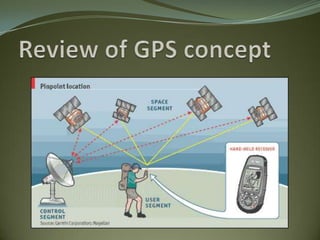
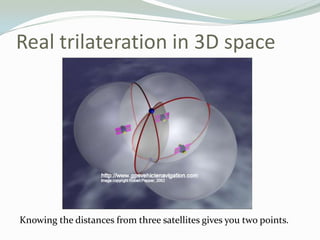
GPS uses trilateration to determine location based on distances to at least three satellites. Each satellite transmits its precise location and time of transmission. The GPS receiver uses the speed of light and transmission time to calculate distances, allowing it to determine its position at the intersection of distance spheres from multiple satellites. Accuracy relies on precise timekeeping of satellites and receivers.