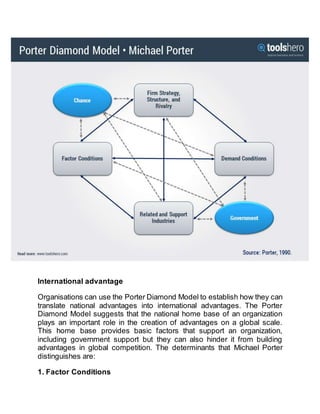
The document discusses Michael Porter's Diamond Model, which analyzes the competitive advantages of nations and industries. The model identifies four key attributes that determine national advantage: factor conditions, related and supporting industries, demand conditions, and firm strategy/rivalry. It provides an example analysis of the mobile telecommunications industry using the Diamond Model framework. The model can help organizations identify national-level factors that build advantages and inform internationalization strategies.