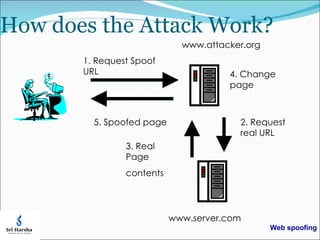
Web spoofing allows an attacker to create a fake version of the entire web in order to trick victims. The attacker rewrites URLs on web pages so they link to the attacker's server instead of the real server. When the victim interacts with forms or links, their data and browsing is redirected to the attacker's server without their knowledge. While the victim sees secure connections, these are actually to the attacker's server, not the intended site. The attacker can then observe and modify any private information submitted by the victim.