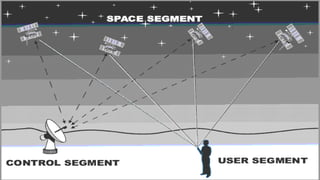
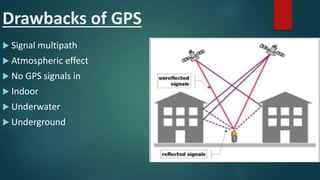
This document contains information about GPS from four group members: Hassan Rohail, Talha Noman, Anas Ali, and Arslan Ikram. Hassan provides a history of GPS, noting it was designed for military use and fully operational by 1995. Talha defines GPS as a space-based system that provides location, weather, and navigation info using 3 segments. Anas will discuss how GPS works. Arslan covers applications of GPS like aviation and mapping, drawbacks like signal issues, and future developments like improved accuracy.