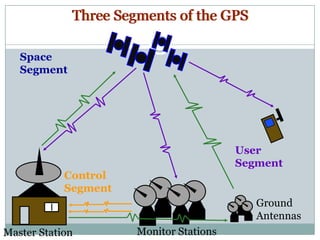
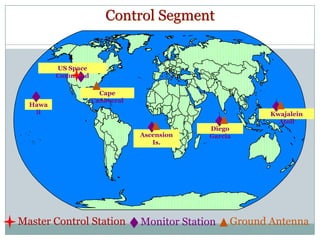
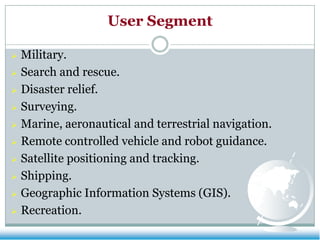
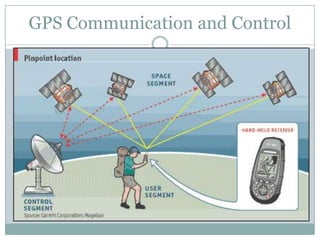
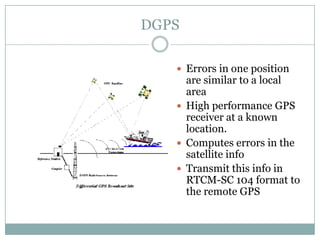
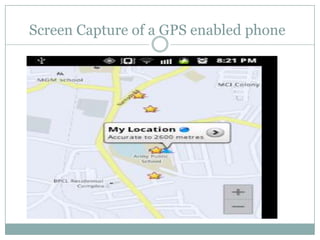
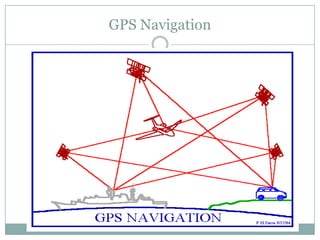
The GPS system uses a constellation of satellites that orbit the Earth and transmit precise time and location data. GPS receivers triangulate their position by calculating the distance to multiple satellites using the travel time of signals. The US government maintains GPS for civilian and military use worldwide. Key applications include navigation for vehicles, ships and aircraft as well as uses in mapping, agriculture, recreation and more. The system provides location and timing data to users with an accuracy as precise as a few meters or centimeters depending on the receiver.