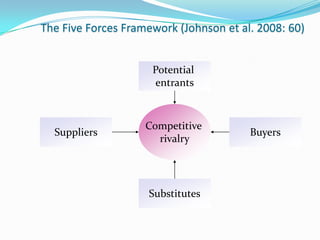
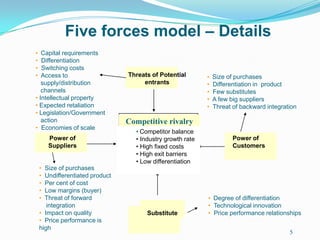
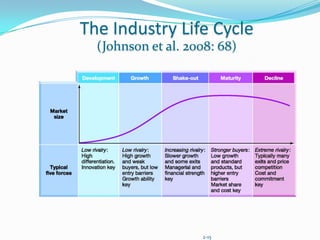
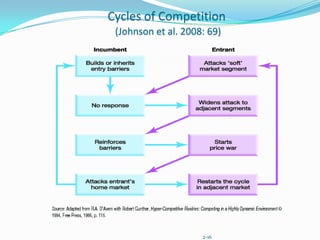
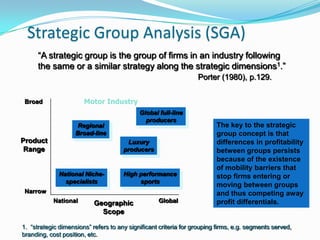
The document discusses tools for conducting external analysis, including PESTEL, Porter's Five Forces framework, industry life cycles, and strategic group, market, and segment analysis. PESTEL involves analyzing political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors in the macro-environment. Porter's Five Forces examines competitive rivalry, potential new entrants, substitutes, suppliers, and buyers. Industry analysis also considers life cycles and competitive dynamics. Competitor profiling involves strategic groups and evaluating market segments. External analysis breaks down the external environment to understand industry trends and competitive forces.