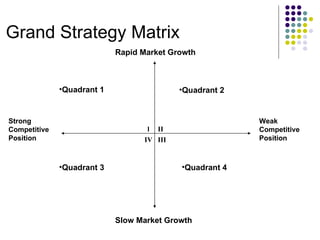
The document discusses grand strategies that provide overall direction for strategic actions of firms operating in multiple industries or business areas. It outlines four main grand strategy alternatives: stability, growth, combination, and retrenchment. Stability involves remaining the same size or growing slowly, while growth can involve internal expansion or external diversification. Combination uses different strategies for different units, and retrenchment shrinks or sells off businesses. The document also presents a grand strategy matrix based on market growth and competitive position, outlining suitable strategies for each quadrant, such as market penetration, product development, or divestiture. It further defines various strategies like forward integration, divestiture, liquidation, and conglomerate diversification.