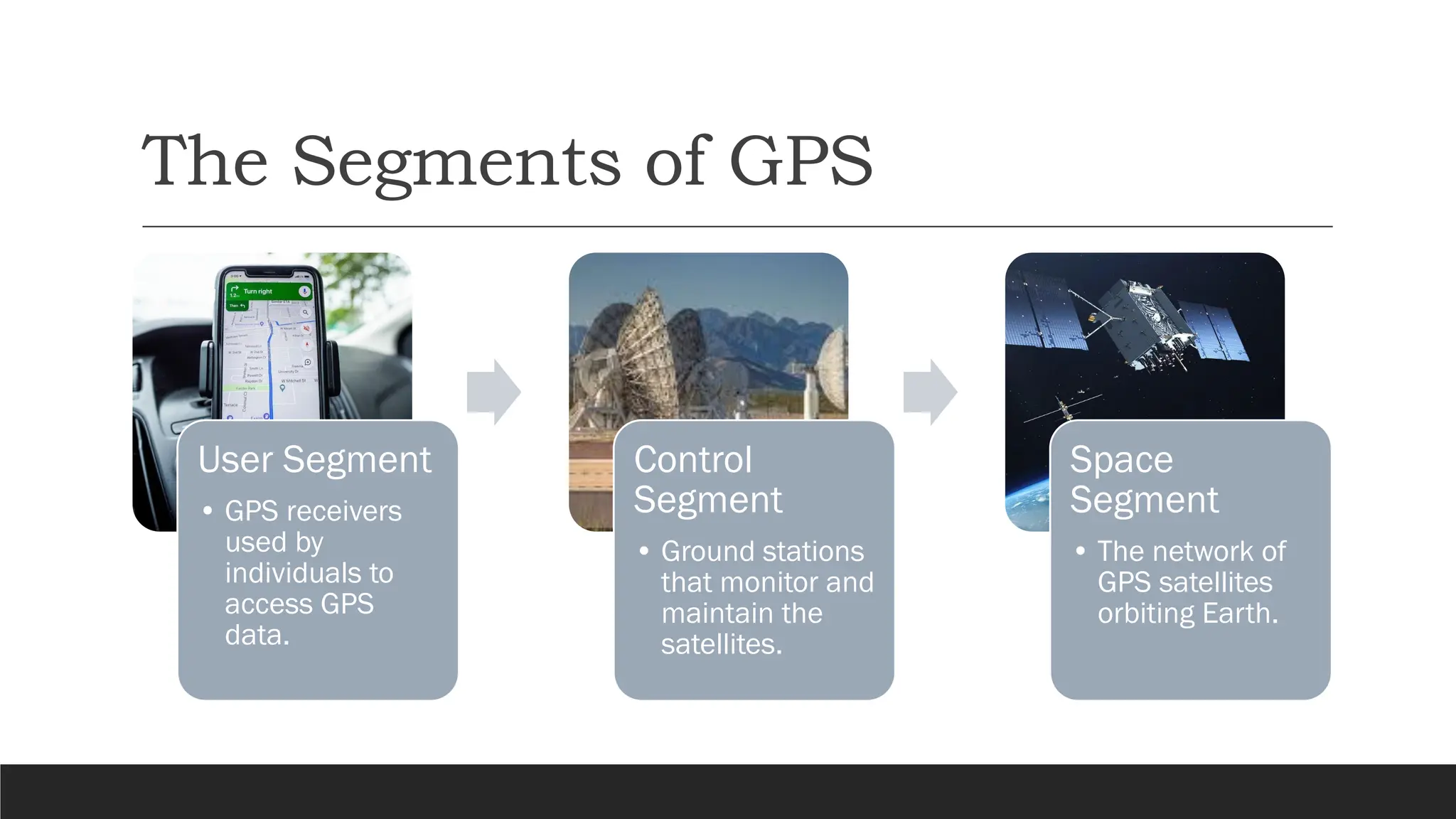
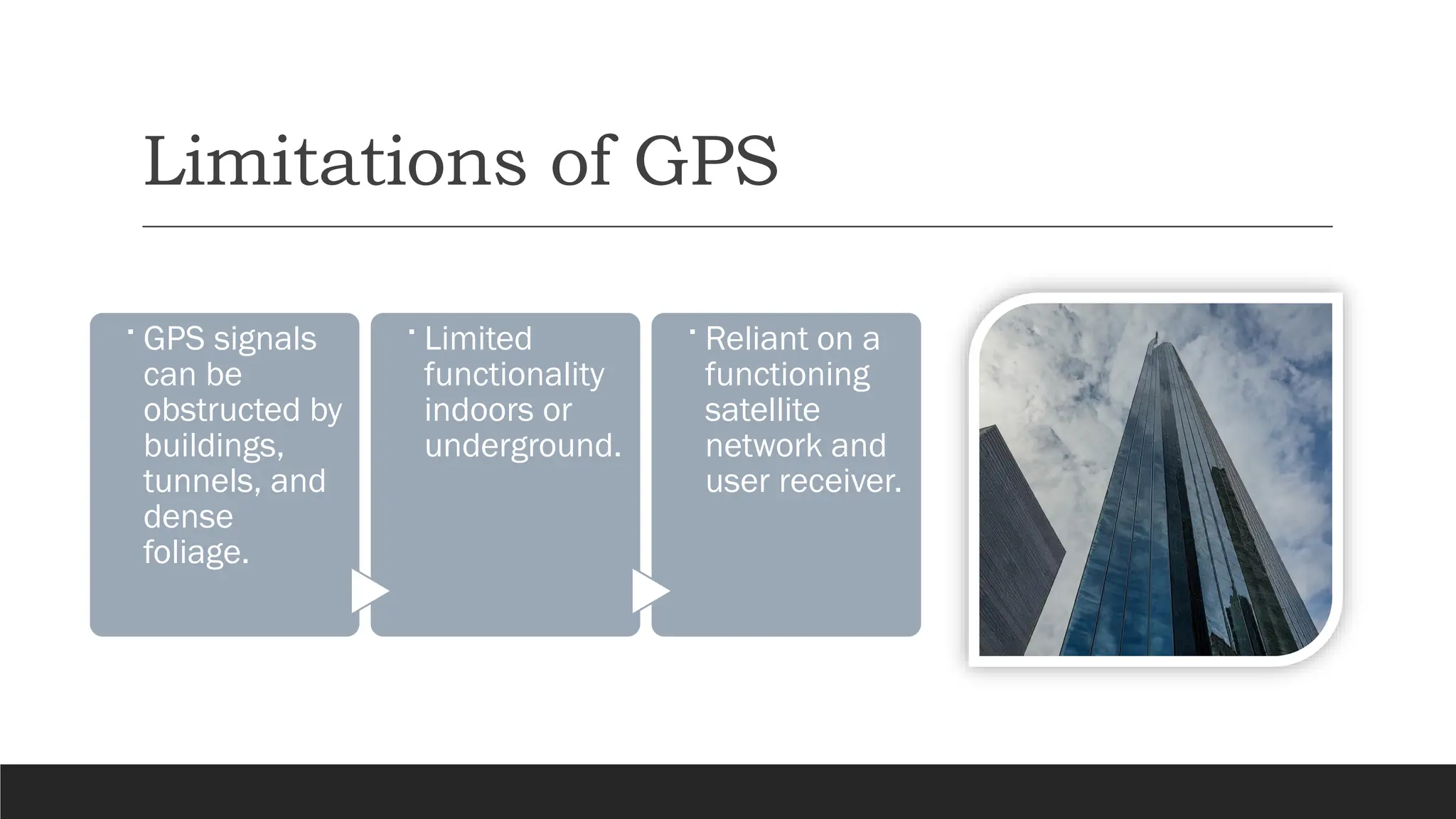
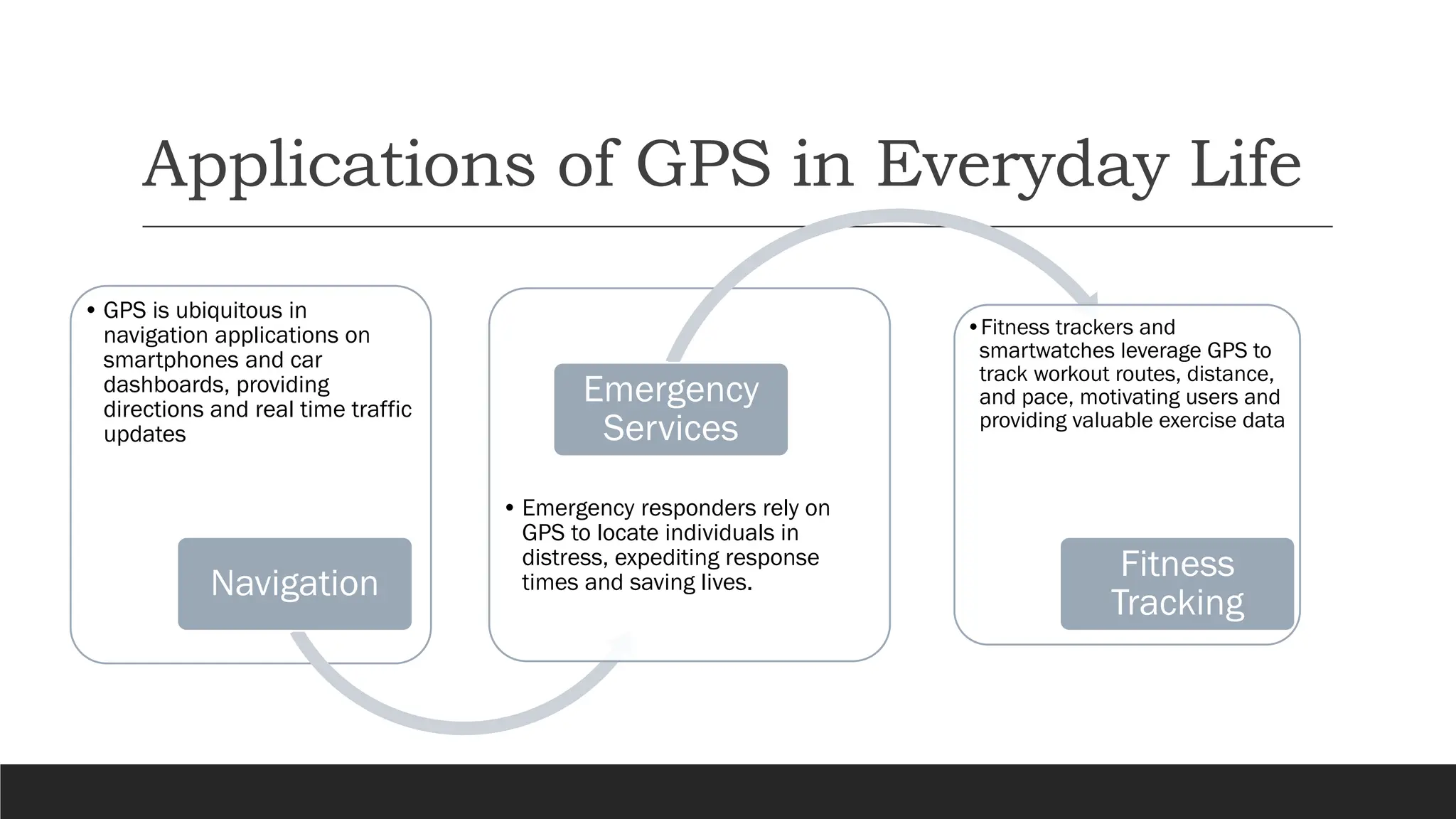
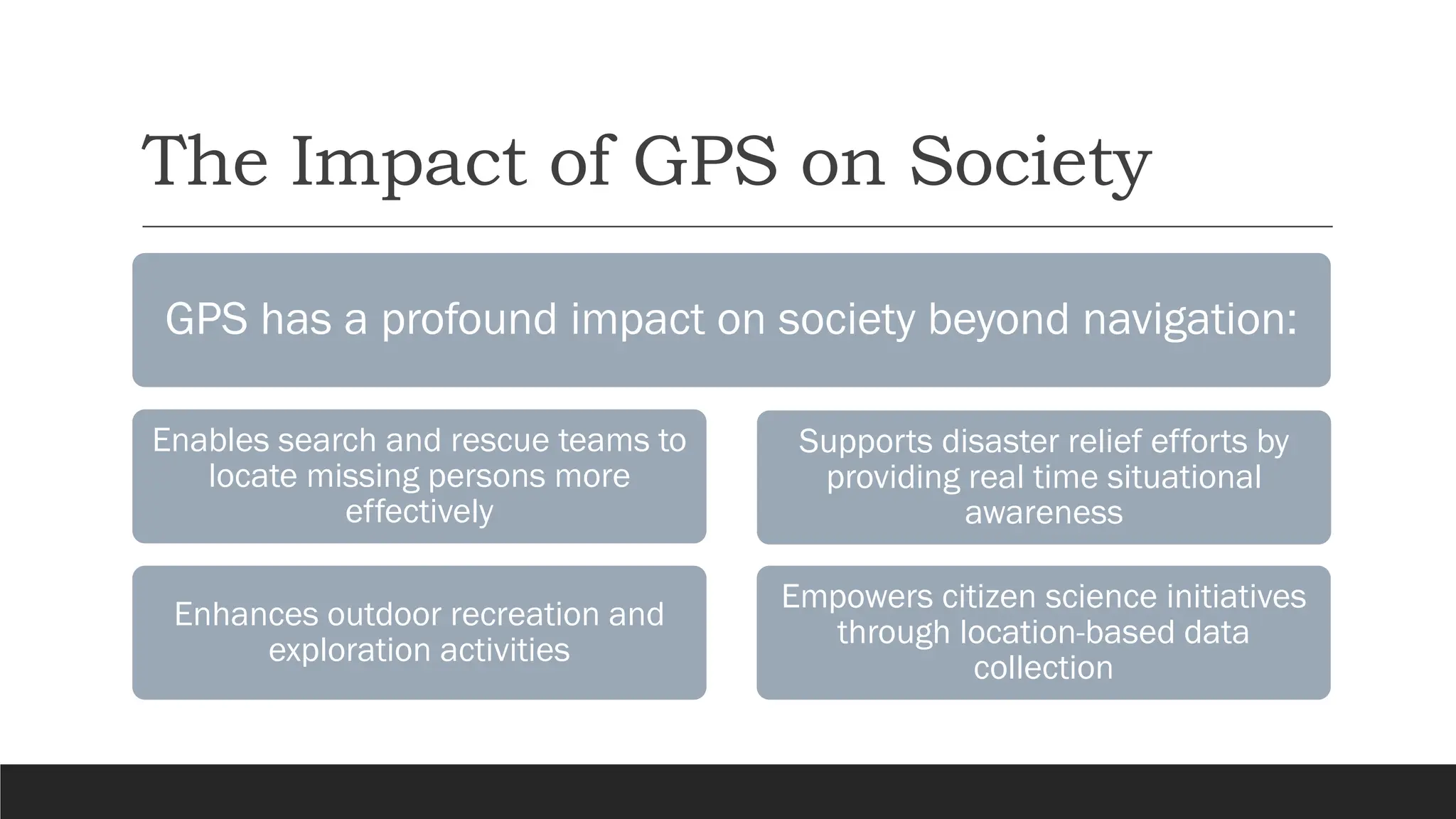
The document discusses the Global Positioning System (GPS), detailing its functionality, components, and applications in everyday life. It explains how GPS works through signals from satellites, trilateration for location determination, and highlights its societal impacts in navigation, emergency services, fitness tracking, and agriculture. Additionally, it addresses the limitations of GPS and the ongoing advancements in technology that could enhance its accuracy and integration with other innovations.