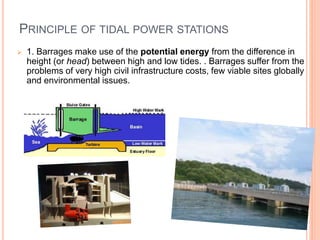
The document discusses tidal power, which harnesses the energy from the ocean's tides caused by gravitational forces of the moon and sun. It details the principles, operation methods, components of tidal power plants, and highlights its advantages such as predictability and low emissions, alongside disadvantages including high costs and ecological impact. Tidal power is presented as a promising alternative energy source with potential benefits for reducing reliance on fossil fuels.