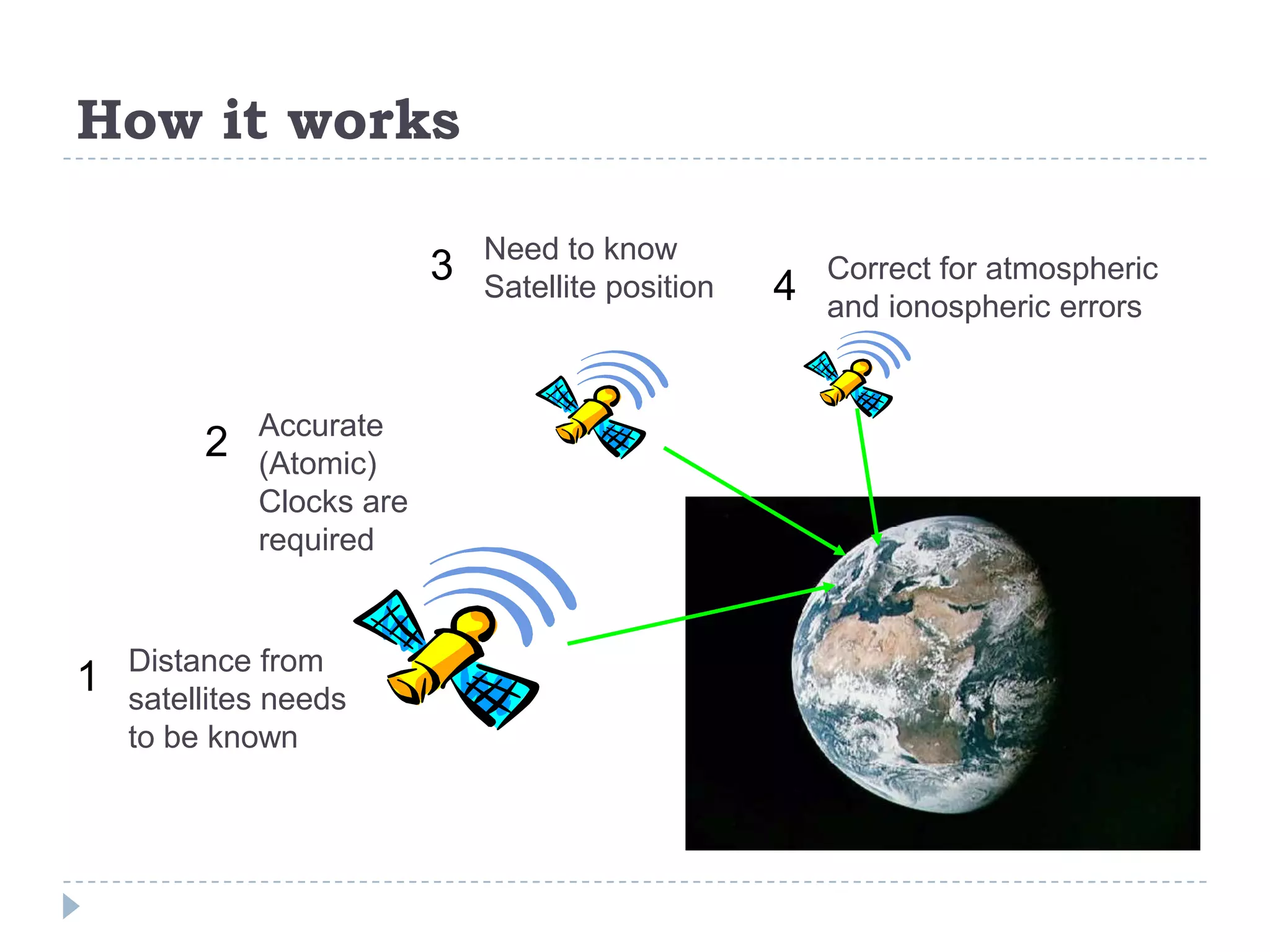
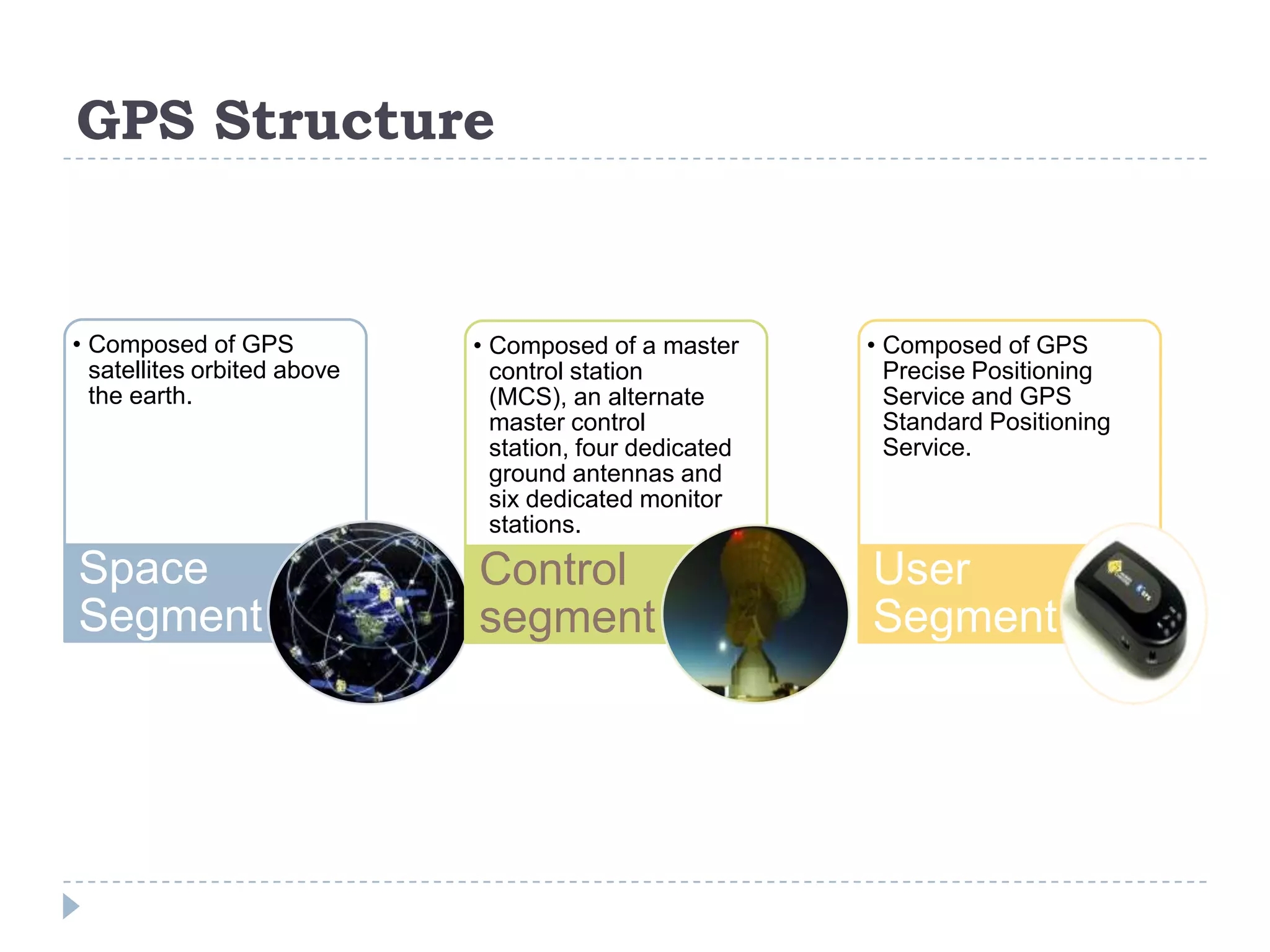
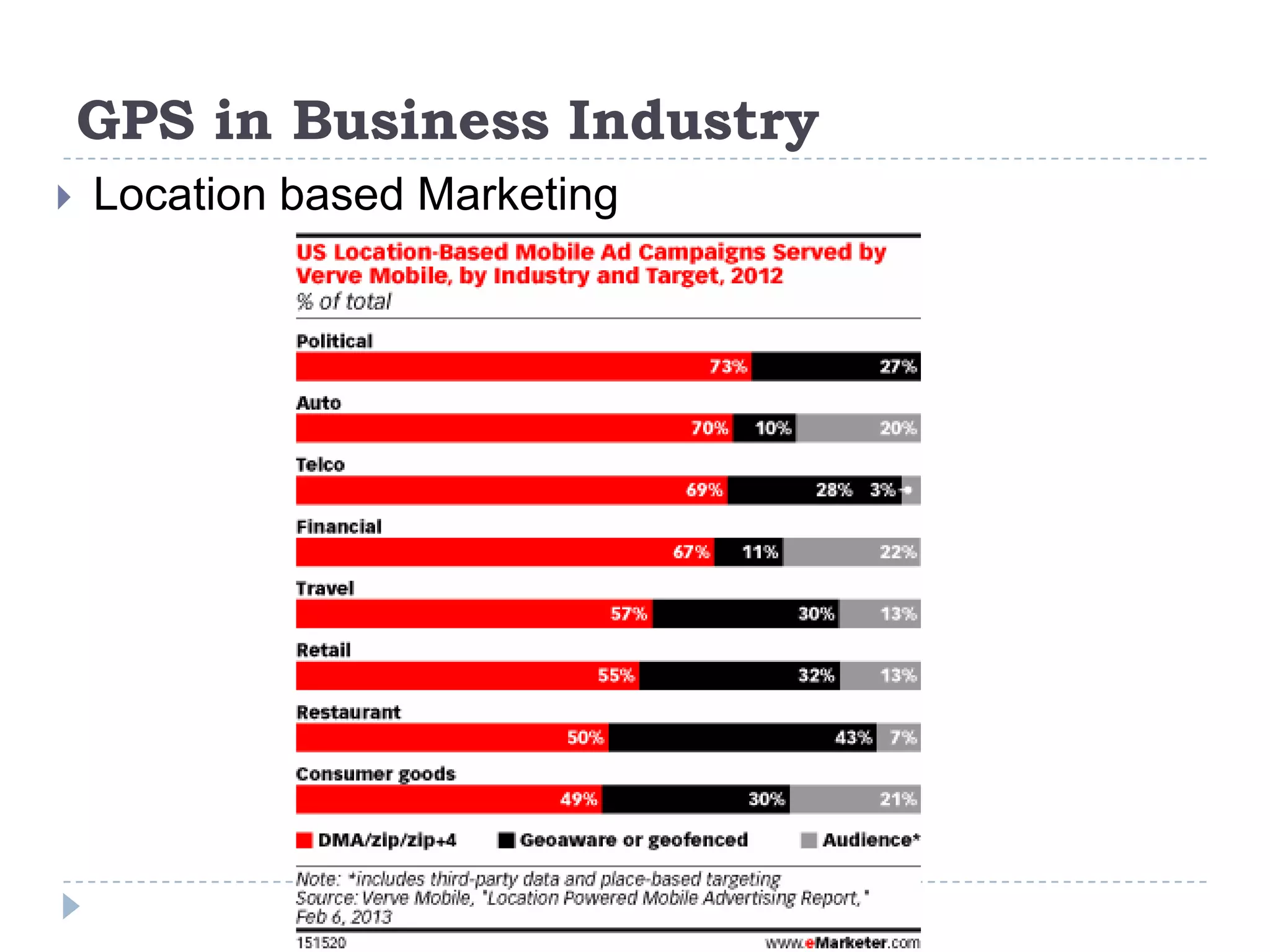
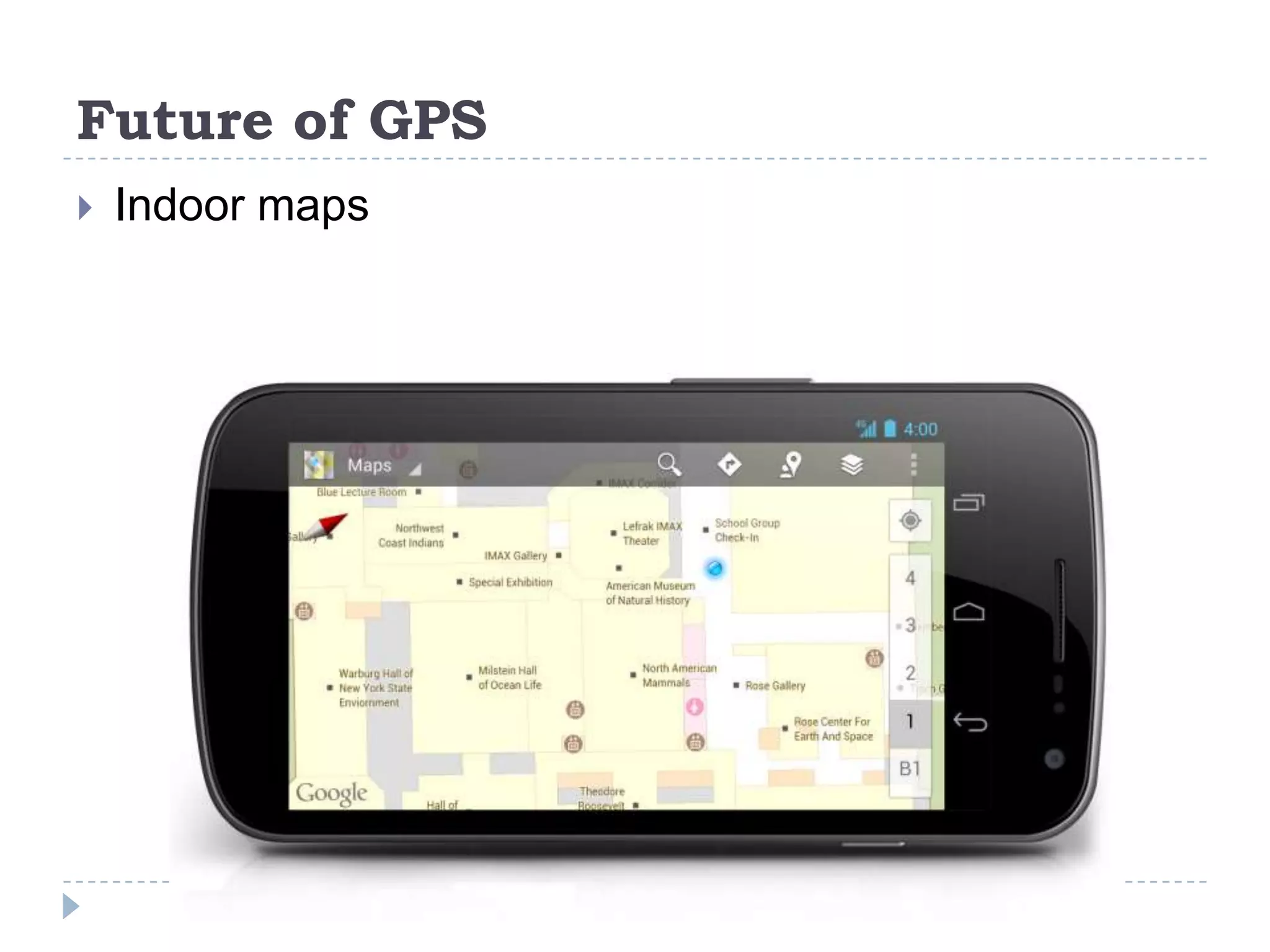
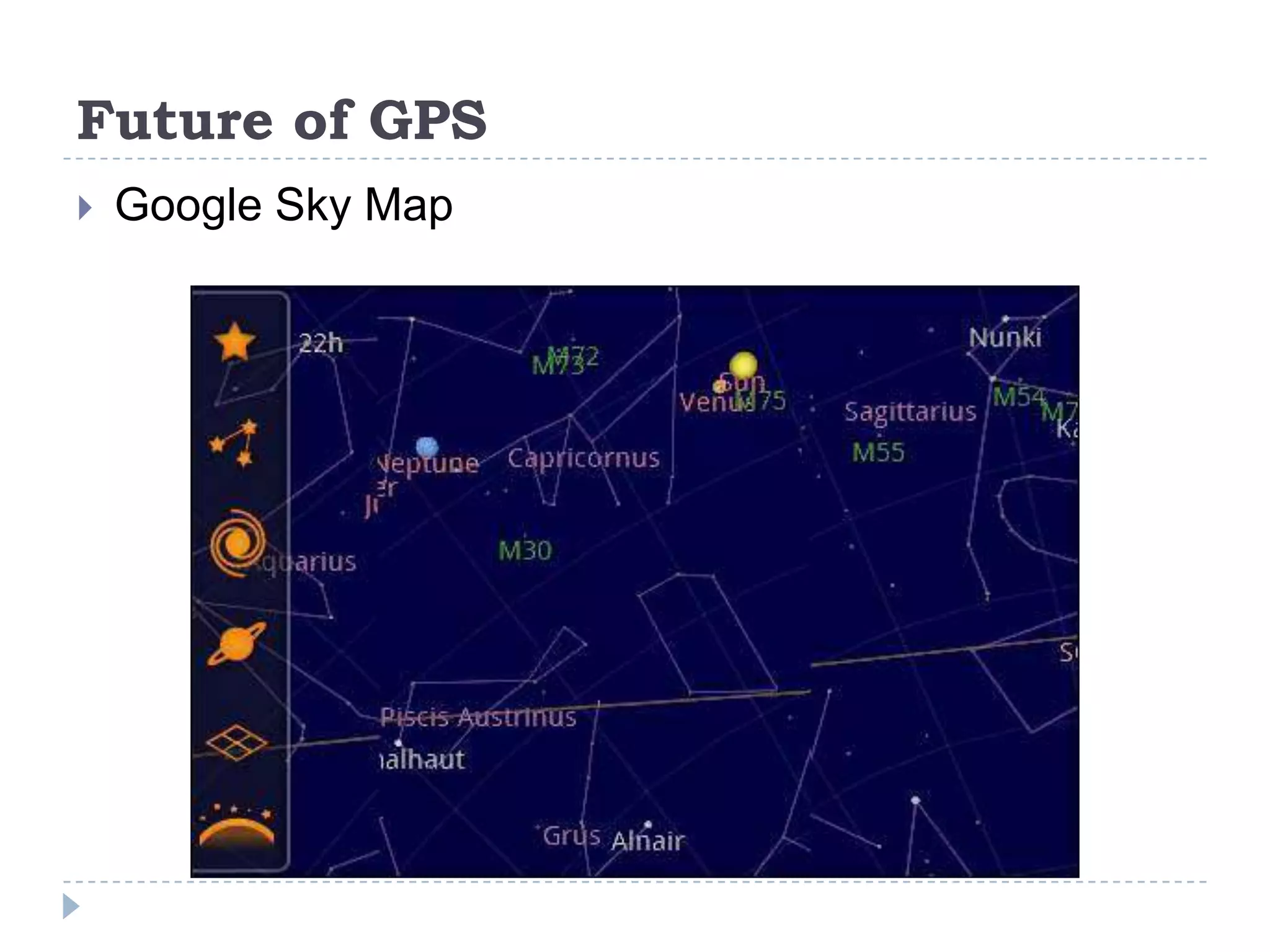
The document discusses Global Positioning Systems (GPS). It provides information on how GPS works using satellites, GPS receiving devices, and applications of GPS in various industries like transportation, sports, healthcare and business. It also outlines advantages of GPS such as ability to track locations anywhere in the world. Limitations including satellite geometry, multipath errors and reliance on technology are mentioned. The future of GPS is discussed including increased usage, indoor maps, augmented reality and applications like Google Sky Map.