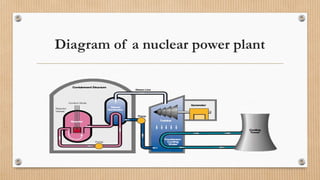
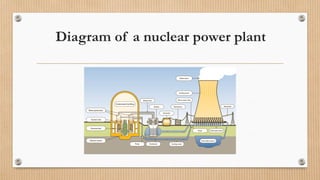
The document discusses nuclear energy, including its definition, operation, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as its presence in Spain, Europe, and worldwide. It highlights the benefits of nuclear energy such as low CO2 emissions and reduced oil dependency, while also noting the significant risks associated with accidents and radioactive waste. The document concludes that while nuclear energy has potential benefits, the dangers of accidents and waste management are serious concerns.