The document provides an overview of the Global Positioning System (GPS) including:
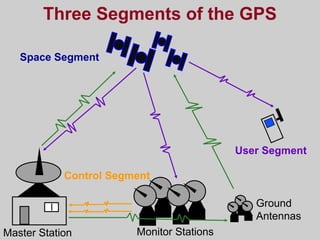
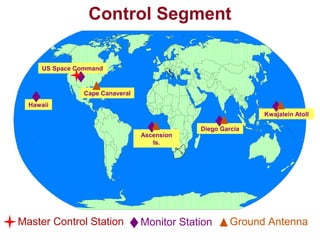
- The three segments that make up GPS - the control segment, space segment, and user segment. The control segment monitors the satellites and ground stations, the space segment consists of GPS satellites, and the user segment includes GPS receivers.
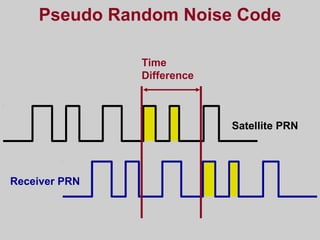
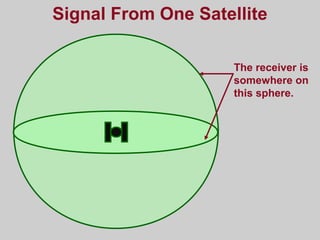
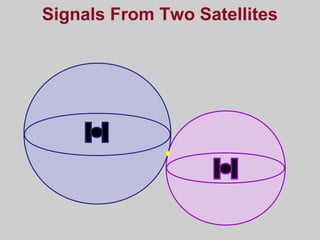
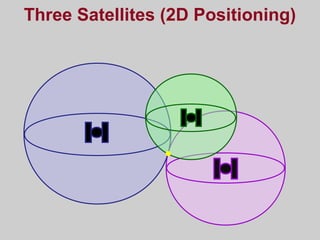
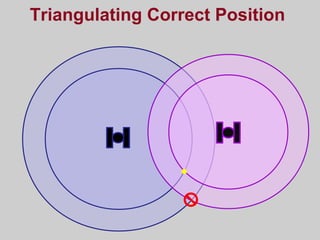
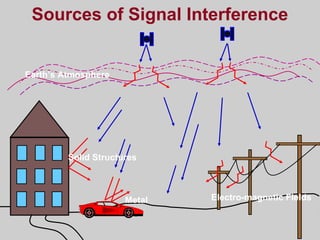
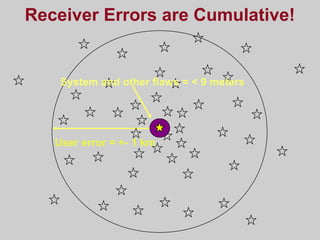
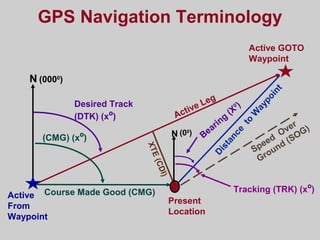
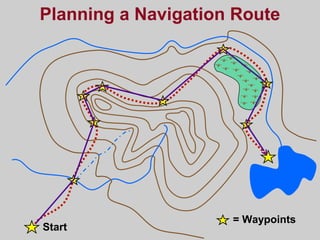
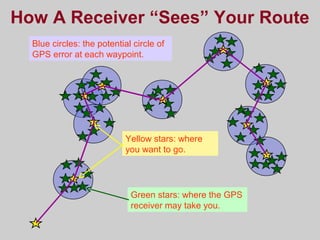
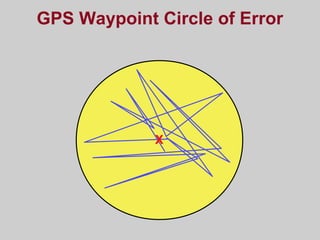
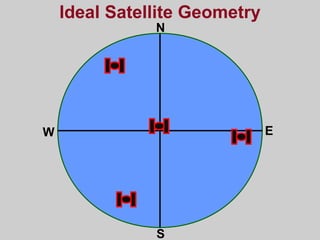
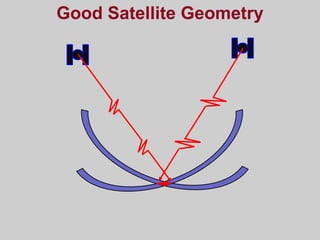
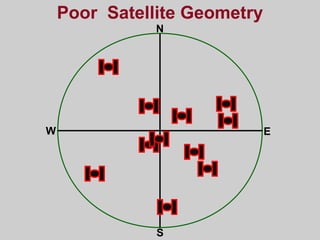
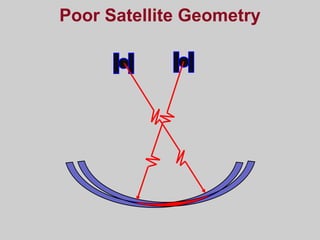
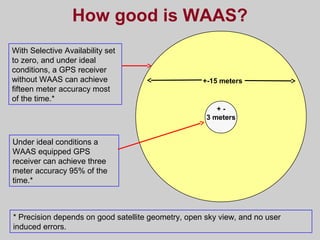
- How GPS works by using trilateration based on precise timing signals from multiple satellites to determine a user's position. Sources of error and ways to improve accuracy are also described.
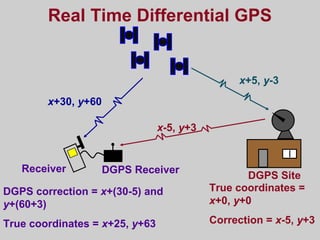
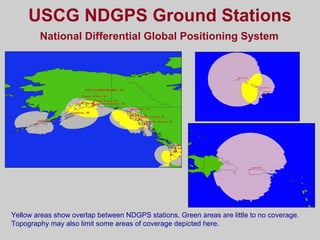
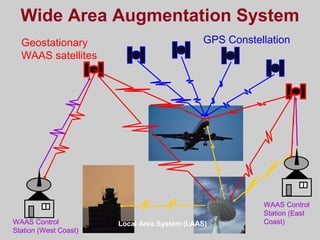
- Differential GPS (DGPS) and the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) which enhance GPS accuracy by correcting for sources of error. DGPS uses reference stations and WAAS uses additional satellites