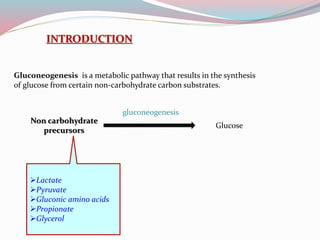
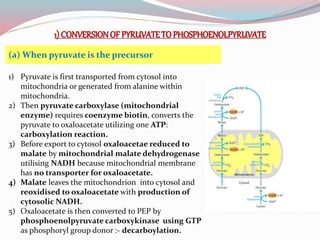
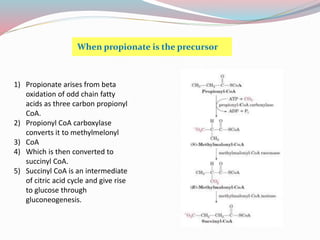
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that synthesizes glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors like lactate, pyruvate, amino acids, and glycerol, primarily in the liver and kidneys. This process is essential for maintaining blood glucose levels during fasting and operates with enzymes in both the cytosol and mitochondria. The pathway includes several key reactions, some of which are the reverse of glycolysis, and is tightly regulated by hormones and the reciprocal relationship between gluconeogenesis and glycolysis.