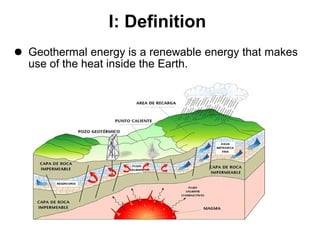
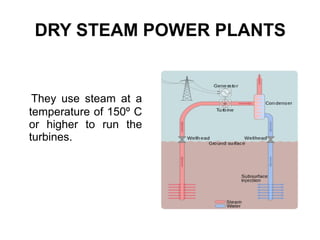
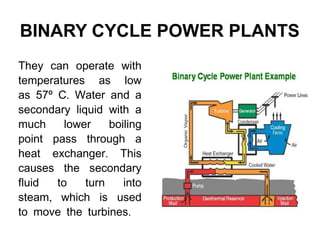
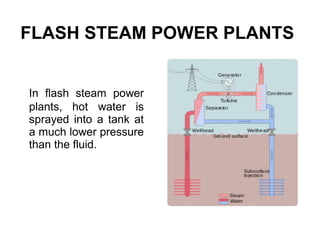
The document provides an overview of geothermal energy, defining it as a renewable resource that utilizes the Earth's internal heat for electricity production. It discusses different types of geothermal reservoirs and power plants, along with their advantages and disadvantages. The document also highlights global production, various applications, and concludes with insights on initial investments and environmental impacts.