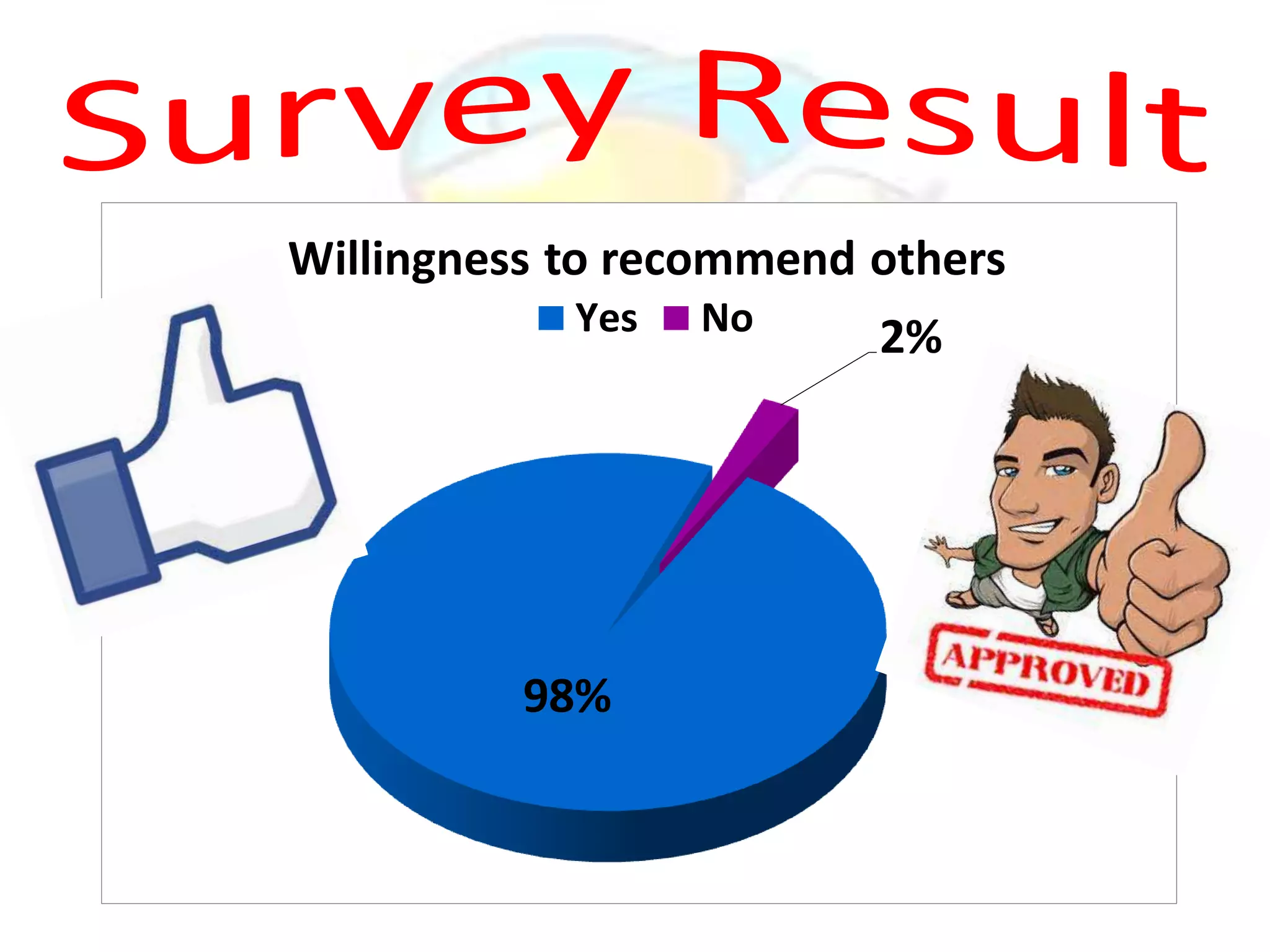
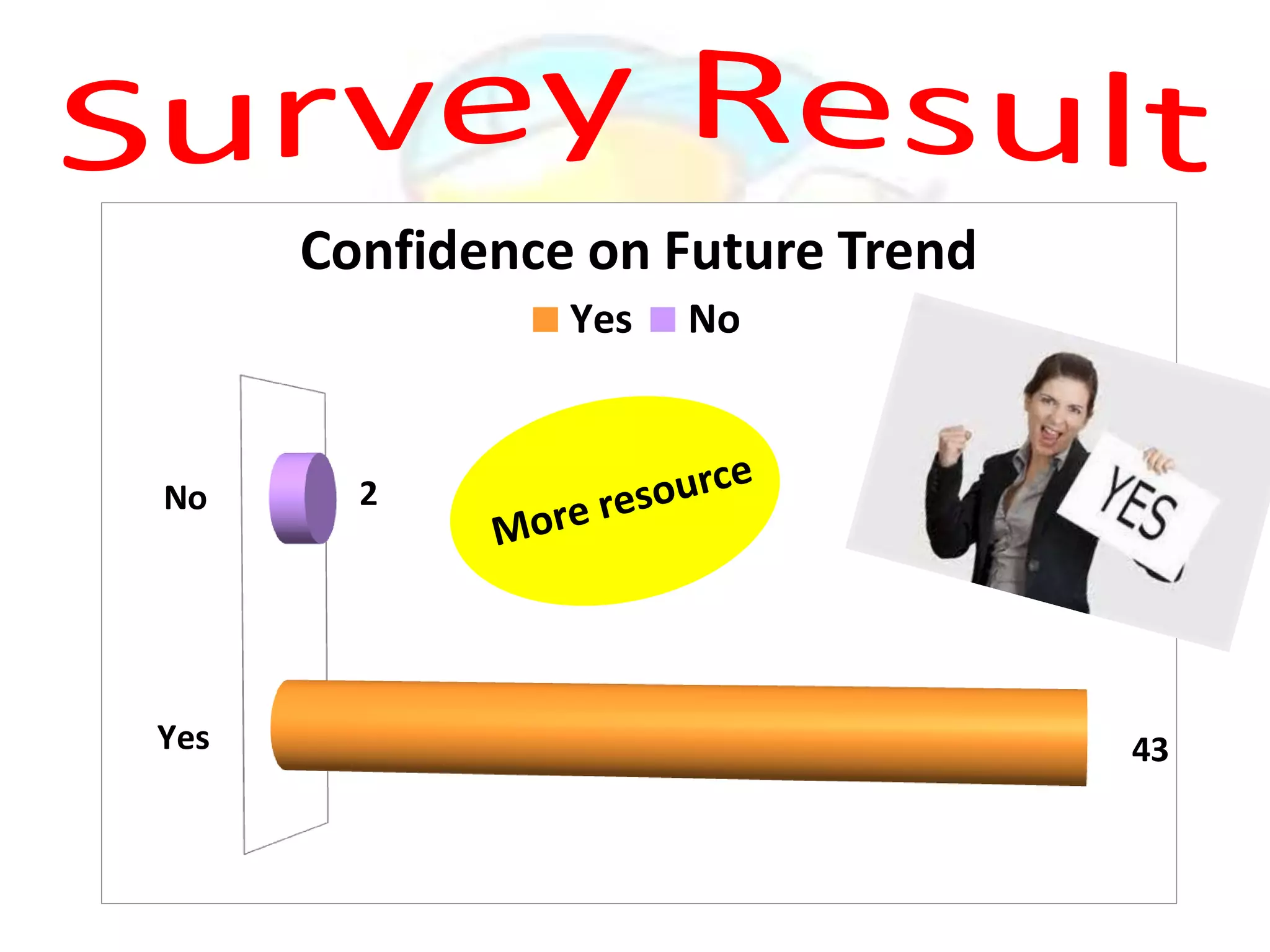
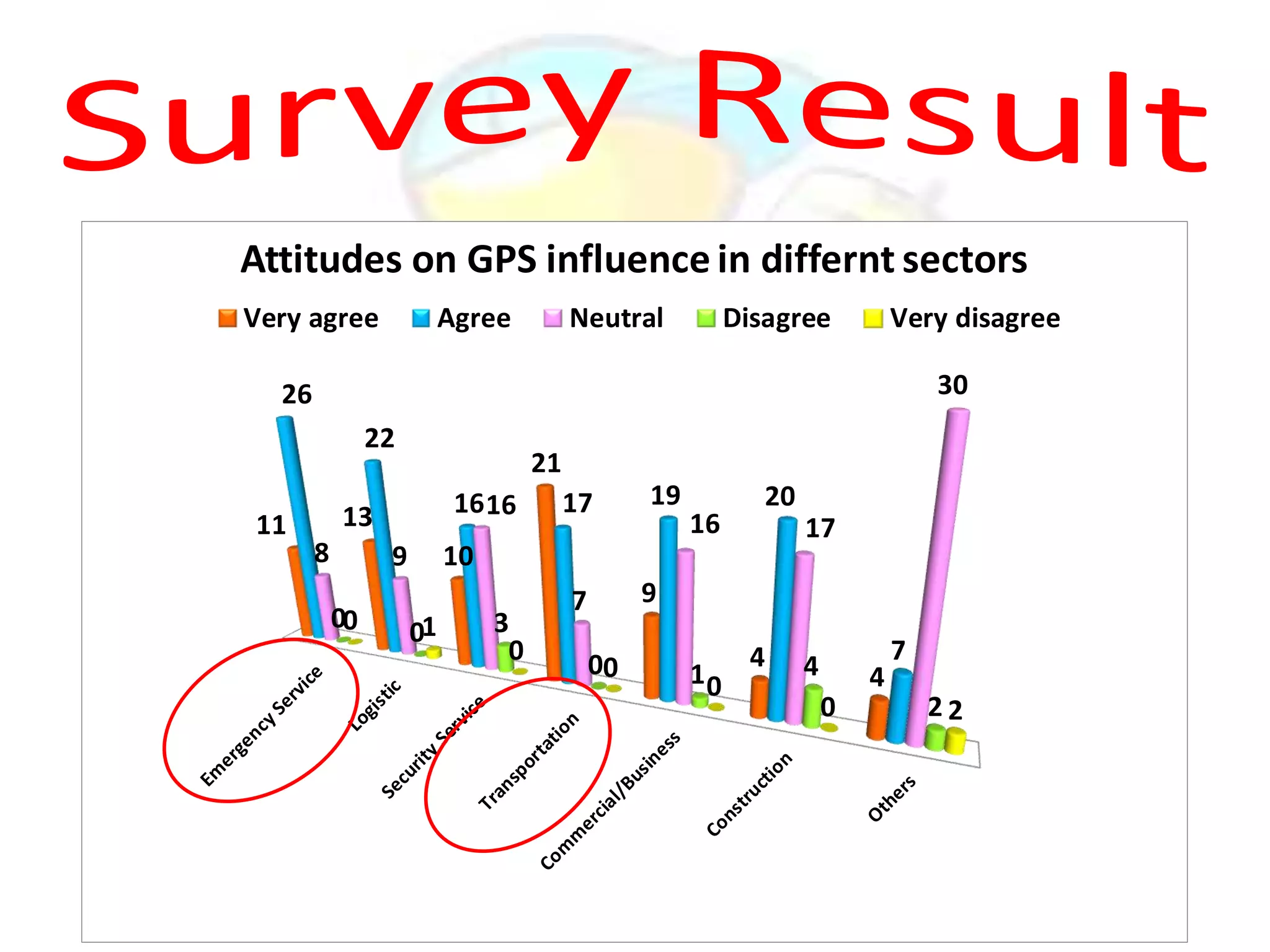
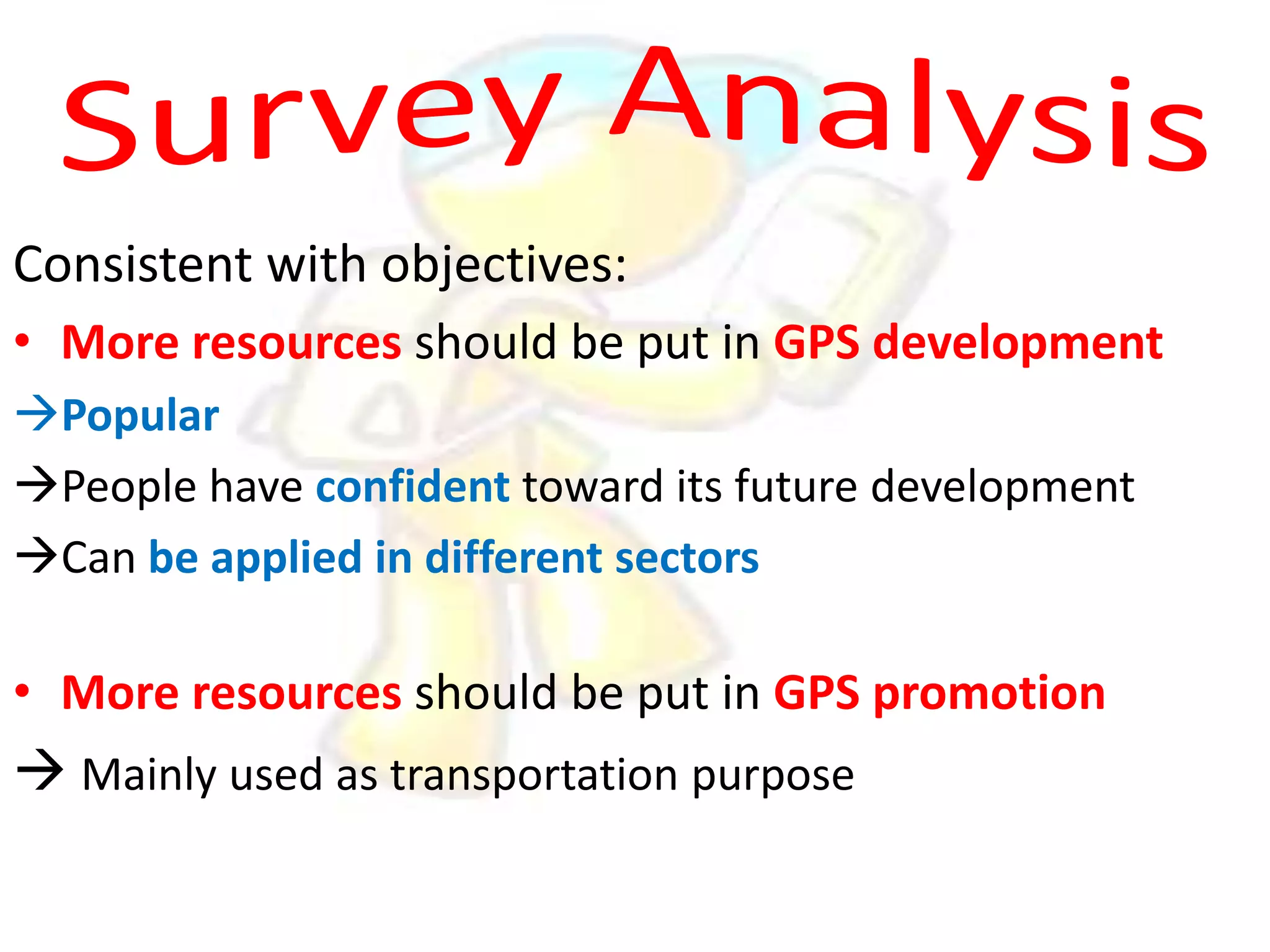
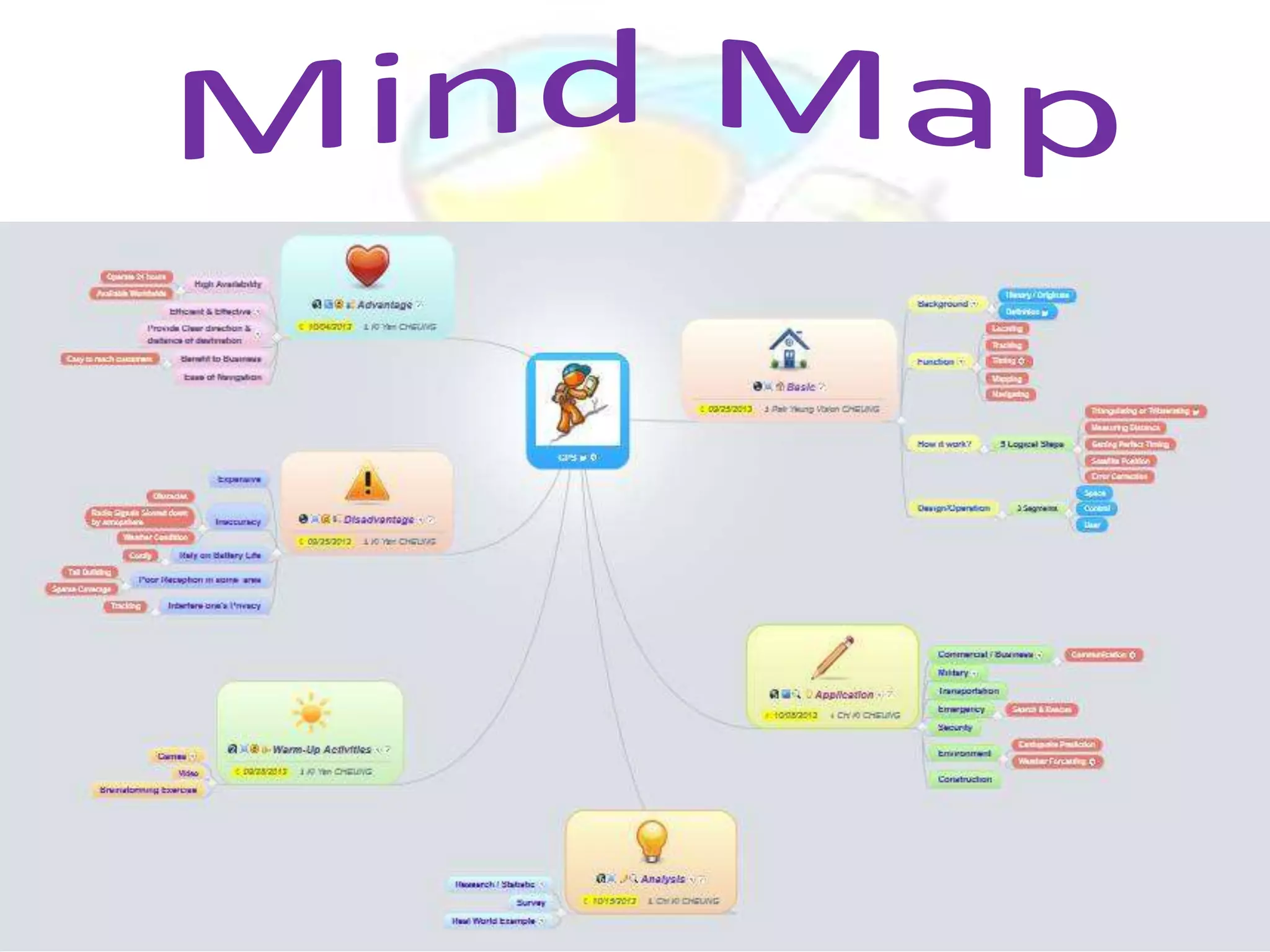
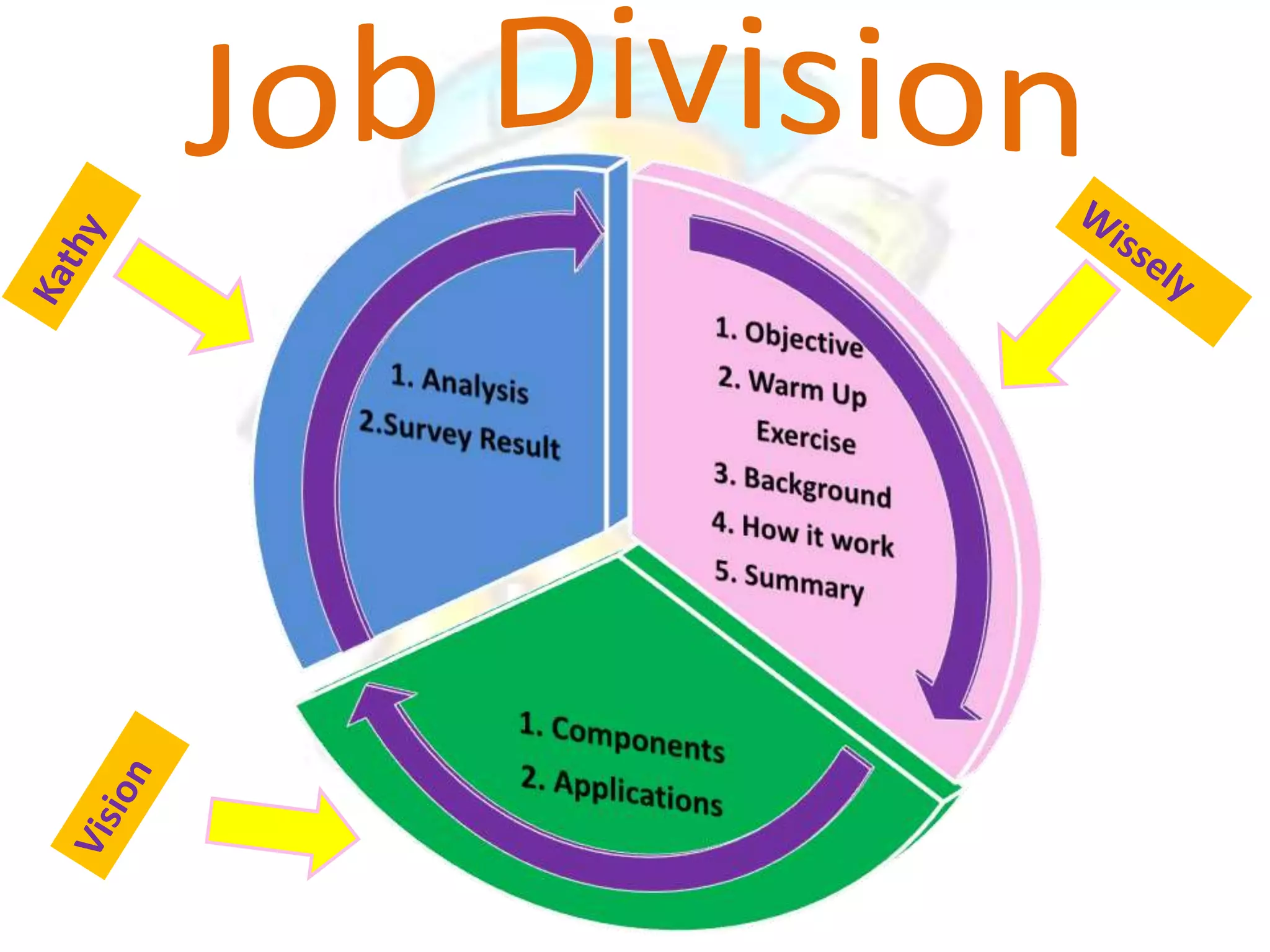
GPS has evolved since its development in the 1970s by the US Department of Defense. It was originally intended for military use but has grown to support many civilian applications. GPS uses a constellation of satellites that transmit timing and location data to receivers, which use triangulation to calculate the user's precise position. It has applications in navigation, tracking, emergency services, and more. A survey found that while GPS is commonly used for transportation, respondents felt it could benefit other sectors as well and its future trends are promising. However, some have privacy concerns about its growing use.