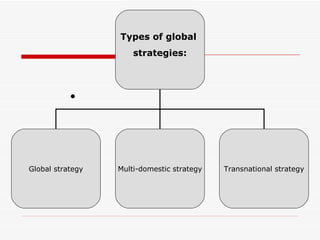
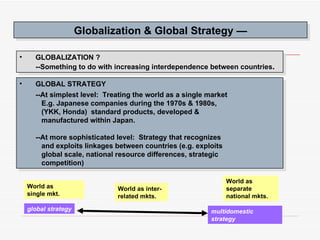
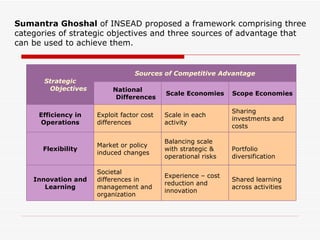
The document discusses global strategies and how companies can globalize. It defines a global strategy as treating the world as a single market by standardizing products across countries. A multi-domestic strategy involves customizing products for each local market. Sources of competitive advantage from a global strategy include economies of scale, exploiting differences in resources between countries, and strategic flexibility. The document also discusses types of global strategies like foreign direct investment, joint ventures, contractual agreements, and licensing.