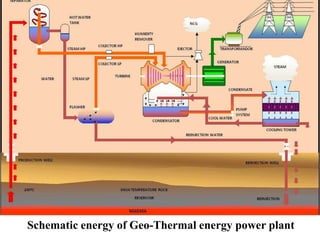
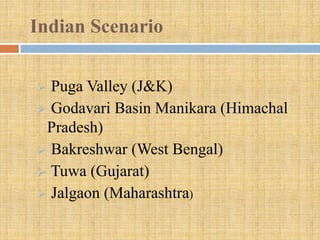
Geothermal energy harnesses heat from below Earth's surface. It is generated by radioactive decay within the earth's crust. Geothermal power plants drill wells to access hot water or steam underground, which is used to power turbines for electricity generation. There are direct uses of geothermal heat as well for heating buildings and greenhouses. While geothermal resources are limited to specific geographic locations, it provides renewable baseload power with fewer emissions than fossil fuels.