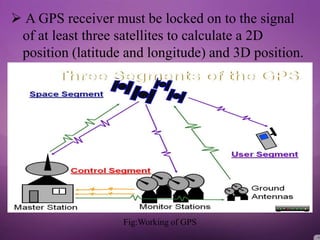
The document provides an overview of the Global Positioning System (GPS). It discusses the history and development of GPS from 1969 to 1995. It describes the three segments that make up the GPS architecture: the space segment consisting of 24 satellites, the control segment of earth-based stations, and the user segment of any device receiving GPS signals. It then explains how GPS works by using triangulation of signals from three or more satellites to calculate a user's position and discusses applications such as vehicle navigation, mapping, and tracking stolen devices. Advantages listed include usability in all weather and coverage of the entire planet. The conclusion discusses expanding civilian uses of GPS for navigation and future autonomous vehicles.