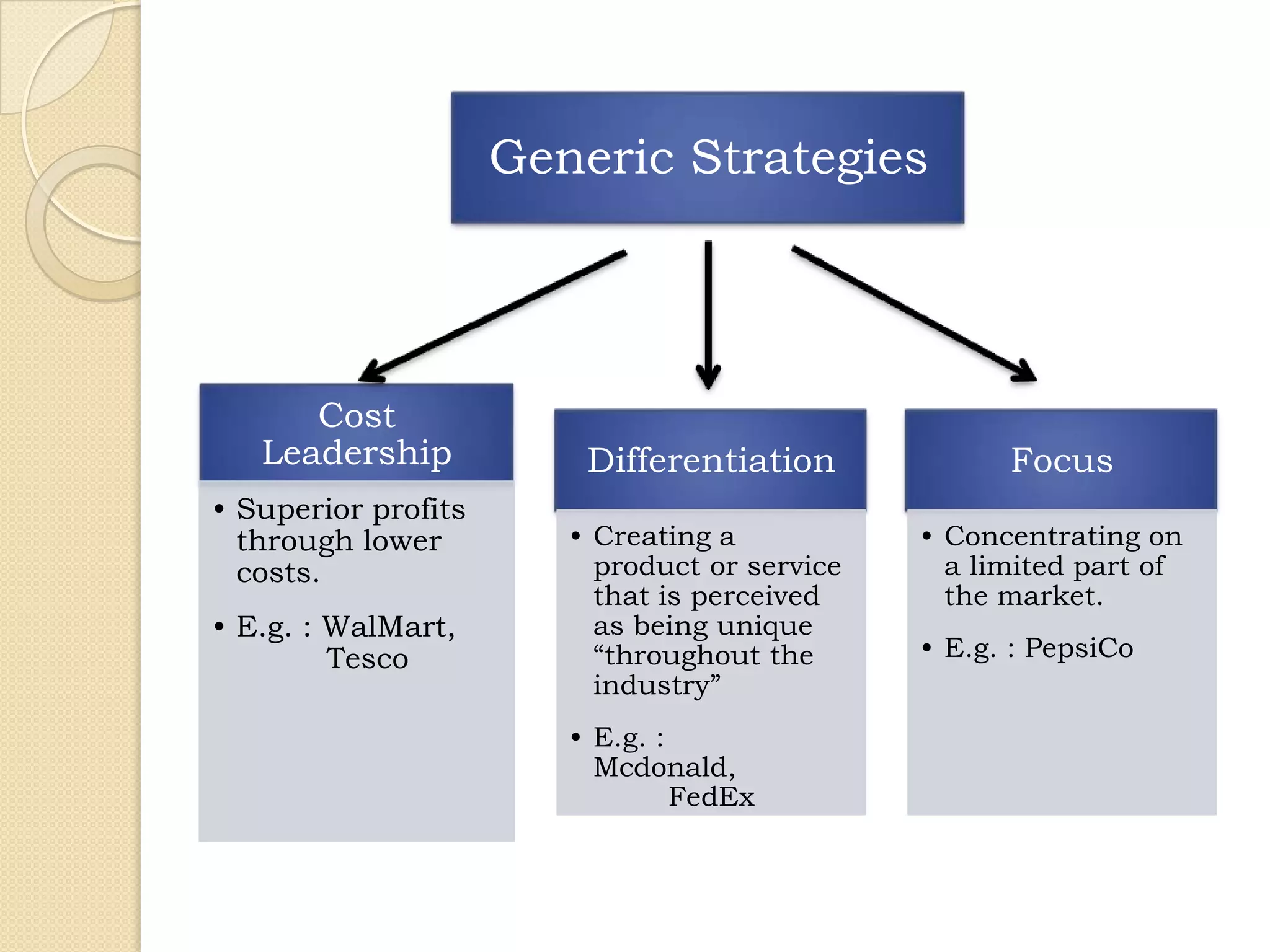
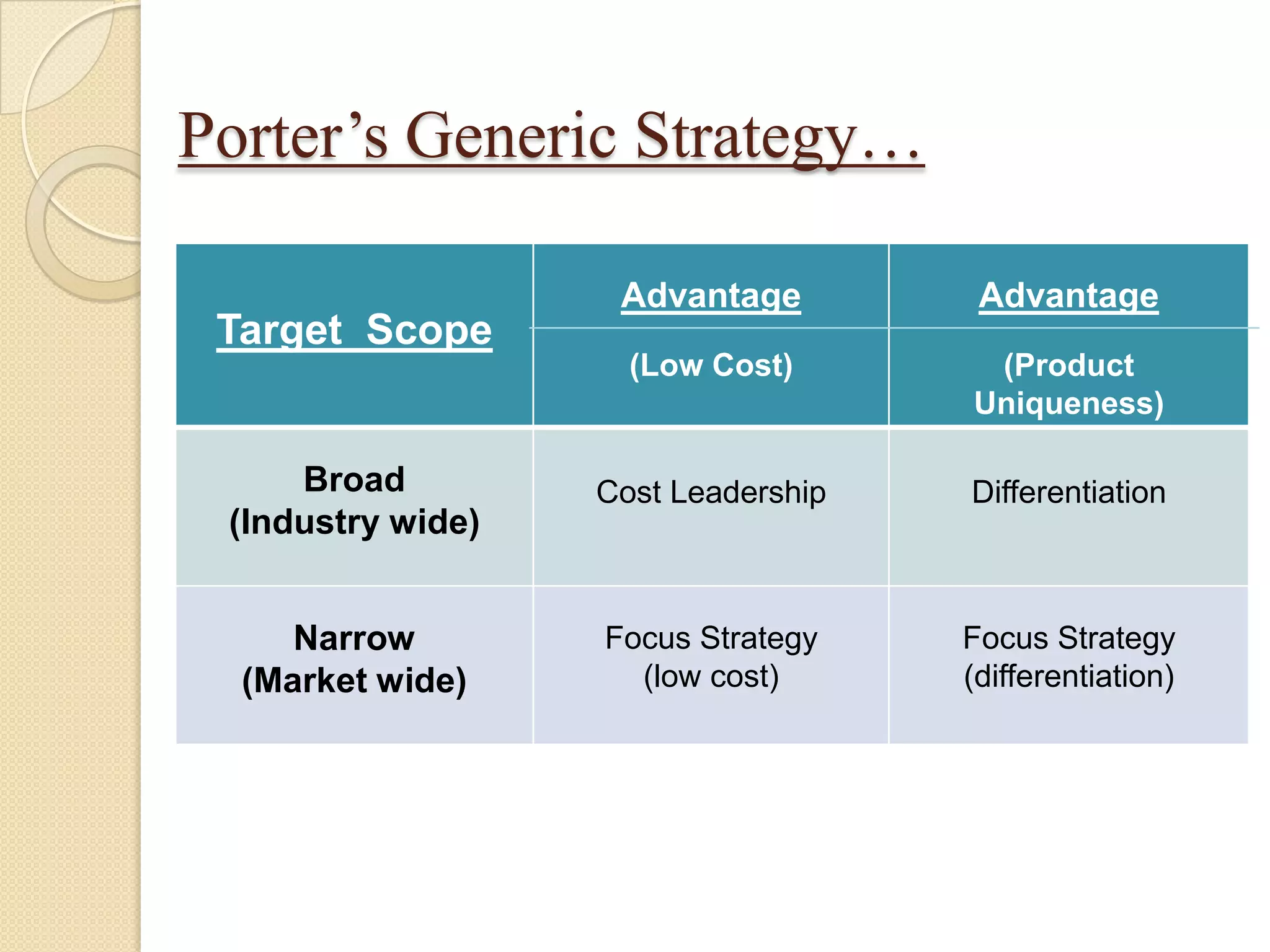
Michael Porter's generic strategies outline three approaches for firms to achieve competitive advantage: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Cost leadership focuses on becoming the lowest-cost producer, while differentiation involves creating unique products perceived as superior, and the focus strategy targets a specific market segment either through cost advantage or differentiation. Companies like Walmart, McDonald's, and PepsiCo exemplify these strategies in their respective industries.