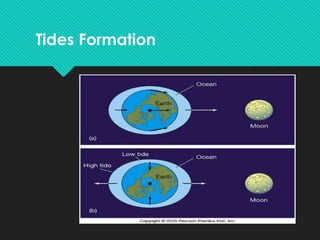
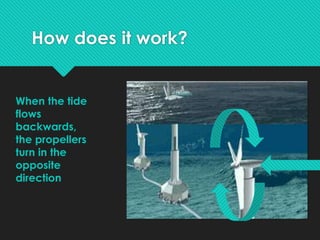
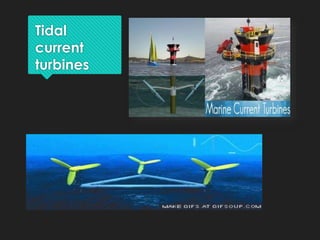
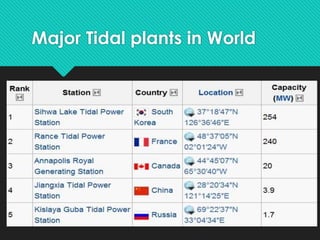
This document discusses tidal energy and how it works. Tidal energy harnesses the power of tides, which are caused by gravitational forces from the moon and sun. There are two main types of tidal power plants - tidal barrages and tidal current turbines. Tidal barrages are dams built across estuaries or bays, while tidal current turbines use the kinetic energy of moving water like wind turbines use wind. Major tidal plants exist in places like France, India, and South Korea. The document outlines the pros and cons of each tidal power technology and notes tidal energy is a renewable source but installation and maintenance can be challenging.