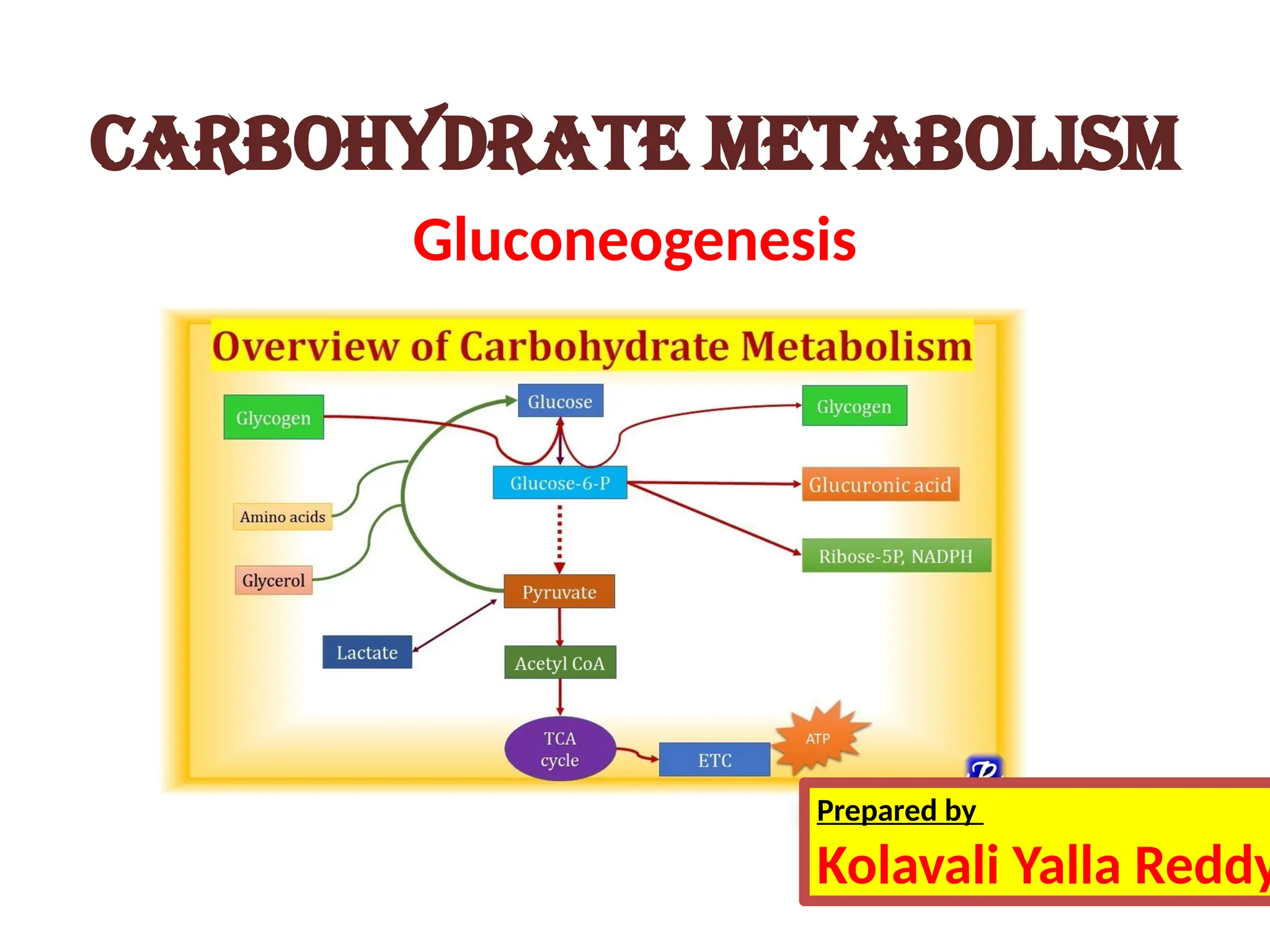
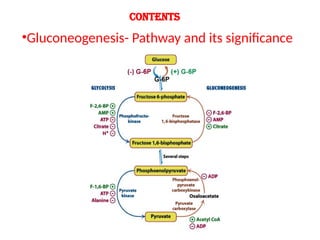
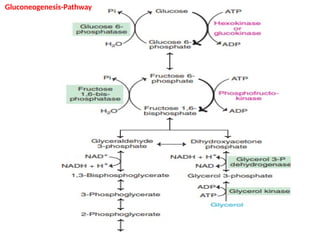
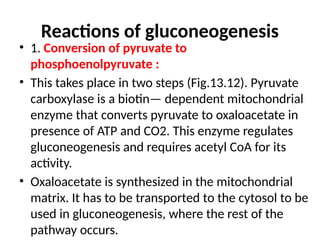
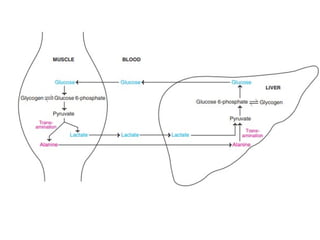
Gluconeogenesis is the metabolic pathway that synthesizes glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, and amino acids, mainly occurring in the liver and kidneys. The process involves several enzymatic reactions, passing through key intermediates like oxaloacetate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, with specific enzymes regulating each critical step. This pathway is vital for maintaining glucose supply to tissues, especially during fasting, ensuring energy availability for the brain and other organs.