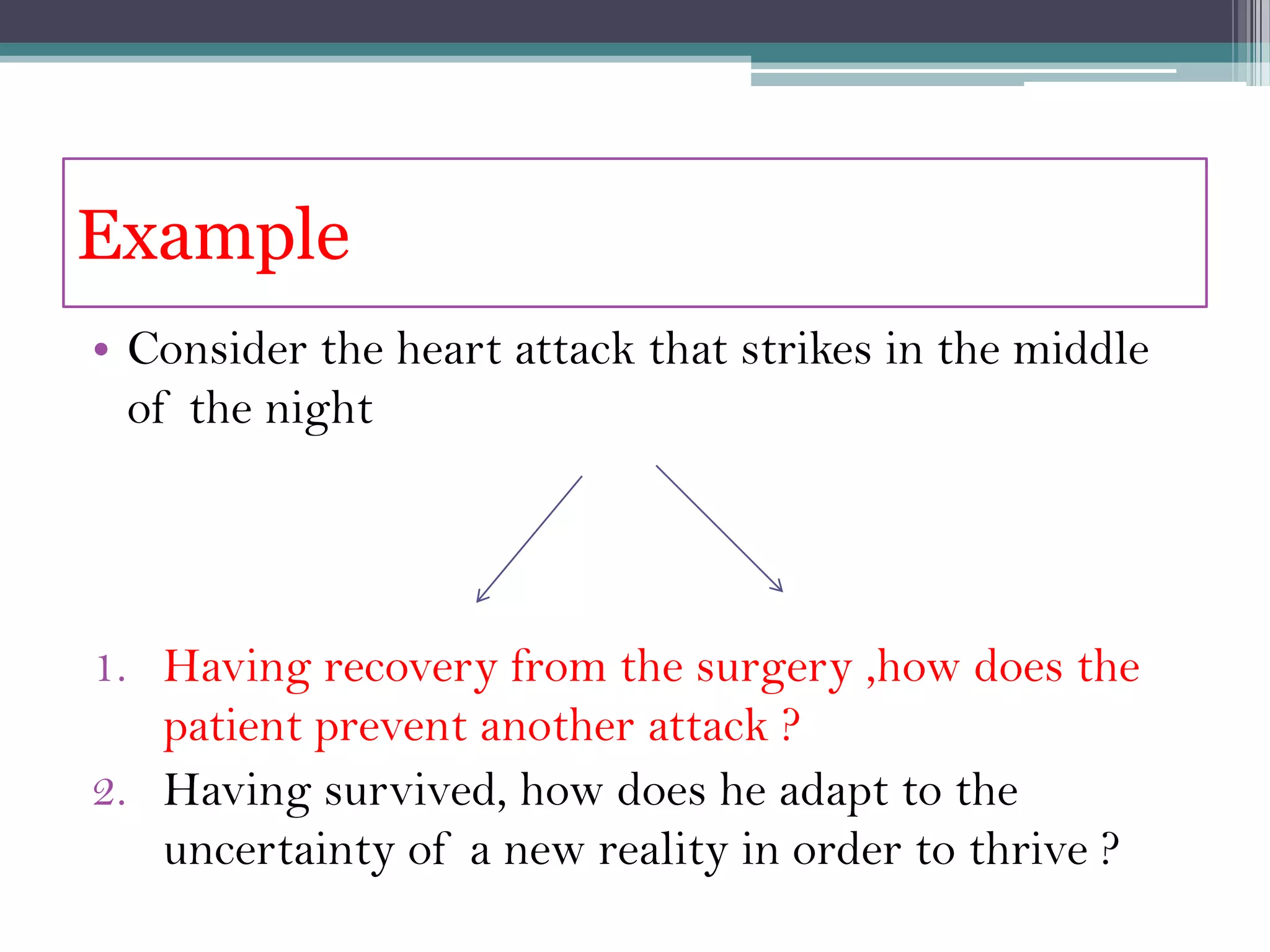
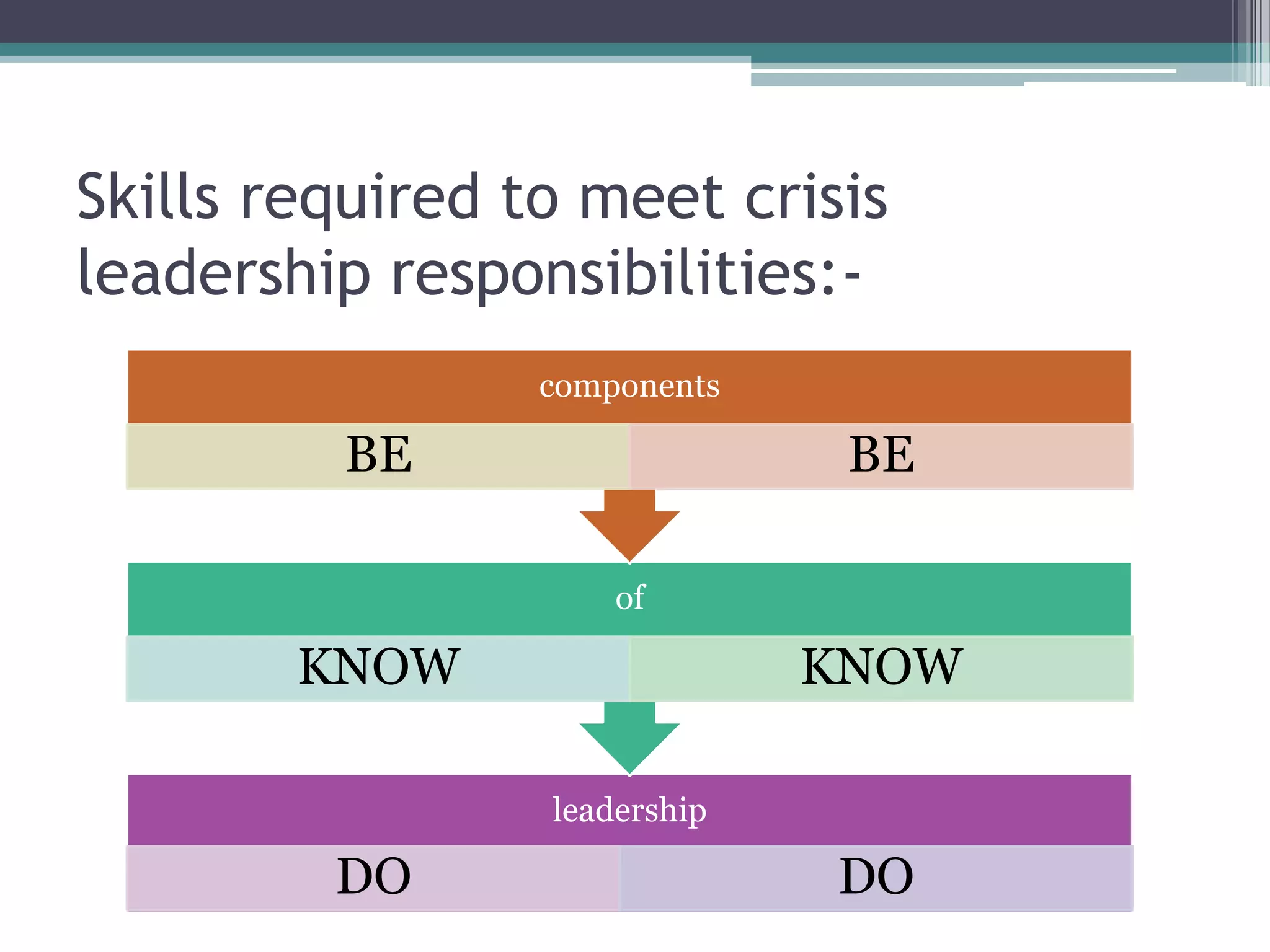
The document discusses leadership skills needed for times of permanent crisis. It outlines that economies now face sustained crises from global challenges, and leadership must foster adaptation, embrace disequilibrium, and generate new leadership to boost economies. Effective crisis leadership requires skills like collaboration, systems thinking, and emotional intelligence to navigate conflicting goals during times of dramatic change.